UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
WASHINGTON, DC 20549
___________________________________________
FORM 10-K
___________________________________________
x | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2019
OR
☐ | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the transition period from to
Commission file number: 001-33292
_________________________________________________________

CORENERGY INFRASTRUCTURE TRUST, INC.
______________________________________________________________________
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
Maryland | 20-3431375 | |
(State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) | (IRS Employer Identification No.) | |
1100 Walnut, Ste. 3350 Kansas City, MO | 64106 | |
(Address of Principal Executive Offices) | (Zip Code) | |
(816) 875-3705 | ||
(Registrant's telephone number, including area code) | ||
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act: | ||||
Title of Each Class | Trading Symbol(s) | Name of Each Exchange On Which Registered | ||
Common Stock, par value $0.001 per share | CORR | New York Stock Exchange | ||
7.375% Series A Cumulative Redeemable Preferred Stock | CORRPrA | New York Stock Exchange | ||
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: None | ||||
___________________________________________
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act.
Yes o No x
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act.
Yes o No x
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes x No o
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically every Interactive Data File required to be submitted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit such files). Yes x No o
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, a smaller reporting company, or an emerging growth company. See the definitions of "large accelerated filer", "accelerated filer", "smaller reporting company", and "emerging growth company" in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
Large accelerated filer | o | Accelerated filer | x | |
Non-accelerated filer | o | Smaller reporting company | x | |
Emerging growth company | o | |||
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. o
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Act) Yes o No x
The aggregate market value of the voting and non-voting common equity held by non-affiliates of the registrant on June 28, 2019, the last business day of the registrant's most recently completed second fiscal quarter, based on the closing price on that date of $39.66 on the New York Stock Exchange was $506,662,643. Common shares held by each executive officer and director and by each person who owns 10% or more of the outstanding common shares (as determined by information provided to the registrant) have been excluded in that such persons may be deemed to be affiliates. This determination of affiliate status is not necessarily a conclusive determination for other purposes.
As of February 26, 2020, the registrant had 13,651,521 common shares outstanding.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
Portions of the registrant's Proxy Statement for its 2020 Annual Meeting of Stockholders to be filed not later than 120 days after the end of the fiscal year covered by this Annual Report on Form 10-K are incorporated by reference into Part III of this Form 10-K.
CorEnergy Infrastructure Trust, Inc.
FORM 10-K
FOR THE FISCAL YEAR ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2019
TABLE OF CONTENTS
____________________________________________________________________________________________
Page No. | |||||
2
PART I
GLOSSARY OF DEFINED TERMS | ||
Certain of the defined terms used in this Report are set forth below:
5.875% Convertible Notes: the Company's 5.875% Convertible Senior Notes due 2025.
7.00% Convertible Notes: the Company's 7.00% Convertible Senior Notes due 2020.
Accretion Expense: the expense recognized when adjusting the present value of the GIGS ARO for the passage of time.
Administrative Agreement: the Administrative Agreement dated December 1, 2011, as amended effective August 7, 2012, between the Company and Corridor.
Amended Pinedale Term Credit Facility: Pinedale LP's $41.0 million Second Amended and Restated Term Credit Agreement and Note Purchase Agreement with Prudential as lender, effective December 29, 2017.
Arc Logistics: Arc Logistics Partners LP, a wholly-owned subsidiary of Zenith Energy U.S., LP. as a result of the completion of a merger on December 21, 2017.
ARO: the Asset Retirement Obligation liabilities assumed with the acquisition of GIGS.
ASC: FASB Accounting Standards Codification.
ASU: FASB Accounting Standard Update.
Bbls: standard barrel containing 42 U.S. gallons.
BOEM: U.S. Federal Bureau of Ocean Energy Management.
BSEE: U.S. Federal Bureau of Safety and Environmental Enforcement.
Code: the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended.
Company or CorEnergy: CorEnergy Infrastructure Trust, Inc. (NYSE: CORR).
Compass SWD: Compass SWD, LLC, the current borrower under the Compass REIT Loan.
Compass REIT Loan: the financing notes between Compass SWD and Four Wood Corridor.
Convertible Notes: collectively, the Company's 5.875% Convertible Notes and the Company's 7.00% Convertible Notes.
CorEnergy BBWS: CorEnergy BBWS, Inc., a wholly-owned taxable REIT subsidiary of CorEnergy.
CorEnergy Credit Facility: the Company's upsized $160.0 million CorEnergy Revolver and the $1.0 million MoGas Revolver with Regions Bank.
CorEnergy Revolver: the Company's $160.0 million secured revolving line of credit facility with Regions Bank.
CorEnergy Term Loan: the Company's $45.0 million secured term loan with Regions Bank that was paid off in conjunction with the amendment and restatement of the CorEnergy Credit Facility on July 28, 2017.
Corridor: Corridor InfraTrust Management, LLC, the Company's external manager pursuant to the Management Agreement.
Corridor MoGas: Corridor MoGas, Inc., a wholly-owned taxable REIT subsidiary of CorEnergy and the holding company of MoGas, United Property Systems and CorEnergy Pipeline Company, LLC.
Corridor Private: Corridor Private Holdings, Inc., an indirect wholly-owned taxable REIT subsidiary of CorEnergy.
Corridor Public: Corridor Public Holdings, Inc., an indirect wholly-owned taxable REIT subsidiary of CorEnergy.
Cox Acquiring Entity: MLCJR LLC, an affiliate of Cox Oil, LLC.
Cox Oil: Cox Oil, LLC.
CPI: Consumer Price Index.
Exchange Act: the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended.
3
GLOSSARY OF DEFINED TERMS (Continued from previous page) | ||
EGC: Energy XXI Ltd, the parent company (and guarantor) of our tenant on the Grand Isle Gathering System lease, emerged from a reorganization under Chapter 11 of the US Bankruptcy Code on December 30, 2016, with the succeeding company named Energy XXI Gulf Coast, Inc. Effective October 18, 2018, EGC became an indirect wholly-owned subsidiary of MLCJR LLC ("Cox Acquiring Entity"), an affiliate of Cox Oil, LLC, as a result of a merger transaction. Throughout this document, references to EGC will refer to both the pre- and post-bankruptcy entities and, for dates on and after October 18, 2018, to EGC as an indirect wholly-owned subsidiary of the Cox Acquiring Entity.
EGC Tenant: Energy XXI GIGS Services, LLC, a wholly-owned operating subsidiary of Energy XXI Gulf Coast, Inc. that is the tenant under Grand Isle Corridor's triple-net lease of the Grand Isle Gathering System.
FASB: Financial Accounting Standards Board.
FERC: Federal Energy Regulatory Commission.
Four Wood Corridor: Four Wood Corridor, LLC, a wholly-owned subsidiary of CorEnergy.
GAAP: U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
GIGS: the Grand Isle Gathering System, owned by Grand Isle Corridor LP and triple-net leased to a wholly-owned subsidiary of Energy XXI Gulf Coast, Inc.
GOM: Gulf of Mexico.
Grand Isle Corridor: Grand Isle Corridor LP, an indirect wholly-owned subsidiary of the Company.
Grand Isle Gathering System: a subsea midstream pipeline gathering system located in the shallow Gulf of Mexico shelf and storage and onshore processing facilities.
Grand Isle Lease Agreement: the June 2015 agreement pursuant to which the Grand Isle Gathering System assets are triple-net leased to EGC Tenant.
Indentures: collectively, (i) that certain Base Indenture, dated June 29, 2015, as supplemented by the related First Supplemental Indenture, dated as of June 29, 2015, between the Company and Computershare Trust Company, N.A., as Trustee for the 7.00% Convertible Notes and (ii) that certain Base Indenture, dated August 12, 2019, between the Company and U.S. Bank National Association, as Trustee for the 5.875% Convertible Notes.
IRS: U.S. Internal Revenue Service.
Joliet: Zenith Energy Terminals Joliet Holdings LLC, an indirect subsidiary of Zenith Energy U.S., LP.
Lightfoot: collectively, Lightfoot Capital Partners, LP and Lightfoot Capital Partners GP LLC.
Management Agreement: the current management agreement between the Company and Corridor entered into May 8, 2015, effective as of May 1, 2015.
MoGas: MoGas Pipeline LLC, an indirect wholly-owned subsidiary of CorEnergy.
MoGas Pipeline System: an approximately 263-mile interstate natural gas pipeline system in and around St. Louis and extending into central Missouri, owned and operated by MoGas.
MoGas Revolver: a $1.0 million secured revolving line of credit facility at the MoGas subsidiary level with Regions Bank.
Mowood: Mowood, LLC, a wholly-owned subsidiary of CorEnergy and the holding company of Omega Pipeline Company, LLC.
Mowood/Omega Revolver: a $1.5 million secured revolving line of credit facility at the Mowood subsidiary level with Regions Bank.
NAREIT: National Association of Real Estate Investment Trusts.
Omega: Omega Pipeline Company, LLC, a wholly-owned subsidiary of Mowood, LLC.
Omega Pipeline: Omega's natural gas distribution system in south central Missouri.
OCS: the Outer Continental Shelf.
Pinedale Credit Facility: a $70.0 million secured term credit facility, with the Company and Prudential as refinance lenders, used by Pinedale Corridor, LP to finance a portion of the acquisition of the Pinedale LGS.
4
GLOSSARY OF DEFINED TERMS (Continued from previous page) | ||
Pinedale LGS: the Pinedale Liquids Gathering System, a system consisting of approximately 150 miles of pipelines and four above-ground central gathering facilities located in the Pinedale Anticline in Wyoming, owned by Pinedale LP and triple-net leased to a wholly-owned subsidiary of Ultra Petroleum.
Pinedale Lease Agreement: the December 2012 agreement pursuant to which the Pinedale LGS assets are triple-net leased to a wholly owned subsidiary of Ultra Petroleum.
Pinedale LP: Pinedale Corridor, LP, an indirect wholly-owned subsidiary of CorEnergy.
Pinedale LP I: Pinedale LP I, LLC, a wholly-owned subsidiary of CorEnergy, which purchased the 18.95 percent outstanding equity interest in Pinedale LGS from Prudential.
Pinedale GP: the general partner of Pinedale LP and a wholly-owned subsidiary of CorEnergy.
PLR: the Private Letter Ruling dated November 16, 2018 (PLR 201907001) issued to CorEnergy by the IRS.
Portland Lease Agreement: the January 2014 agreement pursuant to which the Portland Terminal Facility was triple-net leased to Zenith Terminals, which terminated on December 21, 2018 upon sale of the facility.
Portland Terminal Facility: a petroleum products terminal located in Portland, Oregon sold on December 21, 2018 to Zenith Terminals.
Prudential: the Prudential Insurance Company of America.
QDI: qualified dividend income.
REIT: real estate investment trust.
SEC: Securities and Exchange Commission.
Securities Act: the Securities Act of 1933, as amended.
Series A Preferred Stock: the Company's 7.375% Series A Cumulative Redeemable Preferred Stock, par value $0.001 per share, of which there currently are outstanding approximately 50,197 shares represented by 5,019,727 depositary shares, each representing 1/100th of a whole share of Series A Preferred Stock.
SWD: SWD Enterprises, LLC, the previous debtor of the financing notes with Four Wood Corridor.
TRS: taxable REIT subsidiary.
UPL: Ultra Petroleum Corp.
Ultra Wyoming: Ultra Wyoming LGS LLC, an indirect wholly-owned subsidiary of Ultra Petroleum.
United Property Systems: United Property Systems, LLC, an indirect wholly-owned subsidiary of CorEnergy, acquired with the MoGas transaction in November 2014.
VIE: Variable Interest Entity.
Zenith: Zenith Energy U.S., LP.
Zenith Terminals: Zenith Energy Terminals Holdings, LLC (f/k/a Arc Terminal Holdings, LLC), a wholly-owned operating subsidiary of Arc Logistics LP (and, subsequent to December 21, 2017, an indirect wholly-owned subsidiary of Zenith).
5
ITEM 1. BUSINESS
GENERAL
CorEnergy Infrastructure Trust, Inc. ("CorEnergy") was organized as a Maryland corporation and commenced operations on December 8, 2005. As used in this Annual Report on Form 10-K ("Report"), the terms "we", "us", "our" and the "Company" refer to CorEnergy and its subsidiaries.
COMPANY OVERVIEW
CorEnergy primarily owns and seeks to own assets in the U.S. energy sector that perform utility-like functions, such as pipelines, storage terminals, rail terminals and gas and electric transmission and distribution assets. Our objective has been to generate long-term contracted revenue from operators of our assets, primarily under triple-net participating leases without direct commodity price exposure. We believe our leadership team's energy and utility expertise provides CorEnergy with a competitive advantage to acquire, own and lease U.S. energy infrastructure assets in a tax-efficient, transparent and investor-friendly REIT. Our leadership team also utilizes a disciplined investment philosophy developed through an average of over 25 years of relevant industry experience.
We expect our leases to provide us with contracted base rent, plus participating rent based upon asset-specific criteria. The energy industry commonly employs contracts with participating features, and we provide exposure to both the risk and opportunity of utilization of our assets, which we believe is a hallmark of infrastructure assets of all types. Our participating triple-net leases require the operator to pay all expenses of the business including maintaining our assets in good working order.
The majority of our assets leased to tenants under triple-net leases are dependent upon the tenants' exploitation of hydrocarbon reserves in the fields where our assets are located. These reserves are depleted over time, and therefore, may economically diminish the value of our assets over the period that the underlying reserves are exploited. Accordingly, we expect the contracted base rents under these leases, including fair market renewal rent expectations, to provide for a return-on-capital, as well as a return of our invested capital, over the life of the asset. The portion of rents we believe to constitute a return of our invested capital are utilized for debt repayment and/or are reserved for capital reinvestment activities in order to maintain our long-term earnings and dividend paying capacity. The return-on-capital is that portion of rents which are available for distribution to our stockholders through dividend payouts.
Base rents under our leases are structured on an estimated fair market value rent structure over the initial term, which includes assumptions related to the terminal value of our assets and expectations of tenant renewals. At the conclusion of the initial lease term, our leases often contain fair market value repurchase options or fair market rent renewal terms. These clauses also act as safeguards against our tenants pursuing activities which would undermine or degrade the value of our assets faster than the underlying reserves are depleted. Our participating rents are structured to provide exposure to the successful commercial activity of the tenant, and as such, also provide protection in the event that the economic life of our assets is reduced based on accelerated production by our tenants.
Our assets are predominately mission-critical to our customers, in that utilization of our assets is necessary for the business they seek to conduct and their rental payments are an essential operating expense. For example, our crude oil gathering system assets are necessary to the exploitation of upstream crude oil reserves, so the operators' lease of those assets is economically critical to their operations. Some of our assets are subject to rate regulation by FERC or state public utility commissions. Further, energy infrastructure assets are an essential and growing component of the U.S. economy that give us the opportunity to assist the capital expansion plans and meet the capital needs of various midstream and upstream participants.
On November 16, 2018, the IRS issued the PLR to CorEnergy. The PLR provides to us assurance that fees we may receive for the usage of storage and pipeline capacity on assets we may own, including oil platforms, will qualify as rents from real property for purposes of our qualification as a REIT. As a result, the PLR grants us the opportunity to own and operate certain infrastructure assets under conditions set forth in the PLR. We can consider, and are considering, a broader set of investment opportunities than was available to us prior to issuance of the PLR. For example, prior to the PLR, we could own the Portland Terminal Facility that we previously leased to Zenith Terminals, but we were not then assured that we could operate such an asset and treat the revenues as rents from real property for purposes of the REIT income test. As a result of the PLR, we can now acquire and operate a storage terminal facility such as the Portland Terminal Facility.
We intend to distribute substantially all of our cash available for distribution, less prudent reserves, on a quarterly basis. We regularly assess our ability to pay and to grow our dividend to common stockholders. We target long-term revenue growth of 1-3 percent annually from existing contracts through inflation escalations and participating rents, and additional growth from acquisitions. There can be no assurance that any potential acquisition opportunities will result in consummated transactions. Our management contract includes incentive provisions, aligning our leadership team with our stockholders' interests.
6
We believe these characteristics align CorEnergy with the attractive attributes of other globally listed infrastructure companies, including high barriers to entry and contracts with predictable revenue streams, while mitigating risks and volatility experienced by other companies engaged in the midstream energy sector.
2019 Highlights
Our 2019 fiscal year was highlighted by a number of transactions being completed which enhanced our liquidity and positioned the Company for future growth. These and other key transactions and events during our fiscal year ended December 31, 2019 are highlighted below:
• | On January 16, 2019, we exchanged $43.8 million face amount of our 7.00% Convertible Notes for an aggregate of 837,040 shares of our common stock plus aggregate cash consideration of $19.8 million. |
• | On August 12, 2019, we completed a private placement offering of $120.0 million aggregate principal amount of 5.875% Convertible Notes. On August 15, 2019, we used a portion of the net proceeds from the offering, together with shares of our common stock, to exchange $63.9 million face amount of our 7.00% Convertible Notes. The total cash and stock consideration for the exchange was valued at approximately $93.2 million. This included an aggregate of 703,432 shares of common stock plus cash consideration of approximately $60.2 million. |
• | On August 22, 2019, the FERC approved the settlement of the MoGas rate case filed in May of 2018. The FERC order provides annual rates of approximately $14.8 million. The settlement became effective September 1, 2019, with the new rates retroactively effective December 1, 2018. In conjunction with the settlement, MoGas entered into 5-year firm transportation service agreements with its customers in exchange for modest discounts. |
• | During 2019, we received participating rent of $4.6 million on the Pinedale Lease Agreement based on the volumes of condensate and water that flowed through the Pinedale LGS. |
• | During 2019, we began considering investment structures and opportunities that became available to us as a result of the PLR from the IRS which, among other things, qualifies use fees for storage and pipeline capacity and oil platforms as representing REIT-qualifying rents from real property. |
Assets
Most of our REIT qualifying and other energy infrastructure assets have been acquired at various times since June of 2011, while our legacy private equity investments have been liquidated in accordance with the plans of those entities. Our business currently consists of the assets summarized below. For additional details concerning our energy infrastructure real property, see Item 2, "Properties" in this Report.
Energy Infrastructure Real Property Investments
• | Grand Isle Gathering System: a subsea, midstream 137-mile pipeline system located in the Gulf of Mexico and a 16-acre onshore terminal facility triple-net leased on a long-term basis to a subsidiary of EGC, pursuant to the Grand Isle Lease Agreement. The EGC Tenant's obligations under the lease agreement are guaranteed by EGC. |
• | Pinedale LGS: a system consisting of approximately 150 miles of pipelines and four above-ground central gathering facilities located in the Pinedale Anticline in Wyoming triple-net leased on a long-term basis to a subsidiary of, and guaranteed by, Ultra Petroleum Corp. and Ultra Resources, Inc. pursuant to the Pinedale Lease Agreement. |
• | MoGas Pipeline System: MoGas is the owner and operator of the MoGas Pipeline System, an approximately 263-mile FERC-regulated interstate natural gas pipeline in and around St. Louis and extending into central Missouri. |
• | Omega Pipeline: Omega Pipeline Company, LLC is a natural gas service provider located primarily on the US Army's Fort Leonard Wood military post in south-central Missouri. |
Energy Infrastructure Financing Investments
We have provided financing loans to owners and operators of energy infrastructure real property assets, secured by such assets and related equipment, as well as by the outstanding equity of the borrowers. These loans may include participating features pursuant to which we may receive additional interest tied to increases in utilization of the underlying facilities. See Part IV, Item 15, Note 5 ("Financing Notes Receivable") included in this Report for additional information concerning these investments.
7
Private Equity Investments
Our legacy private equity investments have been liquidated in accordance with the plans of those entities. Certain of our private equity investments were sold or disposed of by the end of 2018, and the remaining interest was liquidated at the end of 2019. For additional information, see Part IV, Item 15, Note 10 ("Fair Value") included in this Report.
Acquisition Strategies and Due Diligence
We primarily rely on our own analysis to determine whether to make an acquisition. In evaluating acquisition opportunities, we consider, among other things, the following aspects of each transaction:
• | Tenant/Borrower/Counterparty Evaluation – We evaluate each potential tenant, borrower or counterparty for its creditworthiness, typically considering factors such as management experience, industry position and fundamentals, operating history, and capital structure, as well as other factors that may be relevant to a particular acquisition. We seek opportunities in which we believe the tenant may have a stable or improving credit profile or credit potential that has not been recognized by the market. In evaluating a possible investment, the creditworthiness of a tenant, borrower or counterparty often will be balanced with the value of the underlying real estate, particularly if the underlying property is specifically suited to the needs of the tenant. Whether a prospective tenant, borrower or counterparty is creditworthy will be determined by our management team and reviewed by the investment committee, as described below. Creditworthy does not necessarily mean "investment grade." |
• | Importance to Tenant/Borrower/Counterparty Operations – We will predominately focus on properties that we believe are essential or important to the ongoing operations of the tenant, borrower or counterparty and/or for the economic production of hydrocarbon resources, which would remain necessary to any owner of the assets. We believe that this type of property will provide a relatively low risk of loss in the case of a potential bankruptcy or abandonment scenario since a tenant/borrower/counterparty is less likely to risk the loss of a critically important lease or property. |
• | Diversification – We attempt to diversify our portfolio to avoid dependence on any one particular tenant, borrower, counterparty, collateral type, and geographic location within the U.S. or tenant/borrower/counterparty industry. By diversifying, we seek to reduce the adverse effect of a single under-performing investment or a downturn in any particular asset or geographic region within the U.S. |
• | Lease Terms – Typically, the net leased properties we will acquire will be leased on a full recourse basis to the tenants or their affiliates. In addition, we often seek to include a clause in each lease that provides for increases in rent over the term of the lease. These increases are fixed or tied to increases in indices such as the CPI. In many cases the lease will also seek to provide for participation in gross revenues of the tenant at the property, thereby providing exposure to the successful commercial activity of the tenant through features such as participating rent. Alternatively, a lease may provide for mandated rental increases on specific dates, and we may adopt other methods in the future. |
• | Asset Evaluation – We review the physical condition of the property and assess the likelihood of replacing the rental payment stream if the tenant defaults. We also engage a third party to conduct, or require the seller to conduct, a preliminary examination, or Phase 1 assessment, of the site to determine the potential for contamination or similar environmental site assessments in an attempt to identify potential environmental liabilities associated with a property prior to its acquisition. |
• | Transaction Provisions to Enhance and Protect Value – We attempt to include provisions in the leases that we believe may help protect a real property asset from changes in the operating and financial characteristics of a tenant that may affect its ability to satisfy its obligations or reduce the value of the real property asset. Such provisions include requiring our consent to specified tenant activity, requiring the tenant to provide indemnification protections, and requiring the tenant to utilize good operating practices consistent with objective criteria. We seek to enhance the likelihood of a tenant's lease obligations being satisfied through a guaranty of obligations from the tenant's corporate parent or other entity or a letter of credit. In some circumstances, we may provide tenants with repurchase options on the leased property. We expect, in those situations that the option purchase price will generally be the greater of the contract purchase price or the fair market value of the property at the time the option is exercised. |
• | Equity Enhancements – We may attempt to obtain equity enhancements in connection with transactions. These equity enhancements may involve warrants exercisable at a future time to purchase stock of the tenant or borrower or their parent. If warrants are obtained, and become exercisable, and if the value of the stock subsequently exceeds the exercise price of the warrant, equity enhancements can help achieve the goal of increasing investor returns. |
• | Other Real Estate Related Assets – As other opportunities arise, we may also seek to expand the portfolio to include other types of real estate-related investments, in all cases within the energy infrastructure sector, such as: |
• | equity investments in real properties that are not long-term net leased to a single-tenant and may include partially leased properties, undeveloped properties and properties subject to short-term net leases, among others; |
8
• | mortgage loans secured by real properties including loans to our taxable REIT subsidiaries; |
• | subordinated interests in first mortgage real estate loans, or B-notes; |
• | mezzanine loans related to real estate, which are senior to the borrower's equity position but subordinated to other third-party financing; |
• | other energy infrastructure assets that we may acquire and operate as provided in the PLR; and |
• | equity and debt securities (including preferred equity, limited partnership interests, trusts and other higher-yielding structured debt and equity investments) issued by companies that are engaged in real-estate-related businesses as defined by regulations promulgated under the Code, including other REITs. |
Use of Taxable REIT Subsidiaries
We operate as a REIT and therefore are generally not subject to U.S. federal corporate income taxes on the income and gains that we distribute to our stockholders, including the income derived through leasing fees and financing revenue from our REIT qualifying investments in energy infrastructure assets. However, even as a REIT, we remain obligated to pay income taxes on earnings from our taxable REIT subsidiaries. The use of TRSs enables us to own certain assets and engage in certain businesses while maintaining compliance with the REIT qualification requirements under the Code. We may, from time to time, change the election of previously designated TRSs to be treated as qualified REIT subsidiaries, and may reorganize and transfer certain assets or operations from our TRSs to other subsidiaries, including qualified REIT subsidiaries. For example, through a series of reorganization events, and based on a favorable IRS private letter ruling received, Omega was converted from a TRS entity to a qualified REIT subsidiary in 2017. Refer to the "Omega Pipeline (Mowood, LLC)" section in Item 2 of this Report for additional details.
Regulatory and Environmental Matters
Our energy infrastructure assets and operations, as well as those of our tenants, are subject to numerous federal, state and local laws and regulations concerning the protection of public health and safety, zoning and land use, and pricing and other matters related to certain of our business operations. For a discussion of the current effects and potential future impacts of such regulations on our business and properties, see the discussion presented in Item 1A of this Report under the subheading "Risks Related to Our Investments in Real Estate and the U.S. Energy Infrastructure Sector." In particular, for a discussion of the current and potential future effects of compliance with federal, state and local environmental regulations, see the discussion titled "Costs of complying with governmental laws and regulations, including those relating to environmental matters, may adversely affect our income and the cash available for distribution to our stockholders" within such section.
Financing Strategies
Consistent with our asset acquisition policies, we use leverage when available on terms we believe are favorable. The amount of leverage that we may employ will depend on our assessment of market conditions and other factors at the time of any proposed borrowing. Although we currently do not anticipate doing so, the amount of total funded debt leverage we employ may exceed 50 percent of our total assets. Secured loans which we obtain, could be recourse or non-recourse to us. A lender on non-recourse mortgage debt often has recourse only to the property collateralizing such debt and not to any of our other assets, while full recourse financing would give the lender recourse to all of our assets. The use of non-recourse debt, helps us to limit the exposure of all of our assets to any one debt obligation. Lenders may, however, have recourse to our other assets in limited circumstances not related to the repayment of the indebtedness, such as under an environmental indemnity. We may have an unsecured line of credit that can be used in connection with refinancing existing debt and making new acquisitions, as well as to meet other working capital needs. We generally intend to incur debt which bears interest at fixed rates, or is effectively converted to fixed rates through interest rate caps or swap agreements.
Competition
We compete with public and private funds, commercial and investment banks and commercial financing companies to make the types of investments that we plan to make in the U.S. energy infrastructure sector. Many of our competitors are substantially larger and have considerably greater financial, technical and marketing resources than us. For example, some competitors may have a lower cost of funds and access to a greater variety of funding sources than are available to us. In addition, some of our competitors may have higher risk tolerances or different risk assessments, allowing them to consider a wider variety of investments and establish more relationships than us. These competitive conditions may adversely affect our ability to make investments in the energy infrastructure sector and could adversely affect our distributions to stockholders.
9
MANAGEMENT
Our Manager
We are externally managed by Corridor. Corridor is a real property asset manager with a focus on U.S. energy infrastructure real property assets. Corridor assists us in identifying infrastructure real property asset acquisition opportunities, and is generally responsible for our day-to-day operations.
Corridor Team
Each of our officers is an employee of Corridor or one of its affiliates. Corridor is not obligated to dedicate certain of its employees exclusively to us, nor are it or its employees obligated to dedicate any specific portion of its or their time to our business. As described below, we pay a management fee and certain other fees to Corridor, which it uses in part to pay compensation to its officers and employees who, notwithstanding that some of them also are our officers, receive no cash compensation directly from us.
We pay Corridor a management fee based on total assets under management. Additionally, in aligning our strategy to focus on distributions and distribution growth, Corridor is paid an incentive fee based on increases in distributions to our stockholders. A percentage of the Corridor incentive fee is reinvested in CorEnergy's common stock. Pursuant to the Management Agreement and Administrative Agreement, Corridor has agreed to use its reasonable best efforts to present us with suitable acquisition opportunities consistent with our investment objectives and policies and is generally responsible, subject to the supervision and review of our Board of Directors, for our day-to-day operations.
Energy Infrastructure Real Property Asset Management and Operation
The Corridor team has experience across several segments of the energy sector and is primarily responsible for investigating, analyzing and selecting potential infrastructure asset acquisition opportunities. Acquisitions and transactions are submitted to our Board of Directors for final approval following a recommendation from the management team.
We believe that effective management of our assets is essential to maintain and enhance property values. Important aspects of asset management include meeting the evolving needs of current tenants, re-leasing properties, refinancing debt, selling properties and knowledge of the bankruptcy process.
We monitor, on an ongoing basis, compliance by tenants with their lease obligations and other factors that could affect the financial performance of any of our properties. Monitoring involves receiving assurances that each tenant has paid real estate taxes, assessments and other expenses relating to the properties it occupies and confirming that appropriate insurance coverage is being maintained by the tenant. We review financial statements of tenants and undertake regular physical inspections of the condition and maintenance of properties. In addition, we periodically analyze each tenant's financial condition and the industry in which each tenant operates.
The PLR creates the opportunity for us to acquire and operate assets in the manner we now do for MoGas and Mowood, but on a broader scale. If we were to undertake to operate assets we acquire, we would rely on Corridor to provide or supervise the employees responsible for operating such assets.
Management Agreement
Under our Management Agreement, Corridor (i) presents us with suitable acquisition opportunities consistent with our investment policies and our objectives, (ii) is responsible for our day-to-day operations and (iii) performs such services and activities relating to our assets and operations as may be appropriate. The Management Agreement does not have a specific term, and will remain in place unless terminated by us or Corridor in the manner permitted pursuant to the agreement.
The terms of the Management Agreement include a quarterly management fee equal to 0.25 percent (1.00 percent annualized) of the value of our Managed Assets as of the end of each quarter. For purposes of the Management Agreement, "Managed Assets" means our total assets (including any securities receivables, other personal property or real property purchased with or attributable to any borrowed funds) minus (A) the initial invested value of all non-controlling interests, (B) the value of any hedged derivative assets, (C) any prepaid expenses and (D) all of the accrued liabilities other than (1) deferred taxes and (2) debt entered into for the purpose of leverage. For purposes of the definition of Managed Assets, our securities portfolio will be valued at then-current market value. For purposes of the definition of Managed Assets, other personal property and real property assets will include real and other personal property owned and our assets invested, directly or indirectly, in equity interests in or loans secured by real estate or personal property (including acquisition-related costs and acquisition costs that may be allocated to intangibles or are unallocated), valued at the aggregate historical cost, before reserves for depreciation, amortization, impairment charges or bad debts or other similar noncash reserves.
10
Corridor voluntarily recommended, and we agreed, that effective solely for the purpose of computing the Managed Assets in calculating the quarterly management fee under the terms of the Management Agreement for the quarters ended September 30, 2019 and December 31, 2019, the net proceeds received during the third quarter of 2019 from the offering of 5.875% Convertible Notes, which closed on August 12, 2019 (other than the cash portion of such proceeds that was utilized in connection with the exchange of our 7.00% Convertible Notes) should be excluded from Managed Assets.
The Management Agreement includes a quarterly incentive fee of 10 percent of the increase in distributions paid over a threshold distribution equal to $0.625 per share per quarter. The Management Agreement also requires at least half of any incentive fees to be reinvested in our common stock. Corridor voluntarily recommended, and we agreed, that that they would waive $470 thousand of the $658 thousand total quarterly incentive fees that would otherwise be payable under the provisions described above with respect to dividends paid on our common stock during the year ended December 31, 2019. Accordingly, Corridor received an incentive fee of $188 thousand during 2019.
Administrative Agreement
Under our Administrative Agreement, Corridor, as our administrator, performs (or oversees or arranges for the performance of) the administrative services necessary for our operation, including without limitation providing us with equipment, clerical, bookkeeping and record keeping services. For these services we pay our administrator an annual fee equal to 0.04 percent of the value of the Company's Managed Assets as of the end of each quarter, with a minimum annual fee of $30 thousand.
Pursuant to the Management and Administrative Agreement, Corridor furnishes us with office facilities and clerical and administrative services necessary for our operation (other than services provided by our custodian, accounting agent, dividend and interest-paying agents and other service providers). Corridor is authorized to enter into agreements with third parties to provide such services. To the extent we request, Corridor will (i) oversee the performance and payment of the fees of our service providers and make such reports and recommendations to the Board of Directors concerning such matters as the parties deem desirable; (ii) respond to inquiries and otherwise assist such service providers in the preparation and filing of regulatory reports, proxy statements, and stockholder communications, and the preparation of materials and reports for the Board of Directors; (iii) establish and oversee the implementation of borrowing facilities or other forms of leverage authorized by the Board of Directors; and (iv) supervise any other aspect of our administration as may be agreed upon by us and Corridor. We have agreed, pursuant to the Management Agreement, to reimburse Corridor for all out-of-pocket expenses incurred in providing the foregoing.
We bear all expenses not specifically assumed by Corridor and incurred in our operations. The compensation and allocable routine overhead expenses of all management professionals of Corridor and its staff, when and to the extent engaged in providing us management services, is provided and paid for by Corridor and not us.
Employees
As we are externally managed, we have no employees at the corporate level. Our subsidiary, Omega, has one part-time and three full-time employees. Our subsidiary MoGas has one part-time employee and 15 full-time employees.
AVAILABLE INFORMATION
We are required to file reports, proxy statements and other information with the SEC. We will make available free of charge our Annual Report on Form 10-K, Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q, Current Reports on Form 8-K and any amendments to those reports on or through our web site at http://corenergy.reit as soon as reasonably practicable after such material is electronically filed with, or furnished to, the SEC. This information may also be obtained, without charge, upon request by calling us at (816) 875-3705 or toll-free at (877) 699-2677. The SEC maintains an Internet site that contains reports, proxy and information statements and other information filed by us with the SEC which is available on the SEC's Internet site at www.sec.gov. Please note that any Internet addresses provided in this Form 10-K are for informational purposes only and are not intended to be hyperlinks. Accordingly, no information found and/or provided at such Internet address is intended or deemed to be included by reference herein.
ITEM 1A. RISK FACTORS
There are many risks and uncertainties that can affect our future business, financial performance or share price. Many of these are beyond our control. A description follows of some of the important factors that could have a material negative impact on our future business, operating results, financial condition or share price. This discussion includes a number of forward-looking statements. You should refer to the description of the qualifications and limitations on forward-looking statements in the first paragraph under Item 7 "Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations" of this Form 10-K.
11
Risks Related to Our Investments in Real Estate and the U.S. Energy Infrastructure Sector
Risks Related to Our Two Largest Investments
The Grand Isle Gathering System and the Pinedale LGS constitute the largest components of our leased infrastructure real property assets and associated lease revenues and will materially impact the results of our business.
The Grand Isle Gathering System represented approximately 32 percent of our total assets as of December 31, 2019, and the lease under the Grand Isle Lease Agreement with the EGC Tenant represented approximately 47 percent of our total revenue for the year ended December 31, 2019. The Pinedale LGS represented approximately 26 percent of our total assets as of December 31, 2019, and the lease payments under the Pinedale Lease Agreement with Ultra Wyoming represented approximately 31 percent of our total revenue for the year ended December 31, 2019. Accordingly, the financial condition of these tenants and related parent guarantors and the ability and willingness of each to satisfy their obligations under the respective lease agreements and guaranties will have an ongoing material impact on our results of operations, ability to service our indebtedness and ability to make distributions.
EGC, the corporate parent and guarantor of the obligations of EGC Tenant under the Grand Isle Lease Agreement and certain entities affiliated with it filed for bankruptcy on April 14, 2016. The EGC Tenant did not file for bankruptcy. On December 13, 2016, EGC announced the confirmation of its Plan of Reorganization by the bankruptcy court and, effective December 30, 2016, EGC emerged from its bankruptcy reorganization under the successor company name Energy XXI Gulf Coast, Inc., and we entered into related agreements effective December 30, 2016 pursuant to which the new EGC entity succeeded to the rights and obligations of pre-bankruptcy EGC under the original purchase agreement for the GIGS and as guarantor of the obligations of our tenant under the Grand Isle Lease Agreement. All payments due to us from the EGC Tenant were timely paid throughout the bankruptcy proceedings. EGC subsequently was acquired by an affiliate of Cox Oil, effective October 18, 2018.
Ultra Wyoming, the lessee of the Pinedale LGS, as well as Ultra Petroleum and Ultra Resources, the guarantors of Ultra Wyoming's obligations as tenant under the Pinedale Lease Agreement, each filed for bankruptcy on April 29, 2016. During the bankruptcy proceedings, Ultra Wyoming agreed to accept our lease without amendment, which was approved by the bankruptcy court on November 28, 2016. On March 14, 2017 the bankruptcy court approved Ultra Petroleum's Plan of Reorganization, and on April 12, 2017, the company announced its successful emergence from bankruptcy. All payments due to us under the Pinedale LGS lease were paid timely throughout the bankruptcy proceedings.
Despite their emergence from bankruptcy, Ultra Petroleum and, prior to its October 2018 acquisition by Cox Oil, EGC, have disclosed a number of risks related to their business in their respective filings with the SEC. A complete discussion of the risks related to Ultra Petroleum's business can be found in its Exchange Act reports filed with the SEC (NASDAQ: UPL through August 7, 2019; OTCQX: UPLC beginning August 8, 2019). Prior to the filing by EGC of a Form 15 with the SEC on October 29, 2018, following its acquisition by an affiliate of Cox Oil, to suspend its SEC reporting obligations, EGC had also disclosed a discussion of risks related to its business in the Exchange Act reports that EGC had filed with the SEC as a public reporting company (NASDAQ: EGC). Since EGC ceased to be a public reporting company on and after such date, it has not disclosed any updates to such risks following the Cox Oil acquisition.
We are subject to the risk of EGC Tenant and Ultra Wyoming transferring their obligations under the Grand Isle Lease Agreement and the Pinedale Lease Agreement, respectively.
Under the terms of the Grand Isle Lease Agreement and the terms of the Pinedale Lease Agreement, both the EGC Tenant and Ultra Wyoming may transfer their respective rights and obligations under the Grand Isle Lease Agreement and the Pinedale Lease Agreement at any time, subject to certain conditions. We thus bear the risk that EGC Tenant will transfer its rights and obligations under the Grand Isle Lease Agreement, or that Ultra Wyoming will transfer its rights and obligations under the Pinedale Lease Agreement, in each case to a third party whose creditworthiness may not be on par with that of our current tenant, which could inhibit such transferee's ability to make timely lease payments under the Grand Isle Lease Agreement or the Pinedale Lease Agreement (as applicable), or increase the likelihood that a downturn in the business of such transferee could give rise to a default under the applicable lease agreement. The occurrence of either of these events could have a material adverse impact on our business and financial condition.
Additional Risks Related to Our Real Estate and Energy Infrastructure Investments
Our focus on the energy infrastructure sector will subject us to more risks than if we were broadly diversified.
Because we specifically focus on the energy infrastructure sector, investments in our common stock may present more risks than if we were broadly diversified over numerous sectors of the economy. Therefore, a downturn in the U.S. energy infrastructure sector would have a larger impact on our assets and performance than on a company that does not concentrate in one sector of the economy. The energy infrastructure sector can be significantly affected by the supply of and demand for specific products and services; the supply and demand for crude oil, natural gas, and other energy commodities; the price of crude oil, natural gas, and other energy commodities; exploration, production and other capital expenditures; government regulation; world and regional events, politics and economic conditions.
12
Production declines and volume decreases could be caused by various factors, including decreased access to capital or loss of economic incentive to drill and complete wells, depletion of resources, catastrophic events affecting production, labor difficulties, political events, OPEC actions, environmental proceedings, increased regulations, equipment failures and unexpected maintenance problems, failure to obtain necessary permits, unscheduled outages, unanticipated expenses, inability to successfully carry out new construction or acquisitions, import or export supply and demand disruptions, or increased competition from alternative energy sources.
We are subject to risks involved in single tenant leases.
A significant portion of our acquisition activities are focused on real properties that are triple-net leased to single tenants. Therefore, the financial failure of, or other default by, a single tenant under its lease: (i) is likely to cause a significant reduction in the operating cash flow generated by the property leased to that tenant, (ii) might decrease the value of that property, and (iii) could expose us to 100 percent of all applicable operating costs.
In addition, if we determine that a renewal of a lease with any present or future tenant of any of our energy infrastructure assets is not in the best interests of our stockholders, if a tenant determines it no longer wishes to be the tenant under a lease upon its expiration, if we desire to terminate a lease as a result of a breach of that lease by the tenant or if we lose any tenant as a result of such tenant's bankruptcy, then in each circumstance we would need to identify a new tenant for the lease. We may not be able to identify a new tenant, as interest in leasing certain of our assets would be dependent on ownership of an interest in nearby mineral rights. In addition, any new tenant would need to be a qualified and reputable operator of such energy infrastructure assets with the wherewithal and capability of acting as our tenant. There is no assurance that we would be able to identify a tenant that meets these criteria, or that we could enter into a new lease with any such tenant on terms that are as favorable as the lease terms that were in place with the prior tenant.
We may be unable to identify and complete acquisitions of real property assets.
Our ability to identify and complete acquisitions of real property assets on favorable terms and conditions are subject to the following risks:
• | we may be unable to acquire a desired asset because of competition from other investors with significant capital, including both publicly traded and non-traded REITs and institutional investment funds; |
• | competition from other investors may significantly increase the purchase price of a desired real property asset or result in less favorable terms; |
• | we may not complete the acquisition of a desired real property asset even if we have signed an agreement to acquire such real property asset because such agreements are subject to customary conditions to closing, including completion of due diligence investigations to our satisfaction; and |
• | we may be unable to finance acquisitions of real property assets on favorable terms or at all. |
Net leases may not result in fair market lease rates over time.
We expect a large portion of our future income to come from net leases. Net leases typically have longer lease terms and, thus, there is an increased risk that if market rental rates increase in future years, the rates under our net leases will be less than fair market rental rates during those years. As a result, our income and distributions could be lower than they would otherwise be if we did not engage in net leases. We often will seek to include a clause in each lease that provides increases in rent over the term of the lease, as well as participating features based on increases in the tenant's utilization of the underlying asset, but there can be no assurance we will be successful in obtaining such a clause.
If a tenant declares bankruptcy and such action results in a rejection of the lease, or if the sale-leaseback transaction is challenged as a fraudulent transfer or re-characterized in the lessee company's bankruptcy proceeding, our business, financial condition and cash flows could be adversely affected.
We enter into sale-leaseback transactions, whereby we purchase an energy infrastructure property and then simultaneously lease the same property back to the seller. If a lessee company declares bankruptcy, our business could be adversely affected by one or both of the following:
• | A sale-leaseback transaction may be re-characterized by a bankruptcy court as either a disguised financing transaction or a functional joint venture. If the sale-leaseback were re-characterized as a financing transaction, we might not be considered the owner of the subject property and, as a result, we should have the status of a secured creditor of the lessee company with regard to the subject property, assuming the securitization measures we take as described below are respected by the bankruptcy court. In that event, we would no longer have the right to sell or encumber our ownership interest in the property. Instead, we would have a claim against the lessee company for the amounts owed under the lease. Although we believe each of our lease agreements constitutes a true lease that should not be subject to recharacterization, there is no guaranty |
13
that a bankruptcy court would agree. In the event of recharacterization, our claim under a lease agreement would either be secured or unsecured. As a preventative measure, we take steps to create and perfect a security interest in property made the subject of our lease agreements to ensure that our claim against the bankrupt lessee would be secured in the event of a recharacterization, but such attempts could be subject to challenge by the debtor or creditors and there is no assurance that a court would find our claim to be secured. The bankrupt lessee under this scenario might have the ability to restructure the terms, interest rate and amortization schedule of its outstanding balance owed under the lease. If approved by the bankruptcy court, we could be bound by the new terms, and prevented from foreclosing any lien on the property, so long as the lessee adhered to the new terms. If the sale-leaseback were re-characterized as a joint venture under applicable, non-bankruptcy law, we and the lessee company could be treated as co-venturers with regard to the property. As a result, we could be held liable, under some circumstances, for debts incurred by the lessee company relating to the property.
• | A lessee could either assume, assign or reject a lease in a bankruptcy case. The bankrupt lessee is required to make rent payments to us during its bankruptcy until it rejects the commercial real property lease (for leases that are personal property leases, the lessee need not make rental payments that arise from the petition date until 60 days after the order for relief is entered in the bankruptcy case). If the lessee assumes the lease, the bankrupt debtor must pay or “cure” all existing monetary defaults under the lease. Further, the lease can only be assumed “as is”. The bankruptcy court would not be able to change the rental amount or any other lease provision that could financially impact us. However, if the lessee rejects the lease, the facility would be returned to us. If a lease is rejected, we may not be able to identify a new tenant, as interest in leasing certain of our assets would be dependent on ownership of an interest in nearby mineral rights. In addition, any new tenant would need to be a qualified reputable operator of such energy infrastructure assets with the wherewithal and capability of acting as our tenant. There is no assurance that we would be able to identify a tenant that meets these criteria, or that we could enter into a new lease with any such tenant on terms that are as favorable as the lease terms that were in place with the prior tenant. If we were able to re-lease the affected facility to a new tenant only on unfavorable terms or after a significant delay, we could lose some or all of the revenue from that facility for an extended period of time. Further, if the lease agreement is rejected, our claim against the lessee and/or parent guarantor could be, in some courts, subject to a statutory cap under section 502(b)(6) of the Bankruptcy Code to the extent the lease agreement is deemed to be a lease for real property rather than a lease for personal property. Such cap generally limits the amount of a claim for lease-based damages in the event of a termination of a commercial real property lease to the greater of one year's rent or 15 percent of the rent reserved for the remaining lease term, not to exceed 3 years. There is a national split of authority as to whether a rejection of such a lease equates a termination, so the outcome will depend on where the bankrupt lessee files its bankruptcy. We believe that any of our lease agreements would be characterized as real property leases rather than personal property leases, though a court could hold to the contrary. |
Energy infrastructure companies are and will be subject to extensive regulation because of their participation in the energy infrastructure sector, which could adversely impact the business and financial performance of our tenants and the value of our assets.
Companies in the energy infrastructure sector are subject to significant federal, state and local government regulation in virtually every aspect of their operations, including how facilities are constructed, maintained and operated, environmental and safety controls, and the prices they may charge for the products and services they provide. Various governmental authorities have the power to enforce compliance with these regulations and the permits issued under them, and violators are subject to administrative, civil and criminal penalties, including civil fines, injunctions or both. Stricter laws, regulations or enforcement policies could be enacted in the future that likely would increase compliance costs, which could adversely affect the business and financial performance of our tenants in the energy infrastructure sector and the value or quality of our assets.
Costs of complying with governmental laws and regulations, including those relating to environmental matters, may adversely affect our income and the cash available for distribution to our stockholders.
We have invested, and expect to continue to invest, in real property assets, which are subject to laws and regulations relating to the protection of the environment and human health and safety. These laws and regulations generally govern the gathering, storage, handling, and transportation of petroleum and other hazardous substances, the emission and discharge of materials into the environment, including wastewater discharges and air emissions, the operation and removal of underground and aboveground storage tanks, the generation, use, storage, treatment, transportation and disposal of solid and hazardous materials and wastes, and the remediation of any contamination associated with such disposals. We own assets related to the storage and distribution of oil and gas, natural gas and natural gas liquids, and storage and throughput of crude oil, which are subject to all of the inherent hazards and risks normally incidental to such assets, such as fires, well site blowouts, cratering and explosions, pipe and other equipment and system failures, uncontrolled flows of oil, gas or well fluids, formations with abnormal pressures, environmental risks and hazards such as gas leaks, oil spills and pipeline ruptures and discharges of toxic gases. Environmental laws and regulations may impose joint and several liability on tenants, owners or operators for the costs to investigate or remediate contaminated properties, regardless of fault or whether the acts causing the contamination were legal. This liability could be substantial. Moreover, if one or more of
14
these hazards occur, there can be no assurance that a response will be adequate to limit or reduce any resulting damage. In addition, the presence of hazardous substances, or the failure to properly remediate these substances, may adversely affect our ability to sell, rent or pledge such property as collateral for future borrowings. We also may be required to comply with various local, state and federal fire, health, life-safety and similar regulations.
Local, state and federal laws in this area are constantly evolving. Compliance with new or more stringent laws or regulations, or stricter interpretation of existing laws, may impose material environmental liability and/or require material expenditures by us to avoid such liability. Further, our tenant companies' operations, the existing condition of land when we buy it or operations in the vicinity of our properties (each of which could involve the presence of underground storage tanks), or activities of unrelated third parties may affect our properties. We intend to monitor these laws and take commercially reasonable steps to protect ourselves from the impact of these laws, including, where deemed necessary, obtaining environmental assessments of properties that we acquire. In addition, any such assessment that we do obtain may not reveal all environmental liabilities or whether a prior owner of a property created a material environmental condition not known to us and may not offer any protection against liability for known or unknown environmental conditions.
Failure to comply with applicable environmental, health, and safety laws and regulations may result in the assessment of sanctions, including administrative, civil or criminal fines or penalties, permit revocations, and injunctions limiting or prohibiting some or all of the operations at our facilities. Any material compliance expenditures, fines, or damages we must pay could materially and adversely affect our business, assets or results of operations and, consequently, would reduce our ability to make distributions.
Regulation of greenhouse gases and climate change could have a negative impact on our and our tenants' businesses.
We cannot predict with certainty the rate at which climate change is occurring. However, scientific studies have suggested that emissions of certain gases, commonly referred to as greenhouse gases ("GHGs") and including carbon dioxide and methane, may be contributing to warming of the earth's atmosphere and other climatic changes. In response to such studies, the issue of the effect of GHG emissions on climate change, in particular emissions from fossil fuels, is attracting increasing attention worldwide. We are aware of the increasing focus of local, state, national and international regulatory bodies on GHG emissions and climate change issues. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency ("EPA") has adopted rules requiring GHG reporting and permitting, and the United States Congress and EPA may consider additional legislation or regulations that could ultimately require new, modified, and reconstructed facilities, and/or existing facilities, to meet emission standards by installing control technologies, adopting work practices, or otherwise reducing GHG emissions. Although it is not possible at this time to predict whether proposed legislation or regulations will be adopted, any such future laws and regulations could result in increased compliance costs or additional operating restrictions that could adversely impact our energy infrastructure assets as well as the businesses of our tenants and customers. If we or our tenants are unable to recover or pass through a significant level of the costs related to complying with any such future climate change and GHG regulatory requirements, it could have a material adverse impact on our or our tenants' business, financial condition and results of operations. Further, to the extent financial markets view climate change and GHG emissions as a financial risk, this could negatively impact our cost of or access to capital. Climate change and GHG regulation could also reduce the demand for hydrocarbons and, ultimately, demand for utilization of our energy infrastructure assets related to the production and distribution of hydrocarbons. Finally, it should be noted that studies suggest that increasing concentrations of GHGs in the Earth's atmosphere may produce climate changes that have significant physical effects, such as increased frequency and severity of hurricanes and other storms, floods and related climatic events. If any such effects were to occur, they could have an adverse effect on our assets and operations, particularly an offshore asset such as the GIGS.
Our operations, as well as those of our tenants, are subject to operational hazards and unforeseen interruptions. If a significant accident or event occurs that results in a business interruption or shutdown for which we or our tenant operators are not adequately insured, such operations and our financial results could be materially adversely affected.
Our assets are subject to many hazards inherent in the transmission of energy products and provision of related services, including:
• | aging infrastructure, mechanical or other performance problems; |
• | damage to pipelines, facilities and related equipment caused by tornadoes, hurricanes, floods, fires and other natural disasters, explosions and acts of terrorism; |
• | inadvertent damage from third parties, including from construction, farm and utility equipment; |
• | leaks of natural gas and other hydrocarbons or losses of natural gas as a result of the malfunction of equipment or facilities; |
• | operator error; |
• | environmental hazards, such as natural gas leaks, product and waste spills, pipeline and tank ruptures, and unauthorized discharges of products, wastes and other pollutants into the surface and subsurface environment, resulting in environmental pollution; and explosions. |
15
These risks could result in substantial losses due to personal injury and/or loss of life, severe damage to and destruction of property and equipment and pollution or other environmental damage and may result in curtailment or suspension of our or our tenants' related operations or services. A natural disaster or other hazard affecting the areas in which we or our tenants operate could have a material adverse effect on our operations and the financial results of our business.
Both we and our tenants depend on certain key customers for a significant portion of our respective revenues. The loss of any such key customers could result in a decline in our business.
Both we and our tenants are subject to risks of loss resulting from nonperformance by customers. We depend on certain key customers for a significant portion of our revenues, particularly operating revenues from MoGas. Our tenants are similarly dependent on revenues from key customers to support their operations and ability to make lease payments to us. The loss of all or even a portion of the contracted volumes of such customers, as a result of competition, creditworthiness, inability to negotiate extensions or replacements of contracts or otherwise, could have a material adverse effect on the business, financial condition and results of operations of us or our tenants (as applicable), unless we or they are able to contract for comparable volumes from other customers at favorable rates.
We are exposed to the credit risk of our tenants and customers and our credit risk management may not be adequate to protect against such risk.
We are subject to the risk of loss resulting from nonpayment and/or nonperformance by our tenants and customers. Our credit procedures and policies may not be adequate to fully eliminate such credit risk. If we fail to adequately assess the creditworthiness of existing or future tenants or customers, unanticipated deterioration in their creditworthiness and any resulting increase in nonpayment and/or nonperformance by them and inability to re-market the resulting capacity, or re-lease the underlying assets, could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations. We may not be able to effectively re-market such capacity, or re-lease such assets, during and after bankruptcy or insolvency proceedings involving a tenant or customer.
Our assets and operations, as well as those of our tenants and other investees and customers, can be affected by extreme weather patterns and other natural phenomena.
Our assets and operations, as well as those of our tenants and other investees and customers, can be adversely affected by floods, hurricanes, earthquakes, landslides, tornadoes and other natural phenomena and weather conditions, including extreme or unseasonable temperatures, making it more difficult for us to realize the historic rates of return associated with our assets and operations. These events also could result in significant volatility in the supply of energy and power, which might create fluctuations in commodity prices and earnings of companies in the energy infrastructure sector. A significant disruption in our operations or those of our tenants, investees or customers, or a significant liability for which we or any affected tenant or investee is not fully insured, could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, and financial condition. Moreover, extreme weather events could adversely impact the valuation of our energy infrastructure assets.
The operation of our energy infrastructure assets could be adversely affected if third-party pipelines, railroads or other facilities interconnected to our facilities become partially or fully unavailable.
Our facilities, as well as those of our tenants, may connect to other pipelines, railroads or facilities owned by third parties. Both we and our tenants depend upon third-party pipelines and other facilities that provide delivery options to and from such facilities. For example, MoGas' pipeline interconnects, directly or indirectly, with most major interstate pipelines in the eastern portion of the U.S. and a significant number of intrastate pipelines. Because we do not own these third-party facilities, their continuing operation is not within our control. Accordingly, these pipelines and other facilities may become unavailable, or available only at a reduced capacity. If these pipeline connections were to become unavailable to us or our tenants for current or future volumes of products due to repairs, damage, lack of capacity or any other reason, our ability, or the ability of our tenants, to operate efficiently and continue shipping products to end markets could be restricted, thereby reducing revenues. Likewise, if any of these third-party pipelines or facilities becomes unable to transport any products distributed or transported through our or our tenants' facilities, our or our tenants' business, results of operations and financial condition could be adversely affected, which could adversely affect our ability to make cash distributions to our stockholders.
The relative illiquidity of our real property and energy infrastructure asset investments may interfere with our ability to sell our assets when we desire.
Investments in real property and energy infrastructure assets are relatively illiquid compared to other investments. Accordingly, we may not be able to sell such assets when we desire or at prices acceptable to us in response to changes in economic or other conditions. This could substantially reduce the funds available for satisfying our obligations and for distribution to our stockholders.
16
Additional Risks Related to the Grand Isle Gathering System and Grand Isle Lease Agreement
The ongoing refusal of EGC and Cox Oil to provide financial statements to us in accordance with the terms of the Grand Isle Lease Agreement has adversely impacted the use of our effective registration statements on Form S-3 and Form S-8 to register the offer and sale of securities. The lack of EGC financial statement information has also limited our ability to issue registered common stock to participants in our dividend reinvestment plan and to use our common stock as a component of compensation for our independent directors. The refusal by EGC and Cox Oil will also either prevent or make more costly our efforts to raise future capital if we are unable to use our universal shelf registration statement on Form S-3.
Under applicable SEC rules, an issuer loses the privilege of using "short form" Form S-3 or Form S-8 registration statements to offer and sell securities unless it has timely filed all periodic and other reports required to be filed under the Exchange Act after the initial filing of such a registration statement. As described elsewhere in this Report, EGC and Cox Oil have refused to provide the financial statement information concerning EGC required to be filed by us pursuant to SEC Regulation S-X, as described in Section 2340 of the SEC Financial Reporting Manual. We believe that EGC and Cox Oil are required to provide us with this information, for inclusion in our SEC reports, pursuant to the terms of the Grand Isle Lease Agreement. The refusal of EGC and Cox Oil to provide these financial statements has adversely impacted our ability to use our currently effective shelf registration statements on Form S-3. In addition, we do not expect that the SEC will declare effective any registration statement that we file on any other form in connection with an offering so long as we remain unable to amend our Annual Reports on Form 10-K for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018 to include the required financial statements of EGC. These circumstances will either prevent or make more costly our efforts to raise future capital through the issuance of our equity and debt securities on a rapid basis. This action by EGC and Cox Oil could also have a negative impact on executing potential acquisitions or other transactions in a timely and efficient manner. While we may be able to raise additional capital through bank financing, private placement transactions or other means, these alternatives could increase both our financing costs and the amount of time required to complete a transaction, and there is no guarantee that we would succeed in raising the additional capital required on a timely basis.
Our dividend reinvestment plan is registered under the Securities Act pursuant to a Form S-3D. As previously disclosed in our Current Report on Form 8-K filed on April 24, 2019, as a result of the refusal by EGC and Cox Oil to provide financial information, we have suspended our dividend reinvestment plan and currently are paying quarterly common stock dividends entirely in cash. Furthermore, the issuance of common stock to our independent directors as a portion of their compensation is registered under the Securities Act pursuant to a Form S-8. We have similarly suspended the issuance of these registered shares under the Company's Director Compensation Plan as a result of our inability to file the required EGC financial statements.
We have engaged in dialogue with the staff of the SEC in an effort to shorten the period during which we do not use these registration statements. We do not expect this period to be shortened until the EGC financial statement information has been received and filed. There is no assurance that we will be successful in obtaining such relief.
Requirements imposed by the BOEM and BSEE related to the decommissioning, plugging, and abandonment of offshore facilities could significantly impact our cost of owning the Grand Isle Gathering System, which could have a material adverse impact on our financial condition and ability to make distributions to our stockholders.
The Bureau of Ocean Energy Management (the "BOEM") issued guidance effective October 15, 2010, following the Deepwater Horizon accident, that effectively established a more stringent regimen for the timely decommissioning of what is known as "idle iron"-wells, platforms and pipelines that are no longer producing or serving exploration or support functions related to an operator's lease-in the Gulf of Mexico ("GOM"). This guidance includes decommissioning requirements providing that pipelines, platforms or other facilities, which would include various components of the Grand Isle Gathering System, that are no longer useful for operations must be removed within five years of the cessation of operations, or as otherwise specified therein. A higher than normal level of decommissioning activity in the GOM at a time when the Grand Isle Gathering System is decommissioned may result in increased demand for salvage contractors and equipment, which in turn could result in increased estimates of plugging, abandonment and removal costs related to these regulatory asset retirement obligations.
To cover these asset retirement obligations, the BOEM generally requires that Outer Continental Shelf ("OCS") lessees, pipeline right-of-way holders and other facility owners demonstrate financial strength and reliability according to regulations or post bonds or other acceptable assurances that such obligations will be satisfied. In July 2016, the BOEM issued a new Notice to Lessees ("NTL") with an effective date of September 12, 2016, requiring additional security for decommissioning activities. The BOEM announced on June 22, 2017 that, pending its review of the NTL, the implementation timeline would be indefinitely extended, subject to certain exceptions. At this time it remains uncertain when or if the new NTL will be implemented. The cost of these bonds or assurances can be substantial and could increase under the BOEM's latest policies, depending on the outcome of the Trump administration's review during the extended implementation period. There is no assurance that such bonds or assurances can be obtained in all cases. While EGC historically has satisfied these requirements with respect to its ownership and operation of the Grand Isle Gathering System, and the terms of the Grand Isle Lease Agreement require EGC to continue to do so, given continued volatility in commodity
17
prices and the unwillingness of the surety companies to post bonds without the requisite collateral from operators such as EGC, there is no assurance that EGC will be able to continue to satisfy the demands for additional collateral for its current bonds or comply with any new supplemental bonding requirements. If EGC were financially unable to satisfy these requirements, Grand Isle Corridor, LP, as the owner of the Grand Isle Gathering System, would be required to do so. There can be no assurance that we would be able to meet any such increased bonding requirements. Under some circumstances, the BOEM may require any of our or our lessee's operations on federal leases, rights-of-way or facilities to be suspended or terminated. Any such suspension or termination could materially adversely affect our financial condition and results of operations. In addition, the BOEM can require supplemental bonding from operators for decommissioning, plugging, and abandonment liabilities if financial strength and reliability criteria are not met. If EGC is unable to fund any such supplemental bonding requirements and our subsidiary were required to bear the cost as owner of the Grand Isle Gathering System, such cost could have a material adverse impact on our financial condition and ability to make distributions to our stockholders.
The Bureau of Safety and Environmental Enforcement ("BSEE") administers regulations governing blowout preventer systems and well control for oil and gas and sulfur operations on the OCS; lease term requirements for continuing operations; and production safety systems. BSEE regulations also require offshore oil and gas lessees and owners of operating rights to submit summaries of their actual expenditures for decommissioning pipelines and wells, platforms, and other facilities on the OCS. These regulations may require capital expenditures and other compliance costs and could result in liability for non-compliance.
Failure to comply with these laws and regulations may trigger a variety of administrative, civil and criminal enforcement measures, including the assessment of monetary penalties, the imposition of remedial requirements and the issuance of orders enjoining future operations. In addition, increases in penalty amounts and limits of liability for damages to reflect inflation and/or increases in the CPI may result in increased exposure to EGC and its indirect parent, Cox Oil. EGC and Cox Oil may be unable to recover some or all of the resulting costs through insurance or increased revenues, which could have a material adverse effect on its business, results of operations and financial condition.
Additional Risks Related to Our Ownership and Operation of MoGas or Other Assets
Our operation of assets such as those at MoGas is subject to extensive regulation, including those relating to environmental matters, which may adversely affect our income and the cash available for distribution.
In addition to the regulations discussed above and pipeline safety regulations discussed below, MoGas' operations, as well as those of assets we may acquire and operate in the future, are subject to extensive federal, regional, state and local environmental laws including, for example, the Clean Air Act (CAA), the Clean Water Act (CWA), the Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation and Liability Act (CERCLA), the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA), the Oil Pollution Act (OPA), the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) and analogous state and local laws. These laws and their implementing regulations may restrict or impact such business activities in many ways, including requiring the acquisition of permits or other approvals to conduct regulated activities, limiting emissions and discharges of pollutants, restricting the manner in which it disposes of wastes, requiring remedial action to remove or mitigate contamination, requiring capital expenditures to comply with pollution control or workplace safety requirements, and imposing substantial liabilities for pollution resulting from its operations. In addition, the regulations implementing these laws are constantly evolving, and the potential impact of recent regulatory actions is unclear. For instance, the EPA adopted final rules establishing new source performance standards for methane emissions from new, modified, or reconstructed oil and gas sources, although a rule proposing reconsideration of these amendments has been proposed. Compliance with new or more stringent laws or regulations, or stricter interpretation of existing laws, may require material expenditures by MoGas, and likewise may require material expenditures at other facilities or systems we may acquire and operate.
Failure to comply with these laws and regulations may trigger a variety of administrative, civil and criminal enforcement measures, including the assessment of monetary penalties, the imposition of remedial requirements and the issuance of orders enjoining future operations. In addition, increases in penalty amounts and limits of liability for damages to reflect inflation and/or increases in the CPI may result in increased exposure to operations such as MoGas. The operator of any such assets may be unable to recover some or all of the resulting costs through insurance or increased revenues, which could have a material adverse effect on its business, results of operations and financial condition.
The PLR grants us the ability to own and to operate storage facilities, pipelines, and oil platforms and to have assurance that the payments we receive are treated as rent from real property for purposes of our qualification as a REIT. To the extent we acquire and operate any such asset, we will be exposed to risks similar to those described above and to which MoGas is exposed. In addition, oil platforms located off the coast of the United States are subject to additional regulatory scrutiny by BOEM and BSEE, as is described above for our Grand Isle Gathering System.
18
MoGas' natural gas transmission operations, and related customer revenue agreements, are subject to regulation by FERC.
MoGas' business operations are subject to regulation by FERC, including the types and terms of services MoGas may offer to its customers, construction of new facilities, expansion of current facilities, creation, modification or abandonment of services or facilities, record keeping and relationships with affiliated companies. Compliance with these requirements can be costly and burdensome and FERC action in any of these areas could adversely affect MoGas' ability to compete for business, construct new facilities, expand current facilities, offer new services, recover the full cost of operating its pipelines or earn its authorized rate of return. This regulatory oversight can result in longer lead times or additional costs to develop and complete any future project than competitors that are not subject to FERC's regulations. To the extent we, in reliance on the PLR, acquire and operate other facilities or systems, those facilities or systems may similarly be subject to FERC regulatory oversight.
In addition, the rates MoGas can charge for its natural gas transmission operations are regulated by FERC pursuant to the Natural Gas Act of 1938 ("NGA") as follows:
• | MoGas may only charge rates that have been determined to be just and reasonable by FERC, subject to a prescribed maximum and minimum, and is prohibited from unduly preferring or unreasonably discriminating against any person with respect to its rates or terms and conditions of service. |
• | MoGas' existing rates may be challenged in a proceeding before FERC, which may reduce MoGas' rates if FERC finds the rates are not just and reasonable or are unduly preferential or unduly discriminatory. Proposed rate increases may be challenged by protest and allowed to go into effect subject to refund. Even if a rate increase is permitted by FERC to become effective, the rate increase may not be adequate. |
To the extent MoGas' costs increase in an amount greater than its revenues increase, or there is a lag between MoGas' cost increases and its ability to file for and obtain rate increases, MoGas' operating results would be negatively affected.
Should FERC find that MoGas has failed to comply with all applicable FERC-administered statutes, rules, regulations, and orders, or with the terms of MoGas' tariffs on file with FERC, MoGas could be subject to substantial penalties and fines. Under the Energy Policy Act of 2005 ("EPAct 2005"), FERC has civil penalty authority under the NGA and Natural Gas Policy Act of 1978 ("NGPA") to impose penalties for violations of up to approximately $1.3 million per day for each violation, to revoke existing certificate authority and to order disgorgement of profits associated with any violation.
On May 31, 2018, MoGas filed a general rate case with FERC seeking a change in its rates to (i) recover increases in capital, operating and maintenance expenditures incurred; (ii) mitigate the revenue impact from the substantial decrease in volumes due to the loss of a firm transportation agreement with a St. Louis natural gas marketing entity; (iii) mitigate the substantial decrease in revenue from the negotiated rate charged to MoGas' largest customer; and (iv) reflect changes in the corporate income tax rate associated with the 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act. MoGas' filing proposed an increase in MoGas' revenue requirement of approximately $8.7 million.
The proposed rates went into effect on December 1, 2018. On August 22, 2019, the FERC approved a settlement agreed to by MoGas and all intervenors in the rate case to provide maximum annual transportation rates that equate to approximately $14.8 million, effective September 1, 2019. As a result of the approved and effective settlement, MoGas has begun to refund the difference between the filed rates and the settlement rates. In conjunction with the settlement, MoGas entered into 5-year firm transportation service agreements with its customers in exchange for modest discounts to its maximum transportation rates. The agreements, which amend prior year-to-year agreements, extend the termination date for the existing firm transportation service agreements to December 31, 2023.
We cannot give any assurance regarding potential future regulations under which MoGas will operate its natural gas transmission business, or the effect that any changes in such future regulations, or in MoGas' agreements with its customers following December 31, 2023, could have on MoGas' business, financial condition and results of operations.
Once the five-year rate agreements described above expire, revenues of MoGas' business with its customers other than Spire will once again be generated under agreements that are subject to cancellation on an annual basis.
Once the term of MoGas' current firm transportation services pricing arrangement with its customers other than its largest customer, Spire, expire on December 31, 2023, revenues for MoGas' business with such other customers will once again be generated under transportation agreements which renew automatically on a year-to-year basis, but will be subject to cancellation by the customer or MoGas on 365 days' notice. When that occurs, if MoGas is unable to succeed in replacing any agreements canceled by its customers or itself that account for a significant portion of its revenues, or in renegotiating such agreements on terms substantially as favorable as the existing agreements, MoGas could suffer a material reduction in its revenues, financial results and cash flows. The maintenance or replacement of agreements with MoGas' customers at rates sufficient to maintain current or projected revenues and cash flows ultimately depends on a number of factors beyond its control, including competition from other pipelines, the proximity of supplies
19
to the markets, and the price of, and demand for, natural gas. In addition, changes in state regulation of local distribution companies may cause them to exercise their cancellation rights in order to turn back their capacity when the agreements expire.
Pipeline safety integrity programs and repairs may impose significant costs and liabilities on MoGas or other operating assets we may acquire.
Regulations administered by the Federal Office of Pipeline Safety within the U.S. Department of Transportation's Pipeline and Hazardous Materials Safety Administration ("PHMSA") require pipeline operators to develop integrity management programs to comprehensively evaluate certain areas along their pipelines and to take additional measures to protect certain pipeline segments. As an operator, MoGas is, and any other systems or facilities we may acquire and operate in reliance on the PLR are likely to be, required to:
• | perform ongoing assessments of pipeline or asset integrity; |
• | identify and characterize applicable threats to pipeline or asset segments that could impact a high consequence area; |
• | improve data collection, integration and analysis; |
• | repair and remediate the pipeline or asset as necessary; and |
• | implement preventative and mitigating actions. |
MoGas is required to maintain pipeline integrity testing programs that are intended to assess pipeline integrity. Any repair, remediation, preventative or mitigating actions could require significant capital and operating expenditures. The regulations implementing these laws are constantly evolving; pursuant to its reauthorization under the Protecting our Infrastructure of Pipelines and Enhancing Safety Act of 2016 (the "PIPES Act"), PHMSA has adopted rules implementing its emergency order authority over pipelines, revising federal pipeline safety regulations related to underground natural gas storage facilities, and imposing additional requirements on the transportation of natural gas and hazardous liquids by pipeline, including more stringent standards for plastic pipe. In October 2019, PHMSA issued final rules amending pipeline safety regulations governing both hazardous liquid pipelines and gas transmission pipelines. These rules extend reporting, inspections, integrity assessment, leak detection, and in-line inspection requirements to include additional pipeline segments, including certain pipeline segments outside high consequence areas. PHMSA also issued a final rule adopting enhanced emergency order procedures implementing certain emergency order authority conferred on the Secretary by the PIPES Act. No further action has been taken on the notice of proposed rulemaking to harmonize the hazardous materials regulations with international regulations and standards. Compliance with new or more stringent laws or regulations, or stricter interpretation of existing laws, could significantly increase compliance costs. Should MoGas fail to comply with the Federal Office of Pipeline Safety's rules and related regulations and orders, it could be subject to significant penalties and fines, including potential future increases in applicable penalty amounts to reflect inflation, which could have a material adverse effect on MoGas' business, results of operations and financial condition. PHMSA also may apply to other systems at facilities that we, in reliance on the PLR, may acquire and operate in the future.
MoGas competes with other pipelines.
The principal elements of competition among pipelines are availability of capacity, rates, terms of service, access to supplies, flexibility, and reliability of service. Additionally, FERC's policies promote competition in natural gas markets by increasing the number of natural gas transmission options available to MoGas' customer base. Any current or future pipeline system or other form of transmission that delivers natural gas into the areas that MoGas serves could offer transmission services that are more desirable to shippers than those MoGas provides because of price, location, facilities or other factors. Increased competition could reduce the volumes of product MoGas transports, result in a reduction in the rates MoGas is able to negotiate with its customers, or cause customers to choose to ship their product on a different competing pipeline. Any one of these consequences could have a material adverse impact on MoGas, or on the operations of any other pipeline owned by the Company. These competitive considerations also could intensify the negative impact of factors that adversely affect the demand for MoGas' services, such as adverse economic conditions, weather, higher fuel costs and taxes or other regulatory actions that increase the cost, or limit the use, of products MoGas transports.
Risks Related to Our Financing Arrangements
Our indebtedness could have important consequences, including impairing our ability to obtain additional financing or pay future distributions, as well as subjecting us to the risk of foreclosure on any mortgaged properties in the event of non-payment of the related debt.
As of December 31, 2019, we had outstanding consolidated indebtedness of approximately $156.0 million. Our leverage could have important consequences. For example, it could:
• | result in the acceleration of a significant amount of debt for non-compliance with the terms of such debt or, if such debt contains cross-default or cross-acceleration provisions, other debt; |
20
• | materially impair our ability to borrow undrawn amounts under existing financing arrangements or to obtain additional financing or refinancing on favorable terms or at all; |
• | require us to dedicate a substantial portion of our cash flow to paying principal and interest on our indebtedness, thereby reducing the cash flow available to fund our business, to pay distributions, including those necessary to maintain REIT qualification, or to use for other purposes; |
• | increase our vulnerability to economic downturns; |
• | limit our ability to withstand competitive pressures; or |
• | reduce our flexibility to respond to changing business and economic conditions. |
It is also important to note that our variable rate indebtedness under the CorEnergy Credit Facility and the Mowood/Omega Revolver use LIBOR as a benchmark for establishing the rate. LIBOR is the subject of recent national, international and other regulatory guidance and proposals for reform. These reforms and other pressures may cause LIBOR to disappear entirely or to perform differently than in the past. The consequences of these developments cannot be entirely predicted, but could include an increase in the cost of our variable rate indebtedness.
In July 2017, the Financial Conduct Authority, the authority that regulates LIBOR, announced it intends to stop compelling banks to submit rates for the calculation of LIBOR after 2021. The Alternative Reference Rates Committee ("ARRC") has proposed that the Secured Overnight Financing Rate ("SOFR") is the rate that represents best practice as the alternative to USD-LIBOR for use in derivatives and other financial contracts that are currently indexed to USD-LIBOR. ARRC has proposed a paced market transition plan to SOFR from USD-LIBOR and organizations are currently working on industry wide and company specific transition plans as it relates to derivatives and cash markets exposed to USD-LIBOR. There is no guarantee that a transition from LIBOR to an alternative will not result in financial market disruptions, significant increases in benchmark rates, or financing costs to borrowers. We have material contracts that are indexed to USD-LIBOR and we are monitoring this activity and evaluating the related risks.
Further, we expect to mortgage many of our properties to secure payment of indebtedness. If we are unable to meet mortgage payments, such failure could result in the loss of assets due to foreclosure and transfer to the mortgagee or sale on unfavorable terms with a consequent loss of income and asset value. A foreclosure of one or more of our properties could create taxable income without accompanying cash proceeds, and could adversely affect our financial condition, results of operations, cash flow, and ability to service debt and make distributions and the market price of our stock.
We face risks associated with our dependence on external sources of capital.
In order to qualify as a REIT, we are required each year to distribute to our stockholders at least 90 percent of our REIT taxable income, and we will be subject to tax on our income to the extent it is not distributed. Because of this distribution requirement, we may not be able to fund all future capital needs from cash retained from operations. As a result, to fund capital needs, we must rely on third-party sources of capital, which we may not be able to obtain on favorable terms, if at all. Our access to third-party sources of capital depends upon a number of factors, including (i) general market conditions; (ii) the market's perception of our growth potential; (iii) our current and potential future earnings and cash distributions; and (iv) the market price of our capital stock. Additional debt financing may substantially increase our debt-to-total capitalization ratio. Additional equity issuances may dilute the holdings of our current stockholders.
Covenants in our loan documents could limit our flexibility and adversely affect our financial condition.
The terms of our various credit agreements and other indebtedness require us to comply with a number of customary financial and other covenants, such as maintaining debt service coverage and leverage ratios and maintaining insurance coverage. These covenants may limit our flexibility in our operations, and breaches of these covenants could result in defaults under the instruments governing the applicable indebtedness even if we had satisfied our payment obligations. If we were to default under credit agreements or other debt instruments, our financial condition would be adversely affected.
We face risks related to "balloon payments" and refinancings.
Certain of our mortgages will have significant outstanding principal balances on their maturity dates, commonly known as "balloon payments." There can be no assurance that we will be able to refinance the debt on favorable terms or at all. To the extent we cannot refinance this debt on favorable terms or at all, we may be forced to dispose of properties on disadvantageous terms or pay higher interest rates, either of which would have an adverse impact on our financial performance and ability to service debt and make distributions.
21
Risks Related to Our Convertible Notes
We expect that the trading price of the Convertible Notes will be significantly affected by the price of our common stock, which may be volatile.
The market price of our common stock, as well as the general level of interest rates and our credit quality, will likely significantly affect the market price of the Convertible Notes. This may result in significantly greater volatility in the trading price of the Convertible Notes than would be expected for nonconvertible debt securities we may issue.
We cannot predict whether the price of our common stock or interest rates will rise or fall. The market price of our common stock will be influenced by our operating results and prospects and by economic, financial, regulatory and other factors. General market conditions, including the level of, and fluctuations in, the trading prices of stocks generally, could affect the price of our common stock.
Holders who receive shares of our common stock upon the conversion of their Convertible Notes will be subject to the risk of volatile and depressed market prices of our common stock. There can be no assurances that the market price of our common stock will not fall in the future. A decrease in the market price of our common stock would likely adversely impact the trading price of the Convertible Notes.
The Convertible Notes are structurally subordinated to all liabilities of our existing or future subsidiaries.
Holders of the Convertible Notes do not and will not have any claim as a creditor against any of our present or future subsidiaries. Indebtedness and other liabilities, including trade payables, whether secured or unsecured, of those subsidiaries are structurally senior to our obligations to holders of the Convertible Notes. In the event of a bankruptcy, liquidation, reorganization or other winding up of any of our subsidiaries, such subsidiaries will pay the holders of their debts, holders of any equity interests, including fund investors, and their trade creditors before they will be able to distribute any of their assets to us (except to the extent we have a claim as a creditor of such subsidiary). Any right that we have to receive any assets of any of the subsidiaries upon the bankruptcy, liquidation, reorganization or other winding up of those subsidiaries, and the consequent rights of holders of Convertible Notes to realize proceeds from the sale of any of those subsidiaries' assets, will be effectively structurally subordinated to the claims of those subsidiaries' creditors, including trade creditors and holders of any preferred equity interests of those subsidiaries.
The Convertible Notes are solely the obligations of the Company and are not guaranteed by any of our subsidiaries; whereas, our operations are conducted through, and substantially all of our consolidated assets are held by, our subsidiaries.
The Convertible Notes are our obligations exclusively and are not guaranteed by any of our operating subsidiaries. Substantially all of our consolidated assets are held by our subsidiaries. Accordingly, our ability to service our debt, including the Convertible Notes, depends on the results of operations of our subsidiaries and upon the ability of such subsidiaries to provide us with cash, whether in the form of dividends, loans or otherwise, to pay amounts due on our obligations, including the Convertible Notes. Our subsidiaries are separate and distinct legal entities and have no obligation, contingent or otherwise, to make payments on the Convertible Notes or to make any funds available for that purpose. In addition, dividends, loans or other distributions to us from such subsidiaries may be subject to contractual and other restrictions set forth in our current and future debt instruments and are subject to other business considerations.
Servicing our debt requires a significant amount of cash, and we may not have sufficient cash flow from our business to pay our substantial debt.
Our ability to make scheduled payments of the principal of, to pay interest on or to refinance our indebtedness, including the Convertible Notes, depends on our future performance, which is subject to economic, financial, competitive and other factors beyond our control. Our business may not continue to generate cash flow from operations in the future sufficient to service our debt and make necessary capital expenditures. If we are unable to generate such cash flow, we may be required to adopt one or more alternatives, such as selling assets, restructuring debt or obtaining additional equity capital on terms that may be onerous or highly dilutive. Our ability to refinance our indebtedness will depend on the capital markets and our financial condition at such time. We may not be able to engage in any of these activities or engage in these activities on desirable terms, which could result in a default on our debt obligations.
Regulatory actions may adversely affect the trading price and liquidity of the Convertible Notes.
Current and future regulatory actions and other events may adversely affect the trading price and liquidity of the Convertible Notes. We expect that many investors in, and potential purchasers of, the Convertible Notes will employ, or seek to employ, a convertible arbitrage strategy with respect to the Convertible Notes. Investors would typically implement such a strategy by selling short the common stock underlying the Convertible Notes and dynamically adjusting their short position while continuing to hold the
22
Convertible Notes. Investors may also implement this type of strategy by entering into swaps on our common stock in lieu of or in addition to short selling the common stock.
The SEC and other regulatory and self-regulatory authorities have implemented various rules and taken certain actions, and may in the future adopt additional rules and take other actions, which may impact those engaging in short selling activity involving equity securities (including our common stock). Such rules and actions include Rule 201 of SEC Regulation SHO, the adoption by the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority, Inc. and the national securities exchanges of a "Limit Up-Limit Down" program, the imposition of market-wide circuit breakers that halt trading of securities for certain periods following specific market declines, and the implementation of certain regulatory reforms required by the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act of 2010. Any governmental or regulatory action that restricts the ability of investors in, or potential purchasers of, the Convertible Notes to effect short sales of our common stock, borrow our common stock or enter into swaps on our common stock could adversely affect the trading price and the liquidity of the Convertible Notes.
We may still incur substantially more debt or take other actions which would intensify the risks discussed above.
We and our subsidiaries may be able to incur substantial additional debt in the future, subject to the restrictions contained in our debt instruments, some of which may be secured debt. We are not restricted under the terms of the Indentures governing the Convertible Notes from incurring additional debt, securing existing or future debt, recapitalizing our debt or taking a number of other actions that are not limited by the terms of the Indentures governing the Convertible Notes that could have the effect of diminishing our ability to make payments on the Convertible Notes when due. Our existing credit facilities restrict our ability to incur additional indebtedness, including secured indebtedness, but we may be able to obtain waivers of such restrictions or may not be subject to such restrictions under the terms of any subsequent indebtedness.
We may not have the ability to raise the funds necessary to repurchase the Convertible Notes upon a fundamental change.
Holders of the Convertible Notes have the right, at their option, to require us to repurchase for cash all of their Convertible Notes, or any portion of the principal thereof that is equal to $1,000, or a multiple of $1,000, upon the occurrence of a fundamental change, as set forth in the Indentures, at a fundamental change repurchase price equal to 100 percent of the principal amount of the Convertible Notes to be repurchased, plus accrued and unpaid interest, if any, thereon to (but excluding) the fundamental change repurchase date. However, we may not have enough available cash or be able to obtain financing at the time we are required to make repurchases of Convertible Notes surrendered therefor. Our failure to repurchase Convertible Notes at a time when the repurchase is required by the Indentures would constitute a default under the Indentures. A default under the Indentures or the fundamental change itself could also lead to a default under agreements governing our existing or future indebtedness. If the repayment of the related indebtedness were to be accelerated after any applicable notice or grace periods, we may not have sufficient funds to repay the indebtedness and repurchase the Convertible Notes or make cash payments upon conversions thereof. Our ability to repurchase the Convertible Notes may also be limited by law or by regulatory authority.
Future sales of shares of our common stock or equity-linked securities in the public market, or the perception that they could occur, may depress the market price for our common stock and adversely impact the trading price of the Convertible Notes.
We may, in the future, sell additional shares of our common stock or equity-linked securities to raise capital. Sales of substantial amounts of additional shares of common stock or equity-linked securities, shares that may be sold by stockholders and shares of common stock underlying the Convertible Notes as well as sales of shares that may be issued in connection with future acquisitions or for other purposes, including to finance our operations and business strategy, or the perception that such sales could occur, may have an adverse effect on the trading price of the Convertible Notes and prevailing market prices for our common stock and our ability to raise additional capital in the financial markets at a time and price favorable to us. The price of our common stock could also be affected by possible sales of our common stock by investors who view the Convertible Notes as a more attractive means of equity participation in our company and by hedging or arbitrage trading activity that we expect will develop involving our common stock.
We have also reserved a substantial amount of shares of our common stock in connection with the Convertible Notes, the issuance of which will dilute the ownership interests of existing stockholders. Any sales in the public market of the common stock issuable upon such issuance or conversion could adversely affect prevailing market prices of our common stock.
We are unable to predict the effect that sales, or the perception that our shares may be available for sale, will have on the prevailing market price of our common stock and the trading price of the Convertible Notes.
23
Holders of Convertible Notes are not entitled to any rights with respect to our common stock, but are subject to all changes made with respect to our common stock.
Holders of Convertible Notes are not entitled to any rights with respect to our common stock (including, without limitation, voting rights and rights to receive any dividends or other distributions on our common stock) prior to the conversion date with respect to any Convertible Notes they surrender for conversion, but are subject to all changes affecting our common stock. For example, if an amendment is proposed to our charter or bylaws requiring stockholder approval and the record date for determining the stockholders of record entitled to vote on the amendment occurs prior to the conversion date related to a holder's conversion of its notes, then such holder will not be entitled to vote on the amendment, although such holder will nevertheless be subject to any changes affecting our common stock.
The Convertible Notes are not protected by restrictive covenants.
The Indentures governing the Convertible Notes do not contain any financial or operating covenants or restrictions on the payments of dividends, the incurrence of indebtedness or the issuance or repurchase of securities by us or any of our subsidiaries. The Indentures contain no covenants or other provisions to afford protection to holders of the Convertible Notes in the event of a fundamental change or other corporate transaction involving us except in limited circumstances as set forth in the Indentures. For example, events such as leveraged recapitalizations, refinancings, restructurings or acquisitions initiated by us may not constitute a fundamental change requiring us to repurchase the Convertible Notes. In the event of any such events, the holders of the Convertible Notes would not have the right to require us to repurchase the Convertible Notes, even though each of these transactions could increase the amount of our indebtedness, or otherwise adversely affect our capital structure or any credit ratings, thereby adversely affecting the trading price of the Convertible Notes.
The adjustment to the conversion rate for 7.00% Convertible Notes converted in connection with a Make-Whole Adjustment Event may not adequately compensate the holders for any lost value of their 7.00% Convertible Notes as a result of such transaction.
If a "Make-Whole Adjustment Event" (as defined in the Indenture for the 7.00% Convertible Notes) occurs, under certain circumstances, we will increase the conversion rate by a number of additional shares of our common stock for 7.00% Convertible Notes converted in connection with such Make-Whole Adjustment Event. The increase in the conversion rate will be determined based on the date on which the specified corporate transaction becomes effective and the price paid (or deemed to be paid) per share of our common stock in such transaction, all as set forth in the Indenture for the 7.00% Convertible Notes. The adjustment to the conversion rate for 7.00% Convertible Notes converted in connection with a make-whole fundamental change may not adequately compensate the holders for any lost value of their 7.00% Convertible Notes as a result of such transaction. In addition, if the price of our common stock in the transaction is greater than $45.00 per share or less than $30.00 per share (in each case, subject to adjustment), no additional shares will be added to the conversion rate. Moreover, in no event will the conversion rate per $1,000 principal amount of 7.00% Convertible Notes as a result of this adjustment exceed 33.3333 shares, subject to adjustments in the same manner as the conversion rate under the terms of the Indenture for the 7.00% Convertible Notes.
Our obligation to increase the conversion rate upon the occurrence of a make-whole fundamental change could be considered a penalty, in which case the enforceability thereof would be subject to general principles of reasonableness and equitable remedies.
The increase in the conversion rate for 5.875% Convertible Notes converted in connection with a make-whole fundamental change or notice of redemption may not adequately compensate the holders for any lost value of their 5.875% Convertible Notes as a result of such make-whole fundamental change or redemption.
If a make-whole fundamental change occurs prior to the maturity date or if we deliver a notice of redemption, under certain circumstances as described in the Indenture for the 5.875% Convertible Notes, we will increase the conversion rate by a number of additional shares of our common stock for 5.875% Convertible Notes converted in connection with such make-whole fundamental change or notice of redemption. The increase in the conversion rate will be determined based on the date on which the specified corporate transaction that constitutes a make-whole fundamental change becomes effective or the date we deliver a notice of redemption and the price paid (or deemed to be paid) per share of our common stock in the make-whole fundamental change or the average of the last reported sale prices of our common stock over the five consecutive trading day period ending on, and including, the trading day immediately preceding the date of the notice of redemption (such average, the “redemption price”), as described in the Indenture for the 5.875% Convertible Notes. The increase in the conversion rate for 5.875% Convertible Notes converted in connection with a make-whole fundamental change or notice of redemption may not adequately compensate the holders for any lost value of their 5.875% Convertible Notes as a result of such transaction or redemption. In addition, if the price per share of our common stock paid (or deemed to be paid) in the transaction or the redemption price, as applicable, is greater than $65.00 per share or less than $44.25 per share (in each case, subject to adjustment), no additional shares will be added to the conversion rate. Moreover, in no event will the conversion rate per $1,000 principal amount of 5.875% Convertible Notes as a result of this adjustment exceed
24
22.5998 shares of our common stock, subject to adjustments in the same manner as the conversion rate as set forth under the terms of the Indenture for the 5.875% Convertible Notes.
Our obligation to increase the conversion rate or 5.875% Convertible Notes converted in connection with a make-whole fundamental change or notice of redemption could be considered a penalty, in which case the enforceability thereof would be subject to general principles of reasonableness and equitable remedies.
The conversion rate of the Convertible Notes may not be adjusted for all dilutive events.
The conversion rate of the Convertible Notes is subject to adjustment for certain events, including, but not limited to, the issuance of certain stock dividends on our common stock, the issuance of certain rights or warrants, subdivisions, combinations, distributions of capital stock, indebtedness, or assets, cash dividends and certain issuer tender or exchange offers. However, the conversion rate will not be adjusted for other events, such as a third-party tender or exchange offer or an issuance of our common stock or derivative instruments for cash or an exercise or conversion of any derivative instrument, that may adversely affect the trading price of the Convertible Notes or our common stock. An event that adversely affects the value of the Convertible Notes may occur, and that event may not result in an adjustment to the conversion rate.
Some significant restructuring transactions and significant changes in the composition of our board may not constitute a fundamental change, in which case we would not be obligated to offer to repurchase the Convertible Notes.
Upon the occurrence of a fundamental change, holders of Convertible Notes have the right to require us to repurchase their Convertible Notes. However, the fundamental change provisions of the Indentures do not afford protection to holders of Convertible Notes in the event of other transactions that could adversely affect the Convertible Notes. For example, transactions such as leveraged recapitalizations, refinancings, restructurings, or acquisitions initiated by us may not constitute a fundamental change requiring us to repurchase the Convertible Notes. In the event of any such transaction, the holders would not have the right to require us to repurchase the Convertible Notes, even though each of these transactions could increase the amount of our indebtedness, or otherwise adversely affect our capital structure or any credit ratings, thereby adversely affecting the holders of Convertible Notes.
In addition, absent the occurrence of a fundamental change, changes in the composition of our Board of Directors will not provide holders with the right to require us to repurchase the Convertible Notes or to an increase in the conversion rate upon conversion.
We have not registered the 5.875% Convertible Notes or the common stock issuable upon conversion of the 5.875% Convertible Notes which will limit the holders ability to resell them.
The 5.875% Convertible Notes and the shares of common stock issuable upon conversion of the 5.875% Convertible Notes have not been registered under the Securities Act or any state securities laws. Unless the 5.875% Convertible Notes and the shares of common stock issuable upon conversion of the 5.875% Convertible Notes have been registered, the 5.875% Convertible Notes and such shares may not be transferred or resold except in a transaction exempt from or not subject to the registration requirements of the Securities Act and applicable state securities laws. We do not intend to file a registration statement for the resale of the 5.875% Convertible Notes and the common stock into which the 5.875% Convertible Notes are convertible.
An active trading market may not develop for the Convertible Notes or, if it develops, may not be maintained or be liquid.
We do not intend to apply to list the Convertible Notes on any securities exchange or to arrange for quotation on any automated dealer quotation system. The underwriters in our public offering of the 7.00% Convertible Notes or the initial purchasers of the 5.875% Convertible Notes may cease their market-making of the respective Convertible Notes at any time without notice. In addition, the liquidity of the trading market in the Convertible Notes, and the market price quoted for the Convertible Notes, may be adversely affected by changes in the overall market for this type of security and by changes in our financial performance or prospects or in the prospects for companies in our industry generally. As a result, an active trading market may not develop for the Convertible Notes. If an active trading market does not develop or is not maintained, the market price and liquidity of the Convertible Notes may be adversely affected. In that case holders of the Convertible Notes may not be able to sell their Convertible Notes at a particular time or they may not be able to sell their Convertible Notes at a favorable price.
The liquidity of the trading market, if any, and future trading prices of the Convertible Notes will depend on many factors, including, among other things, the market price of our common stock, prevailing interest rates, our financial condition, results of operations, business, prospects and credit quality relative to our competitors, the market for similar securities and the overall securities market. The liquidity of the trading market of the Convertible Notes may be adversely affected by unfavorable changes in any of these factors, some of which are beyond our control and others of which would not affect debt that is not convertible into capital stock. Historically, the market for convertible debt has been subject to disruptions that have caused volatility in prices of securities similar to the Convertible Notes. Market volatility could materially and adversely affect the Convertible Notes, regardless of our financial condition, results of operations, business, prospects or credit quality.
25
The Convertible Notes are not rated. Any adverse rating of the Convertible Notes may cause their trading price to fall.
We do not intend to seek a rating on the Convertible Notes. However, if a rating service were to rate the Convertible Notes and if such rating service were to lower its rating on the Convertible Notes below the rating initially assigned to the Convertible Notes or otherwise announces its intention to put the Convertible Notes on credit watch or to withdraw the rating, the trading price of the Convertible Notes could decline.
Upon conversion of the Convertible Notes, holders may receive less valuable consideration than expected because the value of our common stock may decline after they exercise their conversion right.
Under the Convertible Notes, a converting holder will be exposed to fluctuations in the value of our common stock during the period from the date such holder surrenders Convertible Notes for conversion until the date we settle our conversion obligation. We will be required to deliver the shares of our common stock, together with cash for any fractional shares, on the third business day following the relevant conversion date; and for any conversion that occurs on or after the record date for the payment of interest on the Convertible Notes at the maturity date, we will be required to deliver shares on the maturity date. Accordingly, if the price of our common stock decreases during this period, the value of the shares that the holders receive will be adversely affected and would be less than the conversion value of the Convertible Notes on the conversion date.
Conversion of the Convertible Notes may dilute the ownership interest of existing stockholders, including holders who had previously converted their Convertible Notes.
To the extent we issue shares of our common stock upon conversion of the Convertible Notes, the conversion of some or all of the Convertible Notes will dilute the ownership interests of existing stockholders. Any sales in the public market of shares of our common stock issuable upon such conversion of the Convertible Notes could adversely affect prevailing market prices of our common stock. In addition, the existence of the Convertible Notes may encourage short selling by market participants because the conversion of the Convertible Notes could be used to satisfy short positions, or anticipated conversion of the Convertible Notes into shares of our common stock could depress the price of our common stock.
Provisions of the Convertible Notes could discourage an acquisition of us by a third party.
Certain provisions of the Indentures and the Convertible Notes could make it more difficult or more expensive for a third party to acquire us. Upon the occurrence of certain transactions constituting a fundamental change under the Indentures, holders of the Convertible Notes will have the right, at their option, to require us to repurchase all or a portion of their Convertible Notes. We may also be required to increase the conversion rate upon conversion or provide for conversion into the acquirer's capital stock in the event of certain fundamental changes. In addition, the Indentures and the Convertible Notes prohibit us from engaging in certain mergers or acquisitions unless, among other things, the surviving entity assumes our obligations under the Convertible Notes and the Indentures.
Holders of the Convertible Notes may be subject to tax if we make or fail to make certain adjustments to the conversion rate of the Convertible Notes even though they do not receive a corresponding cash distribution.
The conversion rate of the Convertible Notes is subject to adjustment in certain circumstances, including the payment of cash dividends. If the conversion rate is adjusted as a result of a distribution that is taxable to our common stockholders, such as a cash dividend, holders of Convertible Notes may be deemed to have received a dividend subject to U.S. federal income tax without the receipt of any cash. In addition, a failure to adjust (or to adjust adequately) the conversion rate after an event that increases the proportionate interest in us could be treated as a deemed taxable dividend to holders of the Convertible Notes. If, pursuant to the terms of the Indentures, a make-whole fundamental change occurs on or prior to the maturity date, under some circumstances, we will increase the conversion rate for Convertible Notes converted in connection with the make-whole fundamental change. Such increase may also be treated as a distribution subject to U.S. federal income tax as a dividend. For a non-U.S. holder of the Convertible Notes, any deemed dividend may be subject to U.S. federal withholding tax at a 30 percent rate, or such lower rate as may be specified by an applicable treaty, which may be set off against subsequent payments on the Convertible Notes.
Because the Convertible Notes were initially issued in book-entry form, holders must rely on the Depository Trust Company's ("DTC") procedures to receive communications relating to the Convertible Notes and exercise their rights and remedies.
We initially issued the Convertible Notes in the form of one or more global notes registered in the name of Cede & Co., as nominee of DTC. Beneficial interests in global notes will be shown on, and transfers of global notes will be effected only through, the records maintained by DTC. Except in limited circumstances, we will not issue certificated notes. Accordingly, if the holders own a beneficial interest in a global note, then they will not be considered an owner or holder of the Convertible Notes. Instead, DTC or its nominee will be the sole holder of global notes. Unlike persons who have certificated notes registered in their names, owners of beneficial interests in global notes will not have the direct right to act on our solicitations for consents or requests for waivers or other actions from holders. Instead, those beneficial owners will be permitted to act only to the extent that they have received appropriate proxies
26
to do so from DTC or, if applicable, a DTC participant. The applicable procedures for the granting of these proxies may not be sufficient to enable owners of beneficial interests in global notes to vote on any requested actions on a timely basis. In addition, notices and other communications relating to the Convertible Notes will be sent to DTC. We expect DTC to forward any such communications to DTC participants, which in turn would forward such communications to indirect DTC participants. But we can make no assurances that holders will timely receive any such communications.
Risks Related to Our Preferred Stock
An active trading market for our depositary shares may not be maintained.
Our depositary shares, each of which represents 1/100th of a share of our Series A Preferred Stock, are listed on the NYSE; however, we can provide no assurance that an active trading market on the NYSE for the depositary shares may be maintained. As a result, the ability to transfer or sell the depositary shares and any trading price of the depositary shares could be adversely affected.
The market price of the depositary shares representing interests in our Series A Preferred Stock may be adversely affected by the future incurrence of debt or issuance of preferred stock by the Company.
In the future, we may increase our capital resources by making offerings of debt securities and preferred stock of the Company and other borrowings by the Company. The debt securities, preferred stock (if senior to our Series A Preferred Stock) and borrowings of the Company are senior in right of payment to our Series A Preferred Stock, and all payments (including dividends, principal and interest) and liquidating distributions on such securities and borrowings could limit our ability to pay dividends or make other distributions to the holders of depositary shares representing interests in our Series A Preferred Stock.
Because our decision to issue securities and make borrowings in the future will depend on market conditions and other factors, some of which may be beyond our control, we cannot predict or estimate the amount, timing or nature of our future offerings or borrowings. Thus, holders of the depositary shares representing interests in Series A Preferred Stock bear the risk of our future offerings or borrowings reducing the market price of the depositary shares representing interests in our Series A Preferred Stock.
A holder of depositary shares representing interests in the Series A Preferred Stock has extremely limited voting rights.
The voting rights of a holder of depositary shares are limited. Our common stock is the only class of our securities that carries full voting rights. Voting rights for holders of depositary shares exist primarily with respect to (i) the ability to elect (together with the holders of other series of preferred stock on parity with the Series A Preferred Stock, if any) two additional directors to our Board of Directors in the event that six quarterly dividends (whether or not declared or consecutive) payable on the Series A Preferred Stock are in arrears, (ii) voting on amendments to our Charter, including the articles supplementary creating our Series A Preferred Stock (in some cases voting together with the holders of Parity Preferred Stock as a single class) that materially and adversely affect the rights of the holders of depositary shares representing interests in the Series A Preferred Stock and (iii) the creation of additional classes or series of our stock that are senior to the Series A Preferred Stock with respect to the payment of dividends or distributions of assets upon our liquidation, in each case, provided that in any event adequate provision for redemption has not been made. Other than certain limited circumstances, holders of depositary shares do not have any voting rights.
The Change of Control conversion feature of Series A Preferred Stock may not adequately compensate the holders, and the Change of Control conversion and redemption features of the shares of Series A Preferred Stock underlying the depositary shares may make it more difficult for a party to take over the Company or discourage a party from taking over the Company.
Upon the occurrence of a Change of Control (as defined in the Articles Supplementary for Series A Preferred Stock), holders of the depositary shares representing interests in our Series A Preferred Stock will have the right (unless, prior to the Change of Control Conversion Date (as defined in the Articles Supplementary for Series A Preferred Stock), we have provided notice of our election to redeem the depositary shares either pursuant to our optional redemption right or our special optional redemption right) to convert some or all of their depositary shares into shares of our common stock (or equivalent value of Alternative Conversion Consideration). Upon such a conversion, the maximum number of shares of common stock that holders of depositary shares will receive for each depositary share converted will be limited to the Share Cap. These features of the Series A Preferred Stock may have the effect of inhibiting a third party from making an acquisition proposal for the Company or of delaying, deferring or preventing a Change of Control of the Company under circumstances that otherwise could provide the holders of our common stock and Series A Preferred Stock with the opportunity to realize a premium over the then-current market price or that stockholders may otherwise believe is in their best interests.
The market price of the depositary shares could be substantially affected by various factors.
The market price of the depositary shares will depend on many factors, which may change from time to time, including:
• | Prevailing interest rates, increases in which may have an adverse effect on the market price of the depositary shares representing interests in our Series A Preferred Stock; |
27
• | The market for similar securities issued by other REITs; |
• | General economic and financial market conditions; |
• | The financial condition, performance and prospects of us, our tenants and our competitors; |
• | Any rating assigned by a rating agency to the depositary shares; |
• | Changes in financial estimates or recommendations by securities analysts with respect to us, our competitors or our industry; and |
• | Actual or anticipated variations in our quarterly operating results and those of our competitors. |
In addition, over the last several years, prices of equity securities in the U.S. trading markets have been experiencing extreme price fluctuations. As a result of these and other factors, investors holding our depositary shares may experience a decrease, which could be substantial and rapid, in the market price of the depositary shares, including decreases unrelated to our financial condition, performance or prospects. Likewise, in the event that the depositary shares become convertible and are converted into shares of our common stock, holders of our common stock issued upon such conversion may experience a similar decrease, which also could be substantial and rapid, in the market price of our common stock.
Risks Related to REIT Qualification and Federal Income Tax Laws
We have elected to be taxed as a REIT for fiscal 2013 and subsequent years, but the IRS may challenge our qualification as a REIT.
We have elected to be a REIT for federal income tax purposes. In order to qualify as a REIT, a substantial percentage of our income must be derived from, and our assets consist of, real estate assets, and, in certain cases, other investment property. We have acquired and managed investments which satisfy the REIT tests. Whether a particular investment is considered a real estate asset for such purposes depends upon the facts and circumstances of the investment. Due to the factual nature of the determination, the IRS may challenge whether any particular investment will qualify as a real estate asset or realize income which satisfies the REIT income tests. In determining whether an investment is a real property asset, we will look at the Code and the IRS's interpretation of the Code in regulations, published rulings, private letter rulings and other guidance. In the case of a private letter ruling issued to another taxpayer, we would not be able to bind the IRS to the holding of such ruling. If the IRS successfully challenges our qualification as a REIT, we may not be able to achieve our objectives and the value of our stock may decline. As a REIT, our distributions from earnings and profits will be treated as ordinary income and a return of capital, and generally will not qualify as qualified dividend income ("QDI").
Fluctuations in the fair market value of the assets that we own and that are owned by our taxable REIT subsidiaries may adversely affect our continued qualification as a REIT.
We have to satisfy the asset tests at the end of each quarter. Although fluctuations in the fair market value of our assets should not adversely affect our qualification as a REIT, we must satisfy the asset tests immediately after effecting the REIT acquisition of any asset. Thus, we may be limited in our ability to purchase certain assets depending upon the potential fluctuations in the fair market value of our direct and indirect assets. As fair market value determinations are factual, risks exist as to the fair market determination.
Although we believe that the Grand Isle Gathering System and Pinedale LGS constitute real estate assets under the REIT provisions of the Code, that belief is not binding on the IRS or any court and does not guarantee our qualification as a REIT.
On August 31, 2016, the IRS issued final regulations to define real property under the REIT provisions, which provide that interests in real estate include inherently permanent structures such as pipelines and certain related assets. The qualifying real estate assets in the energy infrastructure sector include electric transmission and distribution systems, pipeline systems, and storage and terminaling systems, among others. We believe that substantially all of the Grand Isle Gathering System and Pinedale LGS constitute real estate assets under the REIT provisions consistent with the final regulations and certain private letter rulings. We have not obtained any private letter rulings with respect to the Grand Isle Gathering System. We have received a private letter ruling and certain other confirmation from the IRS that certain Pinedale LGS assets qualify as real property for REIT purposes. If the Grand Isle Gathering System or Pinedale LGS does not constitute a real estate asset for federal income tax purposes, we would likely fail to continue to qualify as a REIT. If that should occur, it likely would prevent us from achieving our business objectives and could cause the value of our stock to decline.
Failure to qualify as a REIT would have significant adverse consequences to us and the value of our common stock.
Beginning with our fiscal year ended December 31, 2013, we believe our income and investments have allowed us to meet the income and asset tests necessary for us to qualify for REIT status and we have elected to be taxed as a REIT for fiscal years 2013 through 2019. Qualification as a REIT involves the application of highly technical and complex provisions of the Internal Revenue Code as
28
to which there may only be limited judicial and administrative interpretations and involves the determination of facts and circumstances not entirely within our control. Future legislation, new regulations, administrative interpretations or court decisions may significantly change the tax laws or the application of the tax laws with respect to qualification as a REIT for federal income tax purposes or the federal income tax consequences of such qualification. Accordingly, we cannot assure you that we will be organized or will operate to qualify as a REIT for future fiscal years. If, with respect to any taxable year, we fail to qualify as a REIT, we would not be allowed to deduct distributions to stockholders in computing our taxable income. After our initial election and qualification as a REIT, if we later failed to so qualify and we were not entitled to relief under the relevant statutory provisions, we would also be disqualified from treatment as a REIT for four subsequent taxable years. If we fail to qualify as a REIT, corporate-level income tax would apply to our taxable income at regular corporate rates. As a result, the amount available for distribution to holders of equity securities would be reduced for the year or years involved, and we would no longer be required to make distributions. In addition, our failure to qualify as a REIT could impair our ability to expand our business and raise capital, and it could adversely affect the value of our common stock.
As a REIT, failure to make required distributions would subject us to federal corporate income tax.
In order to remain qualified for taxation as a REIT, we also are generally required to distribute at least 90 percent of our REIT taxable income (determined without regard to the dividends paid deduction and excluding net capital gain) each year, or in limited circumstances, the following year, to our stockholders. Beginning with our fiscal year ended December 31, 2013, we believe we have satisfied these requirements. While the amount, timing and form of any future distributions will be determined, and will be subject to adjustment, by our Board of Directors, we generally expect to distribute all or substantially all of our REIT taxable income. If our cash available for distribution falls short of our estimates, we may be unable to maintain distributions that approximate our REIT taxable income and may fail to remain qualified for taxation as a REIT. In addition, our cash flows from operations may be insufficient to fund required distributions as a result of differences in timing between the actual receipt of income and the payment of expenses and the recognition of income and expenses for federal income tax purposes, or the effect of nondeductible expenditures, such as capital expenditures, payments of compensation for which Section 162(m) of the Code denies a deduction, interest expense deductions limited by Section 163(j) of the Code, the creation of reserves or required debt service or amortization payments.
To the extent that we satisfy the 90 percent distribution requirement but distribute less than 100 percent of our REIT taxable income, we will be subject to federal corporate income tax on our undistributed taxable income. In addition, we will be subject to a 4 percent nondeductible excise tax on our undistributed taxable income to the extent the actual amount that we distribute to our stockholders for a calendar year is less than the minimum distribution amount specified under the Code.
Ownership limitation provisions in our charter may delay or prevent certain transactions in our shares, and could have the effect of delaying, deferring or preventing a transaction or change of control of our Company.
To maintain our qualification as a REIT for U.S. federal income tax purposes, among other purposes, our charter includes provisions designed to ensure that not more than 50 percent in value of our outstanding stock may be owned, directly or indirectly, by or for five or fewer individuals (as defined in the Internal Revenue Code to include certain entities such as private foundations) at any time during the last half of any taxable year. Subject to the exceptions described below, our charter generally prohibits any person (as defined under the Internal Revenue Code to include certain entities) from actually owning or being deemed to own by virtue of the applicable constructive ownership provisions of the Internal Revenue Code, (i) more than 9.8 percent (in value or in number of shares, whichever is more restrictive) of the issued and outstanding shares of our common stock or (ii) more than 9.8 percent in value of the aggregate of the outstanding shares of all classes and series of our stock, in each case, excluding any shares of our stock not treated as outstanding for federal income tax purposes. We refer to these restrictions as the "ownership limitation provisions." Our charter further prohibits any person from beneficially or constructively owning shares of our capital stock that would result in us being "closely held" under Section 856(h) of the Code or otherwise failing to qualify as a REIT. Our charter also provides that any transfer of shares of our capital stock which would, if effective, result in our capital stock being beneficially owned by fewer than 100 persons (as determined pursuant to the Internal Revenue Code) shall be void ab initio and the intended transferee shall acquire no rights in such shares. These ownership limitation provisions may prevent or delay individual transactions in our stock that would trigger such provisions, and also could have the effect of delaying, deferring or preventing a change in control and, as a result, could adversely affect our stockholders' ability to realize a premium for their shares of common stock. However, our Board of Directors may waive the ownership limitation provisions with respect to a particular stockholder and establish different ownership limitation provisions for such stockholder. In granting such waiver, our Board of Directors may also require the stockholder receiving such waiver to make certain representations, warranties and covenants related to our ability to qualify as a REIT.
Ownership limitations in our charter may impair the ability of holders to convert Convertible Notes into our common stock.
In order to assist us in maintaining our qualification as a REIT for U.S. federal income tax purposes, among other purposes, our charter restricts ownership of more than 9.8 percent (in value or in number, whichever is more restrictive) of our outstanding shares of common stock, or 9.8 percent in value of our outstanding capital stock, subject to certain exceptions. Notwithstanding any other
29
provision of the Convertible Notes or the Indentures, no holder of Convertible Notes will be entitled to receive common stock following conversion of such Convertible Notes to the extent that receipt of such common stock would cause such holder (after application of certain constructive ownership rules) to exceed the ownership limit contained in our charter. We will not be able to deliver our common stock, even if we would otherwise choose to do so, to any holder of Convertible Notes if the delivery of our common stock would cause that holder to exceed the ownership limits described above.
Complying with REIT requirements may affect our profitability and may force us to liquidate or forgo otherwise attractive investments.
To qualify as a REIT, we must continually satisfy tests concerning, among other things, the nature and diversification of our assets, the sources of our income and the amounts we distribute to our stockholders. We may be required to liquidate or forgo otherwise attractive investments in order to satisfy the asset and income tests or to qualify under certain statutory relief provisions. We may also be required to make distributions to stockholders at disadvantageous times or when we do not have funds readily available for distribution. As a result, having to comply with the distribution requirement could cause us to sell assets in adverse market conditions, borrow on unfavorable terms or distribute amounts that would otherwise be invested in future acquisitions, capital expenditures or repayment of debt. Accordingly, satisfying the REIT requirements could materially and adversely affect us.
As a REIT, re-characterization of sale-leaseback transactions may cause us to lose our REIT status.
We intend to purchase certain properties and simultaneously lease those same properties back to the sellers. While we will use our best efforts to structure any such sale-leaseback transaction so that the lease will be characterized as a "true lease," thereby allowing us to be treated as the owner of the property for U.S. federal income tax purposes, the IRS could challenge such characterization. In the event that any sale-leaseback transaction is recharacterized as a financing transaction or loan for U.S. federal income tax purposes, deductions for depreciation and cost recovery relating to such property would be disallowed. If a sale-leaseback transaction were so recharacterized, we might fail to satisfy the REIT qualification "asset tests" or the "income tests" and, consequently, lose our REIT status effective with the year of re-characterization. Alternatively, the amount of our REIT taxable income could be recalculated which might also cause us to fail to meet the distribution requirement for a taxable year.
As a REIT, we are required to make distributions, other than capital gain distributions, to our stockholders each year in the amount of at least 90 percent of our REIT taxable income in order to deduct distributions to our stockholders. As a result, we will continue to need additional capital to make new investments. If additional funds are unavailable or not available on favorable terms, our ability to make new investments will be impaired.
As a REIT, we are required to distribute at least 90 percent of our REIT taxable income in order to deduct distributions to our stockholders, and as such we expect to continue to require additional capital to make new investments or carry existing investments. We may acquire additional capital from the issuance of securities senior to our common stock, including additional borrowings or other indebtedness or the issuance of additional securities. We may also acquire additional capital through the issuance of additional equity. However, we may not be able to raise additional capital in the future on favorable terms or at all. Unfavorable economic conditions could increase our funding costs, limit our access to the capital markets or result in a decision by lenders not to extend credit to us. We may issue debt securities, other instruments of indebtedness or preferred stock, and we may borrow money from banks or other financial institutions, which we refer to collectively as "senior securities." As a result of issuing senior securities, we will also be exposed to typical risks associated with leverage, including increased risk of loss. If we issue preferred securities which will rank "senior" to our common stock in our capital structure, the holders of such preferred securities may have separate voting rights and other rights, preferences or privileges more favorable than those of our common stock, and the issuance of such preferred securities could have the effect of delaying, deferring or preventing a transaction or a change of control that might involve a premium price for security holders or otherwise be in our best interest.
To the extent our ability to issue debt or other senior securities is constrained, we will depend on issuances of additional common stock to finance new investments. If we raise additional funds by issuing more of our common stock or senior securities convertible into, or exchangeable for, our common stock, the percentage ownership of our stockholders at that time would decrease, and you may experience dilution.
If we acquire C corporations in the future, we may inherit material tax liabilities and other tax attributes from such acquired corporations, and we may be required to distribute earnings and profits.
From time to time we may acquire C corporations or assets of C corporations in transactions in which the basis of the corporations' assets in our hands is determined by reference to the basis of the assets in the hands of the acquired corporations, or carry-over basis transactions.
In the case of assets we acquire from a C corporation in a carry-over basis transaction, if we dispose of any such asset in a taxable transaction (including by deed in lieu of foreclosure) during the five-year period beginning on the date of the carry-over basis transaction, then we will be required to pay tax at the highest regular corporate tax rate on the gain recognized to the extent of the
30
excess of (1) the fair market value of the asset over (2) our adjusted tax basis in the asset, in each case determined as of the date of the carry-over basis transaction. Any taxes we pay as a result of such gain would reduce the amount available for distribution to our stockholders. The imposition of such tax may require us to forgo an otherwise attractive disposition of any assets we acquire from a C corporation in a carry-over basis transaction, and as a result may reduce the liquidity of our portfolio of investments. In addition, in such a carry-over basis transaction, we could potentially succeed to any tax liabilities and earnings and profits of any acquired C corporation. To qualify as a REIT, we must distribute any non-REIT earnings and profits by the close of the taxable year in which such transaction occurs. If the IRS were to determine that we acquired non-REIT earnings and profits from a corporation that we failed to distribute prior to the end of the taxable year in which the carry-over basis transaction occurred, we could avoid disqualification as a REIT by paying a "deficiency dividend." Under these procedures, we generally would be required to distribute any such non-REIT earnings and profits to our stockholders within 90 days of the determination and pay a statutory interest charge at a specified rate to the IRS. Such a distribution would be in addition to the distribution of REIT taxable income necessary to satisfy the REIT distribution requirement and may require that we borrow funds to make the distribution even if the then-prevailing market conditions are not favorable for borrowings. In addition, payment of the statutory interest charge could materially and adversely affect us.
Legislative or other actions affecting REITs could have a negative effect on us.
The rules dealing with federal, state and local income taxation are constantly under review by persons involved in the legislative process and by the IRS and the U.S. Department of the Treasury. Changes to the tax laws, with or without retroactive application, could materially and adversely affect our investors or us. On December 22, 2017, the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act was signed into law by the U.S. President. Although we are not aware of any provision in the final tax reform legislation or any pending tax legislation that would adversely affect our ability to qualify as a REIT, we cannot predict how future changes in the tax laws might affect our investors or us. New legislation, Treasury Regulations, administrative interpretations or court decisions could significantly and negatively affect our ability to qualify as a REIT or the income tax consequences of such qualification.
Risks Related to Our Corporate Structure and Governance
Corridor may serve as a manager to other entities, which may create conflicts of interest not in the best interest of us or our stockholders.
Corridor's services under the Management Agreement are not exclusive, and, while it currently does not have any contractual arrangement to do so, it is free to furnish the same or similar services to other entities, including businesses that may directly or indirectly compete with us so long as its services to us are not impaired by the provision of such services to others. Corridor and its members may have obligations to other entities, the fulfillment of which might not be in the best interests of us or our stockholders.
We will be dependent upon key personnel of Corridor for our future success.
We have entered into a management agreement with Corridor to provide full management services to us for real property asset investments. We will be dependent on the diligence, expertise and business relationships of the management of Corridor to implement our strategy of acquiring real property assets. The departure of one or more investment professionals of Corridor could have a material adverse effect on our ability to implement this strategy and on the value of our common stock. There can be no assurance that we will be successful in implementing our strategy.
In addition to the ownership limit provisions discussed above, certain provisions of our charter and of Maryland law may limit the ability of stockholders to control our policies and effect a change of control of our Company.
Our charter authorizes our Board of Directors to amend our charter to increase or decrease the aggregate number of authorized shares of stock, to authorize us to issue additional shares of our common stock or preferred stock and to classify or reclassify unissued shares of our common stock or preferred stock and thereafter to authorize us to issue such classified or reclassified shares of stock. We believe that these provisions in our charter provide us with increased flexibility in structuring possible future financings and acquisitions and in meeting other needs that might arise. The additional classes or series, as well as the additional authorized shares of stock, will be available for issuance without further action by our stockholders, unless such action is required by applicable law or the rules of any stock exchange or automated quotation system on which our securities may be listed or traded. Although our Board of Directors does not currently intend to do so, it could authorize us to issue a class or series of stock that could, depending upon the terms of the particular class or series, delay, defer or prevent a transaction or a change of control of our company that might involve a premium price for holders of our common stock or that our common stockholders otherwise believe to be in their best interests.
31
Provisions of the Maryland General Corporation Law and our charter and bylaws could deter takeover attempts and have an adverse impact on the price of our common stock.
The following considerations related to provisions of Maryland General Corporation Law, and of our charter and bylaws, may have the effect of discouraging, delaying or making difficult a change in control of our Company or the removal of our incumbent directors:
• | We are subject to the Business Combination Act of the Maryland General Corporation Law. However, pursuant to the statute, our Board of Directors has adopted a resolution exempting us from the Maryland Business Combination Act for any business combination between us and any person to the extent that such business combination receives the prior approval of our Board of Directors. |
• | Our bylaws exempt from the Maryland Control Share Acquisition Act acquisitions of stock by any person. If we amend our bylaws to repeal the exemption from the Maryland Control Share Acquisition Act, the Maryland Control Share Acquisition Act also may make it more difficult to obtain control of our Company. |
• | As described above, our charter includes a share ownership limit and other restrictions on ownership and transfer of shares, in each such case designed, among other purposes, to preserve our status as a REIT, which may have the effect of precluding an acquisition of control of us without the approval of our Board of Directors. |
• | Under our charter, our Board of Directors is divided into three classes serving staggered terms, which may make it more difficult for a hostile bidder to acquire control of us. |
• | Our charter contains a provision whereby we have elected to be subject to the provisions of Title 3, Subtitle 8 of the Maryland General Corporation Law relating to the filling of vacancies on our Board of Directors. Further, through provisions in our charter and bylaws unrelated to Subtitle 8, we (1) require a two-thirds vote for the removal of any director from the board, which removal must be for cause, (2) vest in the board the exclusive power to fix the number of directors, subject to limitations set forth in our charter and bylaws, (3) have a classified Board of Directors and (4) require that, unless a special meeting of stockholders is called by the chairman of our Board of Directors, our chief executive officer, our president or our Board of Directors, such a special meeting may be called to consider and vote on any matter that may properly be considered at a meeting of stockholders only at the request of stockholders entitled to cast not less than a majority of all votes entitled to be cast on a matter at such meeting. |
• | In addition, our Board of Directors may, without stockholder action, authorize the issuance of shares of stock in one or more classes or series, including preferred stock. Our Board of Directors also may, without stockholder action, amend our charter to increase the number of shares of stock of any class or series that we have authority to issue. |
• | Our bylaws include advance notice provisions, governing stockholders' director nominations or proposal of other business to be considered at an annual meeting of our stockholders, requiring the continuous ownership by the stockholder(s) putting forth any such nominee or proposal of at least one percent (1 percent) of our outstanding shares for a minimum period of at least three years prior to the date of such nomination or proposal and through the date of the related annual meeting (including any adjournment or postponement thereof), each as specified in the bylaws. |
• | Our bylaws designate certain Maryland courts as the sole and exclusive forum for certain types of actions and proceedings that may be initiated by our stockholders, which could limit our stockholders' ability to obtain a judicial forum that our stockholders believe is favorable for disputes with us or our directors, officers or employees. |
The existence of these provisions, among others, may have a negative impact on the price of our common stock and may discourage third party bids for ownership of our Company. These provisions may prevent any premiums being offered to you for our common stock.
Our ability to pay dividends is limited by the requirements of Maryland law.
Our ability to pay dividends on our common stock and Series A Preferred Stock is limited by the laws of Maryland. Under the Maryland General Corporation Law, a Maryland corporation generally may not make a distribution if, after giving effect to the distribution, the corporation would not be able to pay its debts as the debts become due in the usual course of business, or the corporation's total assets would be less than the sum of its total liabilities plus, unless the corporation's charter provides otherwise, the amount that would be needed, if the corporation were dissolved at the time of the distribution, to satisfy the preferential rights upon dissolution of stockholders whose preferential rights are superior to those receiving the distribution. Accordingly, we may not make a distribution on our common stock and the Series A Preferred Stock if, after giving effect to the distribution, we would not be able to pay our debts as they become due in the usual course of business or our total assets would be less than the sum of our total liabilities plus, unless the terms of such class or series provide otherwise, the amount that would be needed to satisfy the preferential rights upon dissolution of the holders of any shares of any class or series of preferred stock then outstanding, if any, with preferences senior to those of our common stock and the Series A Preferred Stock.
32
Additional Risks to Our Stockholders
Our use of leverage increases the risk of investing in our securities and will increase the costs borne by common stockholders.
Our use of leverage through the issuance of any preferred stock or debt securities, and any additional borrowings or other transactions involving indebtedness (other than for temporary or emergency purposes) are or would be considered "senior securities" and create risks. Leverage may adversely affect common stockholders. If the return on securities acquired with borrowed funds or other leverage proceeds does not exceed the cost of the leverage, the use of leverage could cause us to lose money.
Our issuance of senior securities involves offering expenses and other costs, including interest payments, which are borne indirectly by our common stockholders. Fluctuations in interest rates could increase interest or dividend payments on our senior securities, and could reduce cash available for distribution on common stock. Increased operating costs, including the financing cost associated with any leverage, may reduce our total return to common stockholders.
Rating agency guidelines applicable to any senior securities may impose asset coverage requirements, dividend limitations, voting right requirements (in the case of the senior equity securities), and restrictions on our portfolio composition and our use of certain investment techniques and strategies. The terms of any senior securities or other borrowings may impose additional requirements, restrictions and limitations that are more stringent than those required by a rating agency that rates outstanding senior securities. These requirements may have an adverse effect on us and may affect our ability to pay distributions on common stock and preferred stock. To the extent necessary, we may redeem our senior securities to maintain the required asset coverage. Doing so may require that we liquidate investments at a time when it would not otherwise be desirable to do so.
In addition, lenders from whom we may borrow money or holders of our debt securities may have fixed dollar claims on our assets that are superior to the claims of our stockholders, and we have granted, and may in the future grant, a security interest in our assets in connection with our debt. In the case of a liquidation event, those lenders or note holders would receive proceeds before our stockholders. If the value of our assets increases, then leveraging would cause the book value of our common stock to increase more than it otherwise would have had we not leveraged. Conversely, if the value of our assets decreases, leveraging would cause the book value of our common stock to decline more than it otherwise would have had we not leveraged. Similarly, any increase in our revenue in excess of interest expense on our borrowed funds would cause our net income to increase more than it would without the leverage. Any decrease in our revenue would cause our net income to decline more than it would have had we not borrowed funds and could negatively affect our ability to make distributions on our common stock. Our ability to service any debt that we incur will depend largely on our financial performance and the performance of our investments and will be subject to prevailing economic conditions and competitive pressures.
We cannot assure you that we will be able to pay dividends regularly.
Our ability to pay dividends in the future is dependent on our ability to operate profitably and to generate cash from our operations and the operations of our subsidiaries. We cannot guarantee that we will be able to pay dividends on a regular quarterly basis in the future. Furthermore, any new shares of common stock issued will substantially increase the cash required to continue to pay cash dividends at current levels. Any common stock or preferred stock that may in the future be issued to finance acquisitions, upon exercise of stock options or otherwise, would have a similar effect.
Future sales of shares of our common stock may depress its market price.
We may, in the future, sell additional shares of our common stock to raise capital. Sales of substantial amounts of additional shares of common stock, shares that may be sold by stockholders, shares of common stock underlying the Convertible Notes and shares issuable upon exercise of outstanding options as well as sales of shares that may be issued in connection with future acquisitions or for other purposes, including to finance our operations and business strategy, or the perception that such sales could occur, may have an adverse effect on prevailing market prices for our common stock and our ability to raise additional capital in the financial markets at a time and price favorable to us. The price of our common stock could also be affected by possible sales of our common stock by investors who view the Convertible Notes as a more attractive means of equity participation in our company and by hedging or arbitrage trading activity that we expect will develop involving our common stock.
Risk Related to Terrorism and Cybersecurity
A terrorist attack, act of cyber-terrorism or armed conflict could harm our business.
Terrorist activities, anti-terrorist efforts and other armed conflicts involving the U.S., whether or not targeted at our assets or those of our tenants, investees or customers, could adversely affect the U.S. and global economies and could prevent us from meeting our financial and other obligations. Both we and our tenants and investees could experience loss of business, delays or defaults in payments from customers or disruptions of supplies and markets if domestic and global utilities or other energy infrastructure companies are direct targets or indirect casualties of an act of terror or war. Additionally, both we and our tenants and other investees rely on financial
33
and operational computer systems to process information critically important for conducting various elements of our respective businesses. Any act of cyber-terrorism or other cyber-attack resulting in a failure of our computer systems, or those of our tenants, customers, suppliers or others with whom we do business, could materially disrupt our ability to operate our respective businesses and could result in a financial loss to the Company and possibly do harm to our reputation. Accordingly, terrorist activities and the threat of potential terrorist activities (including cyber-terrorism) and any resulting economic downturn could adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations. Any such events also might result in increased volatility in national and international financial markets, which could limit our access to capital or increase our cost of obtaining capital.
Some losses related to our real property assets, including, among others, losses related to potential terrorist activities, may not be covered by insurance and would adversely impact distributions to stockholders.
Our leases will generally require the tenant companies to carry comprehensive liability and casualty insurance on our properties comparable in amounts and against risks customarily insured against by other companies engaged in similar businesses in the same geographic region as our tenant companies. We believe the required coverage will be of the type, and amount, customarily obtained by an owner of similar properties. However, there are some types of losses, such as catastrophic acts of nature, acts of war or riots, for which we or our tenants cannot obtain insurance at an acceptable cost. If there is an uninsured loss or a loss in excess of insurance limits, we could lose both the revenues generated by the affected property and the capital we have invested in the property if our tenant company fails to pay us the casualty value in excess of such insurance limit, if any, or to indemnify us for such loss. This would in turn reduce the amount of income available for distributions. We would, however, remain obligated to repay any secured indebtedness or other obligations related to the property. Since September 11, 2001, the cost of insurance protection against terrorist acts has risen dramatically. The cost of coverage for acts of terrorism is currently mitigated by the Terrorism Risk Insurance Program Reauthorization Act of 2019 ("TRIPRA"), which extended such program through December 31, 2027. Under TRIPRA, the amount of terrorism-related insurance losses triggering the federal insurance threshold has been increasing gradually from its initial level of $100 million for acts occurring in 2015 to $160 million for acts occurring in 2018, with $180 million being the applicable threshold for acts occurring in 2019 and finally increasing to $200 million for 2020. Additionally, the bill increases insurers' co-payments for losses exceeding their deductibles, from 15 percent in 2015 to 16 percent beginning January 1, 2016, and increasing in annual one percent steps thereafter until reaching 20 percent for 2020. Each of these changes may have the effect of increasing the cost to insure against acts of terrorism for property owners, such as the Company, notwithstanding the other provisions of TRIPRA. Further, if TRIPRA is not continued beyond 2027 or is significantly modified, we may incur higher insurance costs and experience greater difficulty in obtaining insurance that covers terrorist-related damages. Our tenants may also have similar difficulties. There can be no assurance our tenant companies will be able to obtain terrorism insurance coverage, or that any coverage they do obtain will adequately protect our properties against loss from terrorist attack.
We face risks associated with security breaches through cyber attacks, cyber intrusions or otherwise, as well as other significant disruptions of our information technology (IT) networks and related systems.
We rely on information technology systems and network infrastructure, including the Internet, to process transmit and store electronic information and to manage or support a variety of our business processes, including financial transactions and maintenance of records. These systems and infrastructure are essential to the operation of our business and our ability to perform day-to-day operations and, in some cases, may be critical to the operations of certain of our tenants. Cyber attacks targeting our infrastructure could result in a full or partial disruption of our operations, as well as those of our tenants. Although we make efforts to maintain the security and integrity of our IT networks and related systems, and we have implemented various measures to manage the risk of a security breach or disruption, we cannot guarantee that our security efforts and measures will be effective at preventing or detecting any attempted or actual security breaches, or that disruptions caused by any such breaches or attempted breaches will not be successful or damaging to us or others.
A security breach or other significant disruption involving our IT networks and related systems could disrupt the proper functioning of our networks and systems; result in disruption of business operations and loss of service to our tenants and customers; result in significantly decreased revenues; result in increased costs associated in obtaining and maintaining cybersecurity investigations and testing, as well as in implementing protective measures and systems; result in increased insurance premiums and operating costs; result in misstated financial reports, violations of loan covenants and/or missed reporting deadlines; result in our inability to properly monitor our compliance with the rules and regulations regarding our qualification as a REIT; result in the unauthorized access to, and destruction, loss, theft, misappropriation or release of proprietary, confidential, sensitive or otherwise valuable information of ours or others, which others could use to compete against us or for disruptive, destructive or otherwise harmful purposes and outcomes; require significant management attention and resources to remedy any damages that result; subject us to claims for breach of contract, damages, credits, penalties or termination of leases or other agreements; subject us to regulatory investigations and actions; cause harm to our competitive position and business value; and damage our reputation among our tenants and investors generally.
In addition, as part of our business operations, we collect, store and process certain proprietary and sensitive information, including personal information about our customers, shareholders and employees. In some cases, we outsource administration of certain
34
technology functions to vendors that could be targets of cyber attacks. Any theft, loss and/or fraudulent use of data of ours or of any tenant, customer, investor, employee or vendor as a result of a cyber attack on us or our vendors could subject us to significant litigation, liability and costs, as well as adversely impact our reputation.
Risks Related to Our Investments in Loans
Our loans may be impacted by unfavorable real estate market conditions, which could decrease the value of those loans and the return on your investment.
If we make or invest in mortgage loans, we will be at risk of defaults on those loans caused by many conditions beyond our control, including local and other economic conditions affecting real estate values and interest rate levels. We do not know whether the values of the property securing the loans will remain at the levels existing on the dates of origination of the loans. If the values of the underlying properties drop, our risk will increase because of the lower value of the security associated with such loans.
If our borrowers declare bankruptcy, we may be unable to collect interest and principal payments when due under the loan documents.
Either the borrowers under any loan documents we hold or any of borrowers' guarantor affiliates could become debtors under the bankruptcy laws of the United States. Such a bankruptcy filing would bar all efforts by us to collect pre-bankruptcy debts from these entities or their properties, unless we receive authorization from the bankruptcy court to proceed against the debtor entities under the respective loan documents. Post-bankruptcy debts (those debts that accrue after the bankruptcy was filed) are required to be paid on a current basis. Such a bankruptcy could delay efforts to collect past due balances under the loan documents, could ultimately preclude full collection of these sums, and could cause a decrease or cessation of principal and interest payments under the loan documents. If any of these events occur, our cash flow and funds available for distributions to our stockholders would be adversely affected.
Delays in liquidating defaulted mortgage loans could reduce our investment returns.
If there are defaults under our loans, we may not be able to repossess and sell under favorable market conditions any energy infrastructure real property securing such loans. The resulting time delay could reduce the value of our investment in the defaulted loans. An action to foreclose on a property securing a loan is regulated by state statutes and regulations and is subject to many of the delays and expenses of any lawsuit brought in connection with the foreclosure if the defendant raises defenses or counterclaims. If there is a default by a mortgagor, these restrictions, among other things, may impede our ability to foreclose on or sell the mortgaged property or to obtain proceeds sufficient to repay all amounts due to us on the loan.
A foreclosure on the energy infrastructure real property and equipment held by a borrower would create additional ownership risks that could adversely impact the return on our investment.
If we should acquire any of the energy infrastructure real property and/or related equity held by a borrower by foreclosure following a default under the loan documents, we will incur additional economic and liability risks as the owner of such assets, including, among other things, insurance costs, costs of maintenance and taxes relating to such property.
In the event of a foreclosure on the energy infrastructure real property assets held by a borrower, we may not be able to sell such assets at a price equal to, or greater than, the loan amount and accrued unpaid interest under the loan documents, which may lead to a decrease in the value of our assets.
Given the specialized nature of the borrowers' assets and the fact they are predominantly employed in support of the borrowers' operations, there can be no assurance that we would be able to find another buyer for these assets if financial distress on the part of a borrower forced us to foreclose on our security interest. Further, even if we were able to sell the assets, such sale may occur at a price less than the amount required to recover our loan balances and accrued unpaid interest under the loan documents, which could adversely impact the value of our assets and our ability to make distributions to our stockholders.
We may experience an impairment in the value of our loan to a borrower related to a deterioration in the credit worthiness of the borrower or a decline in the fair market value of the energy infrastructure real property assets securing the loan.
A deterioration in the credit worthiness of a borrower, due to changing business conditions or otherwise, or a decline in the fair market value of the energy infrastructure real property assets securing any of our loans to a borrower, could require us to recognize an "other-than-temporary" impairment in the value of the promissory note secured by the assets if we were to determine that such loan was in an unrealized loss position and we did not have the ability and intent to hold such asset to maturity or for a period of time sufficient to allow for recovery of the value of the underlying assets. If such a determination were made, we would recognize unrealized losses through earnings and write down the asset value of such loan to a new cost basis, based on the fair value of the assets on the date they are considered to be other-than-temporarily impaired. Such impairment charges reflect non-cash losses at the time of recognition; a subsequent disposition or sale of the loan through foreclosure or otherwise could further affect our future losses
35
or gains, as they would be based on the difference between the sales price received and the adjusted amortized cost of such loan at the time of sale.
ITEM 1B. UNRESOLVED STAFF COMMENTS
None.
ITEM 2. PROPERTIES
Leased Energy Infrastructure Assets
We are primarily focused on acquiring and financing midstream and downstream real estate assets within the U.S. energy infrastructure sector and concurrently entering into long-term triple-net participating leases with energy companies. The following summarizes our investments in energy infrastructure assets that are leased on a triple-net basis to their respective operators as of December 31, 2019:
Asset Name | Owner/Landlord | Tenant | Asset Location | Asset Description | Encumbrances (1) |
Grand Isle Gathering System | Grand Isle Corridor, LP | Energy XXI GIGS Services, LLC (2) | Gulf of Mexico / Louisiana | Approximately 137 miles of offshore pipeline with total capacity of 120 thousand Bbls/d, including a 16-acre onshore terminal and saltwater disposal system | Security for the Company's $160 million revolving credit facility with Regions Bank |
Pinedale Liquids Gathering System | Pinedale LP | Ultra Wyoming LGS LLC (3) | The Pinedale Anticline in Wyoming | Approximately 150 miles of pipelines and four central storage facilities | Security for the Amended Pinedale Term Credit Facility |
(1) For additional information, see Part IV, Item 15, Note 11 ("Debt") included in this Report. | |||||
(2) Energy XXI GIGS Services, LLC's obligations under the Grand Isle Lease Agreement are guaranteed by EGC. For additional information, see "Additional Information Concerning the Grand Isle Gathering System" below. | |||||
(3) Ultra Wyoming's obligations under the Pinedale Lease Agreement are guaranteed by Ultra Petroleum and Ultra Petroleum's operating subsidiary, Ultra Resources. For additional information, see "Additional Information Concerning the Pinedale LGS" below. | |||||
Additional Information Concerning the Grand Isle Gathering System
Grand Isle Corridor, LP acquired the Grand Isle Gathering System on June 30, 2015 from Energy XXI USA, Inc., which has since become Energy XXI Gulf Coast, Inc. and an indirect wholly owned subsidiary of privately-held Cox Oil as discussed further below. The Grand Isle Gathering System's design capacity is approximately 120 thousand barrels per day. It includes 137 miles of undersea pipeline that transports oil and water from seven offshore fields and a 16-acre onshore terminal. The terminal includes four storage tanks, three saltwater injection wells, and associated pipelines, land, buildings and facilities. As discussed in further detail in Part IV, Item 15, Note 12 ("Asset Retirement Obligation"), during the fourth quarter of 2018, the Company decommissioned a segment of the GIGS pipeline system.
The subsea pipelines forming the majority of the Grand Isle Gathering System and certain other components, such as the buildings and saltwater disposal facilities, have useful lives that extend beyond the initial term of the Grand Isle Lease Agreement, and the system is critical to Cox Oil's central Gulf of Mexico oil production operations. The Grand Isle Gathering System provides shoreline terminal access to 38 offshore platforms producing from seven fields. Some of these fields have produced for over 50 years and continue to produce. During 2017-2018, EGC drilled and successfully completed four new wells. Future wells drilled will be dependent on economics, but several undrilled locations remain in fields served by the Grand Isle Gathering System. From its analysis, CORR assumes average Grand Isle Gathering System well lives of 10 to 20 years depending on the number of productive zones encountered, implying a long-term continued need for transport and terminaling services.
The primary term of the Grand Isle Lease Agreement is 11 years, with an initial renewal term of nine years, subject to certain conditions. During the initial term of the Grand Isle Lease Agreement, the EGC Tenant is required to make minimum monthly rental payments. In year one, the minimum monthly payments were initially $2.6 million. The monthly payments peak in year seven at $4.2 million before declining to $3.5 million in year eleven. In 2020, the minimum monthly rental payments will be $3.2 million through June 2020, and beginning in July 2020, the minimum monthly rental payments will be $4.0 million for the remainder of the year. In addition, the EGC Tenant is required to pay variable rent payments if certain pre-defined revenue thresholds are exceeded. Variable rent obligations are calculated monthly and based on ten percent revenue participation above the thresholds. Revenues are calculated on the volumes of the EGC Tenant's oil that flow through the Grand Isle Gathering System, multiplied by the average daily closing price of crude oil for the applicable calendar month. Participating rent is capped at 39 percent of the total rent for each month. There were no participating rents paid in 2019.
36
Since the Grand Isle Gathering System represents a substantial portion of the Company's net leased property and is a significant source of revenues and operating income, the EGC Tenant's financial condition and ability and willingness to satisfy its obligations under its lease with the Company are expected to have a considerable impact on our results of operations and cash flows.
We believe the terms of the Grand Isle Lease Agreement require we be provided with copies of certain financial statement information that we are required to file pursuant to SEC Regulation S-X, as described in Section 2340 of the SEC Financial Reporting Manual. Prior to October 29, 2018, EGC was subject to the reporting requirements of the Exchange Act and was required to file with the SEC annual reports containing audited financial statements and quarterly reports containing unaudited financial statements. So long as EGC remained a public reporting company, the Grand Isle Lease Agreement provided this requirement was fulfilled by EGC making its financial statements and reports publicly available through the SEC's EDGAR system, in lieu of delivering such information directly to us. On October 18, 2018, EGC was acquired by an affiliate of Cox Oil. Upon the filing by EGC of a Form 15 with the SEC on October 29, 2018, EGC's SEC reporting obligations were suspended and it ceased to file such reports.
As EGC's financial information is no longer publicly available, we are engaged in discussions with Cox Oil/EGC concerning satisfaction of its obligations under the Grand Isle Lease Agreement to provide the required information to us for inclusion in our SEC reports. To date, Cox Oil has not yet fulfilled these obligations. It is our intention to enforce the obligations of EGC to provide the financial statement information that we believe are required under the terms of the Grand Isle Lease Agreement. We expect to file the financial statement information that is required by Regulation S-X by amendment to our Annual Reports on Form 10-K for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018 once such information is made available to us in accordance with the terms of the lease.
EGC's SEC filings prior to October 29, 2018 can be found at www.sec.gov. We make no representation as to the accuracy or completeness of the audited and unaudited financial statements of EGC but we have no reason to doubt the accuracy or completeness of such information. In addition, EGC has no duty, contractual or otherwise, to advise us of any events that might have occurred subsequent to the date of such financial statements which could affect the significance or accuracy of such information. None of the information in the public reports of EGC that are filed with the SEC is incorporated by reference into, or in any way form, a part of this filing.
Additional Information Concerning the Pinedale LGS
Pinedale LP acquired the Pinedale LGS with associated real property rights in the Pinedale Anticline in Wyoming from an indirect wholly-owned subsidiary of Ultra Petroleum on December 20, 2012. Prudential owned an 18.95 percent economic interest in the Pinedale LGS as a co-investor with us through December 29, 2017, at which point Pinedale LP I, our wholly-owned subsidiary, purchased the 18.95 percent economic interest from Prudential.
The Pinedale LGS consists of more than 150 miles of pipelines and four central storage facilities that are utilized by Ultra Petroleum as a method for the gathering of a commingled hydrocarbon and produced water stream. The Pinedale LGS has a current capacity of approximately 52 thousand barrels per day. This stream is separated into its components of water, condensate and natural gas, for the purpose of subsequently storing, selling or disposing of these separated components. Condensate is a valuable hydrocarbon commodity that is sold by Ultra Petroleum; water is transported to disposal wells or a treatment facility for re-use; and natural gas is sold by Ultra Petroleum or otherwise used for fueling on-site operational equipment. Ultra Petroleum's non-operating working interest partners in the Pinedale field where the Pinedale LGS is located pay Ultra Petroleum a fee for the use of Ultra Petroleum's LGS. To date, no major operational issues have been reported with respect to the Pinedale LGS. We believe that the Pinedale LGS is critical in supporting the production of reserves for Ultra Petroleum, which reports the rental expense as part of its Facility Lease Expense.
The underground pipelines constituting the majority of the Pinedale LGS and certain other components, such as the separators, have useful lives that extend beyond the initial term of the Pinedale Lease Agreement. Additionally, we believe that the Pinedale LGS is capable of being expanded at a relatively low incremental cost, for example, by adding additional separating equipment. Pinedale field operators have estimated average well lives as high as 40 years. For its internal analysis, CORR assumes average Pinedale well lives of 35 years. In December of 2019, UPL described Pinedale as having over 4,000 vertical well drilling locations remaining. Actual wells drilled will be dependent on economics, but these data suggest the potential for multiple decades of drilling location inventory with the last of these wells continuing to produce for approximately 35 years thereafter, providing a long-term perspective on the utility of the Pinedale LGS.
Most of Ultra Petroleum's exploration and development in the Pinedale field takes place on land under the jurisdiction of the Bureau of Land Management ("BLM"). The BLM has the authority to approve or deny oil and gas leases or to impose environmental restrictions on leases where appropriate. The BLM issued the Pinedale Record of Decision ("ROD") in September 2008. Under the ROD, Ultra Petroleum gained year-round access to the Pinedale field for drilling and completion activities in development areas,
37
provided Ultra Petroleum conducts an environmental mitigation effort, which includes the use of a liquids gathering system. This additional access resulted in increased drilling efficiencies and allowed for accelerated development of the field.
During the initial fifteen-year term of the Pinedale Lease Agreement, we will receive a fixed minimum annual rent ("base rent"), adjusted annually for changes based on the CPI (subject to a 2.00 percent annual cap). On January 1, 2020, the base rent increased by 1.79 percent to approximately $22.1 million annually. We also are eligible for a participating rent component based on volumes flowing through the Pinedale LGS exceeding a baseline established at inception of the lease, subject to a maximum annual rental payment during the initial fifteen-year term of $27.5 million. Beginning in the third quarter 2017, we received our first variable rent payments since lease inception. Total variable rent payments recorded for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017 were $4.6 million, $4.3 million and $587 thousand, respectively.
In view of the fact that Ultra Petroleum leases a substantial portion of our net leased property, which is a significant source of revenues and operating income, its financial condition and ability and willingness to satisfy its obligations under its lease with us are expected to have a considerable impact on our results of operations and cash flows.
Ultra Petroleum is currently subject to the reporting requirements of the Exchange Act and is required to file with the SEC annual reports containing audited financial statements and quarterly reports containing unaudited financial statements. The audited financial statements and unaudited financial statements of Ultra Petroleum can be found on the SEC's website at www.sec.gov. We make no representation as to the accuracy or completeness of the audited and unaudited financial statements of Ultra Petroleum, but we have no reason to doubt the accuracy or completeness of such information. In addition, Ultra Petroleum has no duty, contractual or otherwise, to advise us of any events that might have occurred subsequent to the date of such financial statements which could affect the significance or accuracy of such information.
Other Energy Infrastructure Assets
MoGas Pipeline System
Our wholly-owned TRS, Corridor MoGas, Inc., owns all of the membership interests in a subsidiary that owns and operates the MoGas Pipeline System, which consists of an approximately 263-mile interstate natural gas pipeline system in and around St. Louis and extending into central Missouri, and certain related real and personal property. The MoGas Pipeline System, which is regulated by FERC, receives natural gas at three separate receipt points from third party interstate gas pipelines and delivers that gas through 24 different delivery points to investor-owned natural gas distribution companies, municipalities and end users. MoGas has eight firm transportation customers. We provide REIT-qualifying intercompany mortgage financing secured by the real property assets of MoGas and United Property Systems, which allows for a maximum principal balance of $90.0 million. Our ownership interest in the MoGas Pipeline System partially secures borrowings under the CorEnergy Credit Facility.
Omega Pipeline (Mowood, LLC)
We indirectly hold 100 percent of the equity interests in Omega through Mowood, which was a TRS of the Company until December 31, 2017, as discussed further below. Mowood is the holding company of Omega, a natural gas service provider located primarily on the Department of Defense's Fort Leonard Wood military post in south-central Missouri. Omega has a long-term contract with the Department of Defense, which was renewed for an additional 10-year term in January 2016, to provide natural gas distribution to Fort Leonard Wood through Omega's approximately 75-mile pipeline distribution system on the post. In addition, Omega has historically provided natural gas marketing services to several customers in the surrounding area.
During 2017, we received a private letter ruling from the IRS which, among other items, qualified the revenue from our long-term contract with Fort Leonard Wood as representing rents from real property. Accordingly, the revenue from the Fort Leonard Wood contract is considered REIT-qualifying income. As a result of the favorable ruling, we converted Omega from a taxable REIT subsidiary to a qualified REIT subsidiary. Omega's natural gas marketing service contracts with customers other than Fort Leonard Wood were sold to a newly created indirect wholly-owned TRS of the Company, Omega Gas Marketing, LLC.
Principal Location
Our principal executive office is located at 1100 Walnut Street, Suite 3350, Kansas City, MO 64106.
ITEM 3. LEGAL PROCEEDINGS
As discussed in further detail in Part IV, Item 15, Note 3 ("Leased Properties And Leases") in this Report, the Company initiated litigation on March 26, 2019 to enforce the terms of the Grand Isle Lease Agreement requiring that we be provided with copies of certain financial statement information that we are required to file pursuant to SEC Regulation S-X, as described in Section 2340 of the SEC Financial Reporting Manual, in the case CorEnergy Infrastructure Trust, Inc. and Grand Isle Corridor, LP v. Energy XXI Gulf Coast, Inc. and Energy XXI GIGS Services, LLC, Case No. 01-19-0228-CV in the 11th District Court of Harris County, Texas.
38
The Company sought and obtained a temporary restraining order mandating that our tenant deliver the required financial statements. On April 1, 2019, that order was stayed pending an appeal by the tenant to the Texas First District Court of Appeals in Houston. On January 6, 2020, that appellate court rejected our tenant's appeal and remanded the case for further proceedings in the 11th District Court of Harris County, Texas. While the appeal was pending, the original temporary restraining order lapsed by its own terms. However, the Company is requesting a hearing for as early in April 2020 as possible to obtain a temporary injunction mandating our tenant deliver the required financial statements. The Company believes that it is entitled to such relief and will continue to pursue this litigation and all viable options to obtain and file the necessary tenant financial statements.
ITEM 4. MINE SAFETY DISCLOSURES
Not applicable.
PART II
ITEM 5. MARKET FOR REGISTRANT'S COMMON EQUITY, RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS AND ISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES
Our common stock is traded on the New York Stock Exchange ("NYSE"), under the symbol "CORR".
On December 1, 2015, we completed a 1-for-5 reverse stock split, which was previously approved by our Board of Directors. All issued and outstanding common stock and per share amounts reflected in this Report have been retroactively adjusted to reflect this reverse stock split for all periods presented. As of December 31, 2019, we had 28 stockholders of record.
Dividends
Our portfolio of real property assets and promissory notes generates cash flow to us from which we pay dividends to stockholders. The amount of any dividend is recorded on the ex-dividend date.
The character of dividends made during the year may differ from their ultimate characterization for federal income tax purposes. Although there is no assurance that we will continue to make regular dividend payments, we believe that a number of actions can be taken to maintain 2020 dividends on a quarterly basis, and an estimated total 2020 annualized dividend of $3.00 per share, consistent with 2019 dividend payments. Refer to Item 7, "Dividends," for further discussion of our dividend.
Federal and State Income Taxation
We have elected to be taxed as a REIT under sections 856 through 860 of the Code and applicable Treasury regulations, which set forth the requirements for qualifying as a REIT, commencing with our taxable year beginning January 1, 2013. We believe that we have been organized and operated in a manner so as to qualify for taxation as a REIT under the Code and we intend to continue to operate in such a manner.
For as long as we qualify for taxation as a REIT, we generally will not be subject to federal corporate income taxes on net income that we currently distribute to stockholders. This treatment substantially eliminates the "double taxation" (at the corporate and security holder levels) that can result from investment in a "C" corporation. A "C" corporation is a corporation that is generally required to pay tax at the corporate level. Double taxation means taxation once at the corporate level when income is earned and once again at the stockholder level when the income is distributed.
As long as we qualify as a REIT, distributions made to our taxable U.S. stockholders out of current or accumulated earnings and profits (and not designated as capital gain dividends or retained capital gains) will be taken into account by them as ordinary income, and corporate stockholders will not be eligible for the dividends received deduction as to such amounts. If we received qualified dividend income and designate such portion of our distributions as qualified dividend income in a written notice mailed no later than 60 days after the close of our taxable year, an individual U.S. stockholder may qualify (provided holding period and certain other requirements are met) to treat such portion of the distribution as qualified dividend income, eligible to be taxed at the reduced maximum rate of 20 percent. Distributions in excess of current and accumulated earnings and profits will not be taxable to a stockholder to the extent that they do not exceed the adjusted basis of such stockholder's common stock, but rather will reduce the adjusted basis of such shares as a return of capital. To the extent that such distributions exceed the adjusted basis of a stockholder's common stock, they will be included in income as long-term capital gains (or short-term capital gain if the shares have been held for one year or less), assuming the shares are a capital asset in the hands of the stockholder. Distributions that we properly designate as capital gain dividends will be taxable to stockholders as gains (to the extent they do not exceed our actual net capital gain for the taxable year) from the sale or disposition of a capital asset held for greater than one year. If we designate any portion of a dividend as a capital gain dividend, a U.S. stockholder will receive an Internal Revenue Service Form 1099-DIV indicating the amount that will be taxable to the stockholder as a capital gain. As a REIT, we will be subject to corporate level tax on certain built-in gains in assets if such assets are sold during the 5-year period following conversion. Built-in gain assets are assets whose fair market value exceeds the
39
REIT's adjusted tax basis at the time of conversion or assets acquired from a C corporation if our initial tax basis in the asset is less than the fair market value of the asset. In addition, a REIT may not have earnings and profits accumulated in a non-REIT year. Thus, upon conversion to a REIT, we paid sufficient dividends in 2013 to distribute all accumulated earnings and profits.
We may, from time to time, own and operate certain properties through C corporation subsidiaries and will treat those subsidiaries as either "qualified REIT subsidiaries," or "taxable REIT subsidiaries." If a REIT owns a corporate subsidiary that is a "qualified REIT subsidiary," the separate existence of that subsidiary generally will be disregarded for federal income tax purposes. A "taxable REIT subsidiary" is an entity taxable as a corporation in which we own stock and that elected with us to be treated as a taxable REIT subsidiary under Section 856(1) of the Code. A taxable REIT subsidiary is subject to federal income tax, and state and local income tax where applicable, as a regular "C" corporation.
Our tax expense or benefit attributable to the taxable REIT subsidiary is included in the Consolidated Statements of Income. Deferred income taxes reflect the net tax effects of temporary differences between the carrying amounts of assets and liabilities for financial reporting purposes and the amounts used for income tax purposes.
Recent Sales of Unregistered Securities
During the fourth quarter ended December 31, 2019, certain holders elected to convert approximately $3.4 million of 7.00% Convertible Notes to CorEnergy common stock at a conversion rate of 30.3030 shares of common stock per $1,000 principal amount, as follows:
Conversion Date | Principal Amount of Convertible Notes Converted | Number of Shares of Common Stock Issued | |||||
November 13, 2019 | $ | 20,000 | 606 | ||||
December 19, 2019 | 15,000 | 454 | |||||
December 19, 2019 | 3,399,000 | 103,000 | |||||
Total | $ | 3,434,000 | 104,060 | ||||
The shares of common stock were issued solely to holders of the 7.00% Convertible Notes upon conversion pursuant to the exemption from registration provided under Section 3(a)(9) of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended. This exemption is available to the Company because the shares of common stock were exchanged by the Company with its existing security holders in accordance with the terms of the indenture governing the 7.00% Convertible Notes with no commission or other remunerations being paid or given for soliciting such an exchange.
Performance Graph
We operate as a REIT and primarily own assets in the midstream and downstream U.S. Energy sectors that perform utility-like functions, such as pipelines, storage terminals, rail terminals and gas transmission and distribution assets. The following graph sets forth the cumulative return on our common stock between January 1, 2015 and December 31, 2019, as compared to the following set of relevant indices: FTSE NAREIT All Equity REIT Index ("FTSE NAREIT"), the Dow Jones Utilities Average Index ("DJ UTIL"), the S&P Global Infrastructure Index ("SPGTIND") and the Alerian MLP Index ("AMZ"). The graph assumes a $100 investment was made on December 31, 2014 in each of our common stock, the FTSE NAREIT, the DJ UTIL, the SPGTIND and the AMZ, and assumes the reinvestment of all cash dividends. The comparisons in the graph below are based on historical data and are not intended to forecast future performance.
40
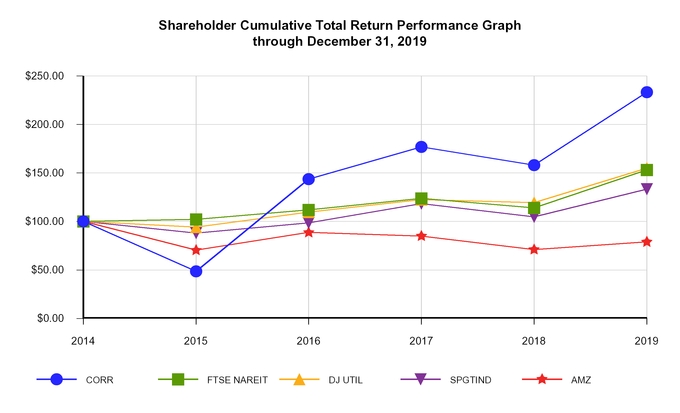
The performance graph shall not be deemed "filed" for purposes of Section 18 of the Exchange Act, or otherwise subject to the liabilities under that section, and shall not be deemed to be incorporated by reference into any filing under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, or the Exchange Act.
Cumulative Value of $100 Investment, through December 31, | |||||||||||||||||||||||
2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | ||||||||||||||||||
CorEnergy Infrastructure Trust, Inc. | $ | 100.00 | $ | 48.70 | $ | 143.61 | $ | 176.95 | $ | 158.04 | $ | 233.21 | |||||||||||
FTSE NAREIT All Equity REIT Index | 100.00 | 102.24 | 111.89 | 123.67 | 114.05 | 153.07 | |||||||||||||||||
Dow Jones Utilities Average Index | 100.00 | 94.22 | 109.52 | 122.57 | 119.39 | 154.86 | |||||||||||||||||
S&P Global Infrastructure Index | 100.00 | 88.04 | 98.68 | 118.35 | 104.75 | 133.20 | |||||||||||||||||
Alerian MLP Index | 100.00 | 70.43 | 88.68 | 85.03 | 71.09 | 78.93 | |||||||||||||||||
Our shares began trading on the New York Stock Exchange ("NYSE") on February 2, 2007. Since December 3, 2012, our common stock has traded under the symbol "CORR".
ITEM 6. SELECTED FINANCIAL DATA
The selected financial data set forth below should be read in conjunction with "Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations," and the financial statements and related notes included in this Report. Our consolidated financial statements include our accounts and our wholly-owned subsidiaries. The financial information presented below has been derived from our audited consolidated financial statements, which financial statements have been audited by Ernst & Young LLP, our independent registered public accounting firm. The historical data is not necessarily indicative of results to be expected for any future period. The balance sheet data below reflects the reclassification of deferred financing costs under FASB Accounting Standards Update (ASU) No. 2015-03, Simplifying the Presentation of Debt Issue Costs, which was adopted on January 1, 2016, retrospectively.
41
For the Years Ended December 31, | |||||||||||||||||||
2019 | 2018 | 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||||||||
Operating Data | |||||||||||||||||||
Total revenue | $ | 85,945,570 | $ | 89,231,598 | $ | 88,749,377 | $ | 89,250,586 | $ | 71,288,935 | |||||||||
Net Income attributable to CorEnergy Stockholders | 4,079,495 | 43,711,876 | 32,602,790 | 29,663,200 | 12,319,911 | ||||||||||||||
Net Income (Loss) attributable to Common Stockholders | (5,175,973 | ) | 34,163,499 | 24,648,802 | 25,514,763 | 8,471,083 | |||||||||||||
Per Share Data | |||||||||||||||||||
Net Income (Loss) attributable to Common stockholders: | |||||||||||||||||||
Basic | $ | (0.40 | ) | $ | 2.86 | $ | 2.07 | $ | 2.14 | $ | 0.79 | ||||||||
Diluted | (0.40 | ) | 2.79 | 2.07 | 2.14 | 0.79 | |||||||||||||
Cash dividends declared per common share | 3.000 | 3.000 | 3.000 | 3.000 | 2.750 | ||||||||||||||
Other Data | |||||||||||||||||||
AFFO attributable to Common stockholders(1) | |||||||||||||||||||
Basic | $ | 4.06 | $ | 4.11 | $ | 4.25 | $ | 4.41 | $ | 3.77 | |||||||||
Diluted | 3.83 | 3.70 | 3.81 | 3.93 | 3.56 | ||||||||||||||
(1) We believe that net income (loss), as defined by U.S. GAAP, is the most appropriate earnings measurement. However, we consider Adjusted Funds From Operations ("AFFO") to be an appropriate measure of operating performance of an equity REIT. See "Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations - Non-GAAP Financial Measures" included in Item 7 of this Report for a reconciliation of AFFO to our GAAP earnings. | |||||||||||||||||||
As of December 31, | |||||||||||||||||||
2019 | 2018 | 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||||||||
Balance sheet data | |||||||||||||||||||
Total assets | $ | 651,455,794 | $ | 624,883,180 | $ | 633,418,113 | $ | 650,732,571 | $ | 677,979,621 | |||||||||
Current debt maturities | 5,612,178 | 3,528,000 | 3,528,000 | 7,128,556 | 66,132,000 | ||||||||||||||
Long-term debt | 146,497,248 | 146,510,380 | 149,249,437 | 193,504,324 | 150,732,752 | ||||||||||||||
CorEnergy equity - Preferred | 125,493,175 | 125,555,675 | 130,000,000 | 56,250,000 | 56,250,000 | ||||||||||||||
CorEnergy equity - Common | 351,246,264 | 329,455,630 | 331,785,632 | 350,218,436 | 361,784,244 | ||||||||||||||
ITEM 7. MANAGEMENT'S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
Certain statements included or incorporated by reference in this Annual Report on Form 10-K may be deemed "forward-looking statements" within the meaning of the federal securities laws. In many cases, these forward-looking statements may be identified by the use of words such as "will," "may," "should," "could," "believes," "expects," "anticipates," "estimates," "intends," "projects," "goals," "objectives," "targets," "predicts," "plans," "seeks," or similar expressions. Any forward-looking statement speaks only as of the date on which it is made and is qualified in its entirety by reference to the factors discussed throughout this Report.
Although we believe the expectations reflected in any forward-looking statements are based on reasonable assumptions, forward-looking statements are not guarantees of future performance or results and we can give no assurance that these expectations will be attained. Our actual results may differ materially from those indicated by these forward-looking statements due to a variety of known and unknown risks and uncertainties. Such risks and uncertainties include, without limitation, the risk factors discussed in Part I, Item 1A of this Report. We disclaim any obligation to update or revise any forward-looking statements to reflect actual results or changes in the factors affecting the forward-looking information.
BUSINESS OBJECTIVE
CorEnergy primarily owns and seeks to own assets in the U.S. energy sector that perform utility-like functions, such as pipelines, storage terminals, rail terminals and gas and electric transmission and distribution assets. We also may provide other types of capital, including loans secured by energy infrastructure assets. Our objective has been to generate long-term contracted revenue from operators of our assets, primarily under triple-net participating leases without direct commodity price exposure. As a result of having received the PLR, we are now able to consider, and are considering, a broader set of investment opportunities than was available to us prior to issuance of the PLR. For additional information, see "Company Overview" in Item 1 of this Report.
The assets are primarily mission-critical, in that utilization of the assets is necessary for the business the operators of those assets seek to conduct and their rental payments are an essential operating expense. We acquire assets that will enhance the stability of our dividend through diversification, while offering the potential for long-term distribution growth. These sale-leaseback or real property mortgage transactions provide the energy company with a source of capital that is an alternative to sources such as corporate borrowing,
42
bond offerings, or equity offerings. We believe our leadership team's energy and utility expertise provides CorEnergy with a competitive advantage to acquire, own and lease U.S. energy infrastructure assets in a tax-efficient, transparent and investor-friendly REIT.
Basis of Presentation
The consolidated financial statements include CorEnergy Infrastructure Trust, Inc., as of December 31, 2019, and its direct and indirect wholly-owned subsidiaries. All significant intercompany accounts and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation.
RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
The following table summarizes the financial data and key operating statistics for CorEnergy for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017. We believe the Operating Results detail presented below provides investors with information that will assist them in analyzing our operating performance. The following data should be read in conjunction with our consolidated financial statements and the notes thereto included in Part IV, Item 15 of this Report.
43
The following table and discussion are a summary of our results of operations for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017:
For the Years Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2019 | 2018 | 2017 | |||||||||
Revenue | |||||||||||
Lease revenue | $ | 67,050,506 | $ | 72,747,362 | $ | 68,803,804 | |||||
Transportation and distribution revenue | 18,778,237 | 16,484,236 | 19,945,573 | ||||||||
Financing revenue | 116,827 | — | — | ||||||||
Total Revenue | 85,945,570 | 89,231,598 | 88,749,377 | ||||||||
Expenses | |||||||||||
Transportation and distribution expenses | 5,242,244 | 7,210,748 | 6,729,707 | ||||||||
General and administrative | 10,596,848 | 13,042,847 | 10,786,497 | ||||||||
Depreciation, amortization and ARO accretion expense | 22,581,942 | 24,947,453 | 24,047,710 | ||||||||
Provision for loan gain | — | (36,867 | ) | — | |||||||
Total Expenses | 38,421,034 | 45,164,181 | 41,563,914 | ||||||||
Operating Income | $ | 47,524,536 | $ | 44,067,417 | $ | 47,185,463 | |||||
Other Income (Expense) | |||||||||||
Net distributions and other income | $ | 1,328,853 | $ | 106,795 | $ | 680,091 | |||||
Net realized and unrealized gain (loss) on other equity securities | — | (1,845,309 | ) | 1,531,827 | |||||||
Interest expense | (10,578,711 | ) | (12,759,010 | ) | (12,378,514 | ) | |||||
Gain on the sale of leased property, net | — | 11,723,257 | — | ||||||||
Loss on extinguishment of debt | (33,960,565 | ) | — | (336,933 | ) | ||||||
Total Other Expense | (43,210,423 | ) | (2,774,267 | ) | (10,503,529 | ) | |||||
Income before income taxes | 4,314,113 | 41,293,150 | 36,681,934 | ||||||||
Income tax expense (benefit), net | 234,618 | (2,418,726 | ) | 2,345,318 | |||||||
Net Income | 4,079,495 | 43,711,876 | 34,336,616 | ||||||||
Less: Net Income attributable to non-controlling interest | — | — | 1,733,826 | ||||||||
Net Income attributable to CorEnergy Stockholders | $ | 4,079,495 | $ | 43,711,876 | $ | 32,602,790 | |||||
Preferred dividend requirements | 9,255,468 | 9,548,377 | 7,953,988 | ||||||||
Net Income (Loss) attributable to Common Stockholders | $ | (5,175,973 | ) | $ | 34,163,499 | $ | 24,648,802 | ||||
Other Financial Data(1) | |||||||||||
Adjusted EBITDAre | $ | 71,435,331 | $ | 69,395,739 | $ | 67,944,360 | |||||
NAREIT FFO | 16,870,068 | 46,796,201 | 46,308,969 | ||||||||
FFO | 16,857,484 | 47,959,311 | 46,046,781 | ||||||||
AFFO | 53,012,786 | 49,024,120 | 50,536,194 | ||||||||
(1) Refer to the "Non-GAAP Financial Measures" section that follows for additional details. | |||||||||||
Year Ended December 31, 2019 Compared to Year Ended December 31, 2018
Revenue. Consolidated revenues were $85.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2019 compared to $89.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2018, representing a decrease of $3.3 million. Lease revenue was $67.1 million and $72.7 million for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively, with the decrease of approximately $5.7 million driven primarily by (i) the sale of the Portland Terminal Facility, partially offset by (ii) an increase in variable rent collected on the Pinedale lease during the year ended December 31, 2019.
Transportation and distribution revenue from our subsidiaries MoGas and Omega was $18.8 million and $16.5 million for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively. The $2.3 million increase primarily resulted from higher rates going into effect on December 1, 2018 related to the rate case filed by MoGas with the FERC, net of the final refund liability. The FERC rate case settlement was approved in August of 2019. Refer to "Asset Portfolio and Related Developments" for further discussion related to the FERC rate case settlement.
Transportation and Distribution Expenses. Transportation and distribution expenses were $5.2 million and $7.2 million for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively, representing a decrease of $2.0 million. The decrease relates primarily to lower legal, consulting and maintenance costs at MoGas.
44
General and Administrative Expenses. General and administrative expenses were $10.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2019 compared to $13.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2018. The most significant components of the variance from the prior year are outlined in the following table and explained below:
For the Years Ended December 31, | |||||||
2019 | 2018 | ||||||
Management fees | $ | 6,786,637 | $ | 7,591,750 | |||
Acquisition and professional fees | 2,413,617 | 3,759,505 | |||||
Other expenses | 1,396,594 | 1,691,592 | |||||
Total | $ | 10,596,848 | $ | 13,042,847 | |||
Management fees are directly proportional to our asset base. For the year ended December 31, 2019, management fees decreased $805 thousand compared to the prior year due to (i) cash utilized for the 7.00% Convertible Notes exchange in the first quarter of 2019, (ii) management fee waivers in the third and fourth quarters of 2019 to exclude the net proceeds from the 5.875% Convertible Notes offering (other than the cash portion of such proceeds utilized in connection with the exchange of the Company's 7.00% Convertible Notes) and (iii) lower incentive fees due to decreased revenue from the sale of the Portland Terminal in December 2018. See Part IV, Item 15, Note 9 ("Management Agreement") for additional information.
Acquisition and professional fees for the year ended December 31, 2019 decreased $1.3 million from the prior year primarily due to a decrease in professional fees. Professional fees decreased $1.0 million during the current year while asset acquisition expenses decreased $336 thousand. Generally, we expect asset acquisition expenses to be repaid over time from income generated by acquisitions. However, any particular period may reflect significant expenses arising from third party legal, engineering, and consulting fees that are incurred in the early to mid-stages of due diligence. The decrease in professional fees during the year ended December 31, 2019 was primarily attributable to higher legal and consulting costs in the prior year related to monitoring our GIGS asset and the sale of the Portland Terminal Facility, partially offset by legal and consulting costs incurred in the current year related to the ongoing litigation with EGC/Cox Oil. Refer to Part IV, Item 15, Note 3 ("Leased Properties And Leases") for additional information.
Other expenses for the for the year ended December 31, 2019 decreased $295 thousand compared to the prior year. The decrease is primarily related to a loss on settlement of ARO related to the decommissioning of a segment of the GIGS pipeline system during the prior year.
Depreciation, Amortization and ARO Accretion Expense. Depreciation, amortization and ARO accretion expense was $22.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2019 compared to $24.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2018. The $2.4 million decrease was primarily driven by depreciation expense, which decreased approximately $2.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2019 compared to the year ended December 31, 2018. The decrease in depreciation expense was driven by (i) the sale of the Portland Terminal Facility in December of 2018 and (ii) updates made to the estimated useful lives of certain ARO segments of GIGS at the end of 2018.
Provision for loan gain. For the year ended December 31, 2018, we recorded a provision for loan gain of approximately $37 thousand related to the satisfaction of the SWD loans with Four Wood Corridor upon sale of the assets securing the loans to Compass SWD, LLC in exchange for (i) a new loan agreement with Compass SWD, LLC for $1.3 million and (ii) cash proceeds from the sale recognized as principal payments on the SWD loans. For additional information, see Part IV, Item 15, Note 5 ("Financing Notes Receivable"). There were no loan (gain) loss provisions recorded for the year ended December 31, 2019.
Net Distributions and Other Income. Net distributions and other income for the year ended December 31, 2019 was $1.3 million compared to $107 thousand for the year ended December 31, 2018. The increase was primarily related to interest income, which increased approximately $1.2 million from the prior-year period, due to a higher cash balance maintained during 2019. Net distributions of approximately $0.1 million recognized for each of the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018 were impacted by (i) the sale of a large portion of the Lightfoot investment as a result of the Arc Logistics merger with Zenith, completed on December 21, 2017, (ii) Lightfoot's disposition of its remaining asset interest at the end of 2018 and (iii) and the liquidation of Lightfoot at the end of 2019.
The portion of distributions and dividends deemed to be income versus a return of capital in any period are estimated at the time such distributions are received. These estimates may be subsequently revised based on information received from the portfolio company after their tax reporting periods are concluded. The following table provides a reconciliation of the gross cash distributions and dividend income received from our investment securities for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018 to the net distributions and other income recorded on the Consolidated Statements of Income.
45
For the Years Ended December 31, | |||||||
2019 | 2018 | ||||||
Gross cash distributions and other income received from investment securities | $ | 1,328,853 | $ | 770,734 | |||
Add: | |||||||
Cash distributions received in prior period previously deemed a return of capital (dividend income) which have been reclassified as income (return of capital) in a subsequent period | — | — | |||||
Less: | |||||||
Cash distributions and dividends received in current period deemed a return of capital and not recorded as income (recorded as a cost reduction) in the current period | — | 663,939 | |||||
Net distributions and other income | $ | 1,328,853 | $ | 106,795 | |||
Net Realized and Unrealized Loss on Other Equity Securities. For the year ended December 31, 2018, we recorded a net loss on other equity securities of $1.8 million. The net loss recorded during the year ended December 31, 2018 related to valuation considerations surrounding the arbitration award delivered to Eni USA and Gulf LNG as well as other market information. Due to the sale or asset disposition related to our investment securities at the end of 2018 and the liquidation of the remaining investment interest at the end of 2019, we no longer have an interest in other equity securities.
Interest Expense. For the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018, interest expense totaled approximately $10.6 million and $12.8 million, respectively. The decrease was primarily attributable to (i) a decrease in interest expense as a result of the 7.00% Convertible Notes exchanges and conversions that occurred during the year ended December 31, 2019, partially offset by (ii) additional interest expense from the 5.875% Convertible Notes Offering in August of 2019. For additional information, see Part IV, Item 15, Note 11 ("Debt").
Gain on the sale of leased property. For the year ended December 31, 2018, a gain on the sale of leased property totaling approximately $11.7 million was recorded in connection with the sale of the Portland Terminal Facility to Zenith Terminals on December 21, 2018. For additional information, see Part IV, Item 15, Note 3 ("Leased Properties And Leases"). There was no gain on the sale of leased property recorded for the year ended December 31, 2019.
Loss on Extinguishment of Debt. For the year ended December 31, 2019, a loss on extinguishment of debt totaling approximately $34.0 million was recorded in connection with the 7.00% Convertible Notes exchanges completed in the first and third quarters of 2019. For additional information, see Part IV, Item 15, Note 11 ("Debt"). There was no loss on extinguishment of debt recorded for the year ended December 31, 2018.
Income Tax Expense (Benefit). Income tax expense was $235 thousand for the year ended December 31, 2019 compared to an income tax benefit of $2.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2018. The income tax expense recorded in the current year is primarily the result of (i) a change in our state effective rate due to changes in state law and state operations by certain of our TRS entities, (ii) certain fixed asset, deferred contract revenue and loan loss activities, partially offset by (iii) the impact of the refund liability related to the FERC rate case settlement and (iv) capital losses generated from the Lightfoot liquidation that will be carried back against capital gains from prior years. The income tax benefit recorded in the prior year was primarily attributable to (i) higher losses generated by our TRS subsidiaries and (ii) the capital losses generated from the sale of our interest in Joliet to Zenith Terminals and Lightfoot's disposition of its remaining asset interest that were carried back against capital gains generated from the sale of a portion of the Lightfoot investment in prior years.
Net Income. Net income was $4.1 million and $43.7 million for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively, representing a decrease of $39.6 million. After deducting $9.3 million and $9.5 million for the portion of preferred dividends that are allocable to each respective period, net income (loss) attributable to common stockholders for the year ended December 31, 2019 was $(5.2) million, or $(0.40) per basic and diluted common share, as compared to $34.2 million, or $2.86 per basic and $2.79 diluted common share, for the prior year.
Year Ended December 31, 2018 Compared to Year Ended December 31, 2017
Revenue. Consolidated revenues were $89.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2018 compared to $88.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2017, representing an increase of $482 thousand. Lease revenue was $72.7 million and $68.8 million for the years ended December 31, 2018 and 2017, respectively, with the increase of approximately $3.9 million driven primarily by variable rent collected on the Pinedale lease during 2018. Transportation and distribution revenue from our subsidiaries MoGas and Omega was $16.5 million and $19.9 million for the years ended December 31, 2018 and 2017, respectively. The $3.5 million decrease primarily resulted from a change to straight-line revenue recognition on MoGas' long-term contract with Spire under the new revenue recognition standard that was adopted on January 1, 2018. Revenue recognized for the year ended December 31, 2018 was approximately $3.2 million lower under the new accounting standard. Refer to Part IV, Item 15, Note 4 ("Transportation And Distribution Revenue") for additional details.
46
Transportation and Distribution Expenses. Transportation and distribution expenses were $7.2 million and $6.7 million for the years ended December 31, 2018 and 2017, respectively, representing an increase of $481 thousand. The increase relates primarily to MoGas, which had higher legal and consulting costs during 2018 related to the FERC rate case. The increase was partially offset by lower costs from the timing of projects performed by Omega for Fort Leonard Wood.
General and Administrative Expenses. General and administrative expenses were $13.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2018 compared to $10.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2017. The most significant components of the variance from the prior year are outlined in the following table and explained below:
For the Years Ended December 31, | |||||||
2018 | 2017 | ||||||
Management fees | $ | 7,591,750 | $ | 7,213,720 | |||
Acquisition and professional fees | 3,759,505 | 2,380,918 | |||||
Other expenses | 1,691,592 | 1,191,859 | |||||
Total | $ | 13,042,847 | $ | 10,786,497 | |||
Management fees are directly proportional to our asset base. For the year ended December 31, 2018, management fees increased $378 thousand compared to the prior year due to the acquisition of the non-controlling interest in Pinedale LP, which closed on December 29, 2017. See Part IV, Item 15, Note 9 ("Management Agreement") for additional information.
Acquisition and professional fees for the year ended December 31, 2018 increased $1.4 million from the prior year primarily due to an increase in professional fees. The increase in professional fees for the year ended December 31, 2018 is primarily attributable to (i) higher legal and consulting costs in the current-year related to monitoring our GIGS asset, (ii) higher legal and consulting fees related to the sale of the Portland Terminal Facility and (iii) a prior-year reimbursement of legal fees received in 2017 for costs incurred during UPL's bankruptcy.
Asset acquisition costs for the year ended December 31, 2018 were relatively consistent with the prior year, decreasing $71 thousand, due to continued focus on potential acquisition opportunities. Generally, we expect asset acquisition expenses to be repaid over time from income generated by acquisitions. However, any particular period may reflect significant expenses arising from third party legal, engineering, and consulting fees that are incurred in the early to mid-stages of due diligence.
Other expenses for the for the year ended December 31, 2018 increased $500 thousand compared to the prior year. The increase is primarily related to (i) a loss on settlement of ARO related to the decommissioning of a segment of the GIGS pipeline system during 2018 and (ii) a non-cash gain recorded on settlement of accounts payable in the prior year.
Depreciation, Amortization and ARO Accretion Expense. Depreciation, amortization and ARO accretion expense was $24.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2018 compared to $24.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2017. This $900 thousand increase was primarily driven by an increase in ARO depreciation based on updates made to the estimated useful lives of certain segments of GIGS at the end of 2017.
Provision for loan gain. For the year ended December 31, 2018, we recorded a provision for loan gain of approximately $37 thousand related to the satisfaction of the SWD loans with Four Wood Corridor upon sale of the assets securing the loans to Compass SWD, LLC in exchange for (i) a new loan agreement with Compass SWD, LLC for $1.3 million and (ii) cash proceeds from the sale recognized as principal payments on the SWD loans. There were no loan (gain) loss provisions recorded for the year ended December 31, 2017.
Net Distributions and Other Income. Net distributions and other income for the year ended December 31, 2018 was $107 thousand compared to $680 thousand for the year ended December 31, 2017. The portion of distributions and dividends deemed to be income versus a return of capital in any period are estimated at the time such distributions are received. These estimates may be subsequently revised based on information received from the portfolio company after their tax reporting periods are concluded. The following table provides a reconciliation of the gross cash distributions and dividend income received from our investment securities for the years ended December 31, 2018 and 2017 to the net distributions and other income recorded as income on the Consolidated Statements of Income.
47
For the Years Ended December 31, | |||||||
2018 | 2017 | ||||||
Gross cash distributions and other income received from investment securities | $ | 770,734 | $ | 949,646 | |||
Add: | |||||||
Cash distributions received in prior period previously deemed a return of capital (dividend income) which have been reclassified as income (return of capital) in a subsequent period | — | (148,649 | ) | ||||
Less: | |||||||
Cash distributions and dividends received in current period deemed a return of capital and not recorded as income (recorded as a cost reduction) in the current period | 663,939 | 120,906 | |||||
Net distributions and other income | $ | 106,795 | $ | 680,091 | |||
For the year ended December 31, 2018 compared to the year ended December 31, 2017, the decline in net distributions and dividends recorded as income versus the prior-year period was primarily due to (i) the sale of a large portion of the Lightfoot investment as a result of the Arc Logistics merger with Zenith, completed on December 21, 2017 and (ii) Lightfoot's disposition of its remaining asset interest at the end of 2018.
Net Realized and Unrealized Gain (Loss) on Other Equity Securities. For the years ended December 31, 2018 and 2017, we recorded a net loss on other equity securities of $1.8 million and a net gain on other equity securities of $1.5 million, respectively, resulting in a decrease of $3.4 million. The net gain and loss recorded are directly related to fluctuations in the valuation, sale and liquidation plan of our investments in private securities. The net loss recorded during the year ended December 31, 2018 related to (i) the sale of our equity interest in Joliet to Zenith Terminals and (ii) Lightfoot's disposition of its remaining asset interest at the end of 2018. The net gain recorded during the year ended December 31, 2017 was primarily due to gains realized related to Lightfoot upon completion of the Arc Logistics merger and valuation of the remaining investment in the Lightfoot LP and GP interests. See Part IV, Item 15, Note 10 ("Fair Value") for additional information.
Interest Expense. For the years ended December 31, 2018 and 2017, interest expense totaled approximately $12.8 million and $12.4 million, respectively. This increase was attributable to (i) increased interest on the Amended Pinedale Term Credit Facility during 2018 as a result of the refinancing with Prudential on December 29, 2017, partially offset by (ii) interest incurred on outstanding borrowings on the CorEnergy Revolver and CorEnergy Term Loan during the prior year.
Gain on the sale of leased property. For the year ended December 31, 2018, a gain on the sale of leased property totaling approximately $11.7 million was recorded in connection with the sale of the Portland Terminal Facility to Zenith Terminals on December 21, 2018. For additional information, see Part IV, Item 15, Note 3 ("Leased Properties And Leases"). There was no gain on the sale of leased property recorded for the year ended December 31, 2017.
Loss on Extinguishment of Debt. For the year ended December 31, 2017, a loss on extinguishment of debt totaling approximately $337 thousand was recorded in connection with entering into the amended and restated CorEnergy Credit Facility on July 28, 2017 and Amended Pinedale Term Credit Facility on December 29, 2017. There was no loss on extinguishment of debt recorded for the year ended December 31, 2018. For additional information, see Part IV, Item 15, Note 11 ("Debt").
Income Tax Expense (Benefit). Income tax benefit was $2.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2018 compared to income tax expense of $2.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2017. The increased benefit in 2018 was primarily attributable to (i) higher losses generated by our TRS subsidiaries and (ii) the capital losses generated from the sale of our interest in Joliet to Zenith Terminals and Lightfoot's disposition of its remaining asset interest that will be carried back against capital gains generated from the sale of a portion of the Lightfoot investment in the prior year. Income tax expense for the year ended December 31, 2017 was primarily attributable to (i) the transition tax adjustment associated with application of lower effective tax rates from the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act enacted in December 2017 to existing deferred tax asset balances at our TRS entities, (ii) the write-off of certain deferred tax assets in connection with the reorganization of Omega from a TRS subsidiary to a qualified REIT subsidiary and (iii) realized and unrealized gains recorded associated with our Lightfoot investment.
Net Income. Net income was $43.7 million and $34.3 million for the years ended December 31, 2018 and 2017, respectively, representing an increase of $9.4 million. For the years ended December 31, 2018 and 2017, net income attributable to CorEnergy stockholders was $43.7 million and $32.6 million, respectively. After deducting $9.5 million and $8.0 million for the portion of preferred dividends that are allocable to each respective period, net income attributable to common stockholders for the year ended December 31, 2018 was $34.2 million, or $2.86 per basic and $2.79 diluted common share, as compared to $24.6 million, or $2.07 per basic and diluted common share, for the prior year.
48
Common Equity Attributable to CorEnergy Stockholders per Share
As of December 31, 2019, our common equity increased by approximately $21.8 million to $351.2 million from $329.5 million as of December 31, 2018. This increase principally consists of: (i) $66.1 million of common stock issued pursuant to exchanges and conversion of 7.00% Convertible Notes and (ii) $404 thousand of common stock issued pursuant to reinvestment of dividends through the dividend reinvestment plan; partially offset by (iii) net loss attributable to CorEnergy common stockholders of approximately $5.2 million and (iv) dividends paid to our stockholders of approximately $39.5 million.
Book Value Per Common Share | |||||||
Analysis of Equity | December 31, 2019 | December 31, 2018 | |||||
Series A Cumulative Redeemable Preferred Stock 7.375%, $125,493,175 and $125,555,675 liquidation preference ($2,500 per share, $0.001 par value), 10,000,000 authorized; 50,197 and 50,222 issued and outstanding at December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, respectively | $ | 125,493,175 | $ | 125,555,675 | |||
Capital stock, non-convertible, $0.001 par value; 13,638,916 and 11,960,225 shares issued and outstanding at December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018 (100,000,000 shares authorized) | 13,639 | 11,960 | |||||
Additional paid-in capital | 360,844,497 | 320,295,969 | |||||
Retained earnings (deficit) | (9,611,872 | ) | 9,147,701 | ||||
Total CorEnergy Stockholders' Equity | $ | 476,739,439 | $ | 455,011,305 | |||
Subtract: 7.375% Series A Preferred Stock | (125,493,175 | ) | (125,555,675 | ) | |||
Total CorEnergy Common Equity | $ | 351,246,264 | $ | 329,455,630 | |||
Common shares outstanding | 13,638,916 | 11,960,225 | |||||
Book Value per Common Share | $ | 25.75 | $ | 27.55 | |||
NON-GAAP FINANCIAL MEASURES
We use certain financial measures that are not recognized under GAAP. The non-GAAP financial measures used in this Report include earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation and amortization as defined by the National Association of Real Estate Investment Trusts ("EBITDAre"); EBITDAre as adjusted in the manner described below ("Adjusted EBITDAre"); NAREIT funds from operations ("NAREIT FFO"); funds from operations adjusted for securities investments ("FFO"); and FFO as further adjusted in the manner described below ("AFFO"). These supplemental measures are used by our management team and are presented because we believe they help investors understand our business, performance and ability to earn and distribute cash to our stockholders by providing perspectives not immediately apparent from net income. The presentation of EBITDAre, Adjusted EBITDAre, NAREIT FFO, FFO and AFFO are not intended to be considered in isolation or as a substitute for, or superior to, the financial information prepared and presented in accordance with GAAP.
We offer these measures to assist the users of our financial statements in assessing our operating performance under U.S. GAAP, but these measures are non-GAAP measures and should not be considered measures of liquidity, alternatives to net income or indicators of any other performance measure determined in accordance with GAAP, nor are they indicative of funds available to fund our cash needs, including capital expenditures (if any), to make payments on our indebtedness or to make distributions. Our method of calculating these measures may be different from methods used by other companies and, accordingly, may not be comparable to similar measures as calculated by other companies. Investors should not rely on these measures as a substitute for any GAAP measure, including net income, cash flows from operating activities or revenues.
EBITDAre and Adjusted EBITDAre
EBITDAre and Adjusted EBITDAre are non-GAAP financial measures that management and external users of our consolidated financial statements, such as industry analysts, investors and lenders may use to evaluate our ongoing operating results, including (i) the performance of our assets without regard to the impact of financing methods, capital structure or historical cost basis of our assets and (ii) the overall rates of return on alternative investment opportunities. EBITDAre, as established by NAREIT, is defined as net income (loss) (calculated in accordance with GAAP) excluding interest expense, income tax, depreciation and amortization, gains or losses on disposition of depreciated property (including gains or losses on change of control), impairment write-downs of depreciated property and of investments in unconsolidated affiliates caused by a decrease in value of depreciated property in the affiliate, and adjustments to reflect the entity's pro rata share of EBITDAre of unconsolidated affiliates. Our presentation of Adjusted EBITDAre represents EBITDAre adjusted for net realized and unrealized (gain) loss on securities, non-cash; (gain) loss on extinguishment of debt; provision for loan (gain) loss; preferred dividend requirements; distributions and dividends received in prior period previously deemed a return of capital (recorded as a cost reduction) and reclassified as income in a subsequent period; (gain) loss on settlement of ARO; and non-cash settlement of accounts payable.
We believe that the presentation of EBITDAre and Adjusted EBITDAre provide useful information to investors in assessing our financial condition and results of operations. Our presentation of EBITDAre is calculated in accordance with standards established by NAREIT, which may not be comparable to measures calculated by other companies that do not use the NAREIT definition of
49
EBITDAre. In addition, although EBITDAre is a useful measure when comparing our results to other REITs, it may not be helpful to investors when comparing to non-REITs. Adjusted EBITDAre presented by other companies may not be comparable to our presentation, since each company may define these terms differently. EBITDAre and Adjusted EBITDAre should not be considered measures of liquidity and should not be considered as alternatives to operating income, net income or other indicators of performance determined in accordance with GAAP.
The following table presents a reconciliation of Income Attributable to Common Stockholders, as reported in the Consolidated Statements of Income and Comprehensive Income to EBITDAre and Adjusted EBITDAre:
For the Years Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2019 | 2018 | 2017 | |||||||||
Income (Loss) Attributable to Common Stockholders | $ | (5,175,973 | ) | $ | 34,163,499 | $ | 24,648,802 | ||||
Add: | |||||||||||
Interest expense, net | 10,578,711 | 12,759,010 | 12,378,514 | ||||||||
Depreciation, amortization, and ARO accretion | 22,581,942 | 24,947,453 | 24,047,710 | ||||||||
Less: | |||||||||||
Gain on the sale of leased property, net | — | 11,723,257 | — | ||||||||
Income tax (expense) benefit | (234,618 | ) | 2,418,726 | (2,345,318 | ) | ||||||
Non-controlling interest attributable to depreciation, amortization, and interest expense | — | — | 2,283,024 | ||||||||
EBITDAre(1) | $ | 28,219,298 | $ | 57,727,979 | $ | 61,137,320 | |||||
Add: | |||||||||||
Loss on extinguishment of debt | 33,960,565 | — | 336,933 | ||||||||
Provision for loan gain | — | (36,867 | ) | — | |||||||
Preferred dividend requirements | 9,255,468 | 9,548,377 | 7,953,988 | ||||||||
Distributions and dividends received in prior period previously deemed a return of capital (recorded as a cost reduction) and reclassified as income in a subsequent period(2) | — | — | 148,649 | ||||||||
Loss on settlement of ARO | — | 310,941 | — | ||||||||
Less: | |||||||||||
Net realized and unrealized gain (loss) on securities, non-cash(3) | — | (1,845,309 | ) | 1,410,921 | |||||||
Non-cash settlement of accounts payable | — | — | 221,609 | ||||||||
Adjusted EBITDAre(1) | $ | 71,435,331 | $ | 69,395,739 | $ | 67,944,360 | |||||
(1) Effective March 31, 2018, we now present EBITDAre, reported in accordance with NAREIT guidelines, and Adjusted EBITDAre as supplemental measures of our performance. Our prior year presentation has been updated to conform with the current year presentation. | |||||||||||
(2) We characterize distributions received from private investments estimated based on prior year activity. After receiving the K-1s, which depict our share of income and losses from the investment in the security, previously unrealized gains can be reclassified as dividend income. | |||||||||||
(3) Realized gains of $1.2 million related to the sale of interests in Lightfoot LP and Lightfoot GP have been excluded from Adjusted EBITDA for the year ended December 31, 2017. Refer to Part IV, Item 15, Note 10 ("Fair Value") for additional discussion. | |||||||||||
NAREIT FFO
FFO is a widely used measure of the operating performance of real estate companies that supplements net income (loss) determined in accordance with GAAP. As defined by NAREIT, NAREIT FFO represents net income (loss) (computed in accordance with GAAP), excluding gains (or losses) from sales of depreciable operating property, impairment losses of depreciable properties, real estate-related depreciation and amortization (excluding amortization of deferred financing costs or loan origination costs) and other adjustments for unconsolidated partnerships and non-controlling interests. Adjustments for non-controlling interests are calculated on the same basis. We define FFO attributable to common stockholders as defined above by NAREIT less dividends on preferred stock. Our method of calculating FFO attributable to common stockholders may differ from methods used by other REITs and, as such, may not be comparable.
FFO ADJUSTED FOR SECURITIES INVESTMENTS (FFO)
Due to the legacy investments that we held, we have also historically presented a measure of FFO, to which we refer herein as FFO Adjusted for Securities Investments which is derived by further adjusting NAREIT FFO for distributions received from investment securities, income tax expense (benefit) from investment securities, net distributions and other income and net realized and unrealized gain or loss on other equity securities.
We present NAREIT FFO and FFO Adjusted for Securities Investments because we consider it an important supplemental measure of our operating performance and believe that it is frequently used by securities analysts, investors, and other interested parties in
50
the evaluation of REITs, many of which present FFO when reporting their results. FFO is a key measure we use in assessing performance and in making resource allocation decisions.
Both NAREIT FFO and FFO Adjusted for Securities Investments are intended to exclude GAAP historical cost depreciation and amortization of real estate and related assets, which assumes that the value of real estate diminishes ratably over time. Historically, however, real estate values have risen or fallen with market conditions, and that may also be the case with certain of the energy infrastructure assets in which we invest. NAREIT FFO and FFO Adjusted for Securities Investments exclude depreciation and amortization unique to real estate and gains and losses from property dispositions and extraordinary items. As such, these performance measures provide a perspective not immediately apparent from net income when compared to prior-year periods. These metrics reflect the impact to operations from trends in base and participating rents, company operating costs, development activities, and interest costs.
We calculate NAREIT FFO in accordance with standards established by the Board of Governors of the National Association of Real Estate Investment Trusts in its March 1995 White Paper (as amended in November 1999 and April 2002) and FFO Adjusted for Securities Investment as NAREIT FFO with additional adjustments described above due to our legacy investments. This may differ from the methodology for calculating FFO utilized by other REITs and, accordingly may not be comparable to such other REITs. NAREIT FFO and FFO Adjusted for Securities Investments do not represent amounts available for management's discretionary use because of needed capital for replacement or expansion, debt service obligations, or other commitments and uncertainties. NAREIT FFO and FFO Adjusted for Securities Investments, as we have historically reported, should not be considered as an alternative to net income (loss) (computed in accordance with GAAP), as an indicator of our financial performance, or to cash flow from operating activities (computed in accordance with GAAP), as an indicator of our liquidity, or as an indicator of funds available for our cash needs, including our ability to make distributions or to service our indebtedness.
AFFO
Management uses AFFO as a measure of long-term sustainable operational performance. AFFO in excess of dividends is used for debt repayment, capital reinvestment activities, funding our ARO liability, or other commitments and uncertainties which are necessary to sustain our dividend over the long term. AFFO should not be considered as an alternative to net income (loss) (computed in accordance with GAAP), as an indicator of our financial performance, or as an alternative to cash flow from operating activities (computed in accordance with GAAP), as an indicator of our liquidity, or as an indicator of funds available for our cash needs, including our ability to make distributions or service our indebtedness.
For completeness, the following table sets forth a reconciliation of our net income (loss) as determined in accordance with GAAP and our calculations of NAREIT FFO, FFO Adjusted for Securities Investments, and AFFO for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017. AFFO is a supplemental, non-GAAP financial measure which we define as FFO Adjusted for Securities Investment plus (gain) loss on extinguishment of debt, provision for loan (gain) loss, net of tax, transaction costs, amortization of debt issuance costs, amortization of deferred lease costs, accretion of asset retirement obligation, amortization of above market leases, income tax expense (benefit) unrelated to securities investments, non-cash costs associated with derivative instruments, (gain) loss on the settlement of ARO, and certain costs of a nonrecurring nature, less maintenance, capital expenditures (if any), amortization of debt premium, and other adjustments as deemed appropriate by Management. Also presented is information regarding the weighted-average number of shares of our common stock outstanding used for the computation of per share data:
51
NAREIT FFO, FFO Adjusted for Securities Investment, and AFFO Reconciliation | |||||||||||
For the Years Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2019 | 2018 | 2017 | |||||||||
Net Income attributable to CorEnergy Stockholders | $ | 4,079,495 | $ | 43,711,876 | $ | 32,602,790 | |||||
Less: | |||||||||||
Preferred Dividend Requirements | 9,255,468 | 9,548,377 | 7,953,988 | ||||||||
Net Income (Loss) attributable to Common Stockholders | $ | (5,175,973 | ) | $ | 34,163,499 | $ | 24,648,802 | ||||
Add: | |||||||||||
Depreciation | 22,046,041 | 24,355,959 | 23,292,713 | ||||||||
Less: | |||||||||||
Gain on the sale of leased property, net | — | 11,723,257 | — | ||||||||
Non-Controlling Interest attributable to NAREIT FFO reconciling items | — | — | 1,632,546 | ||||||||
NAREIT funds from operations (NAREIT FFO) | $ | 16,870,068 | $ | 46,796,201 | $ | 46,308,969 | |||||
Add: | |||||||||||
Distributions received from investment securities | 1,328,853 | 106,795 | 949,646 | ||||||||
Income tax expense (benefit) from investment securities | (12,584 | ) | (682,199 | ) | 1,000,084 | ||||||
Less: | |||||||||||
Net distributions and other income | 1,328,853 | 106,795 | 680,091 | ||||||||
Net realized and unrealized gain (loss) on other equity securities | — | (1,845,309 | ) | 1,531,827 | |||||||
Funds from operations adjusted for securities investments (FFO) | $ | 16,857,484 | $ | 47,959,311 | $ | 46,046,781 | |||||
Add: | |||||||||||
Loss of extinguishment of debt | 33,960,565 | — | 336,933 | ||||||||
Transaction costs | 185,495 | 521,311 | 592,068 | ||||||||
Amortization of debt issuance costs | 1,226,139 | 1,414,457 | 1,661,181 | ||||||||
Amortization of deferred lease costs | 91,932 | 91,932 | 91,932 | ||||||||
Accretion of asset retirement obligation | 443,969 | 499,562 | 663,065 | ||||||||
Non-cash loss associated with derivative instruments | — | — | 33,763 | ||||||||
Loss on settlement of ARO | — | 310,941 | — | ||||||||
Less: | |||||||||||
Non-cash settlement of accounts payable | — | — | 221,609 | ||||||||
Income tax (expense) benefit | (247,202 | ) | 1,736,527 | (1,345,234 | ) | ||||||
Provision for loan gain | — | 36,867 | — | ||||||||
Non-Controlling Interest attributable to AFFO reconciling items | — | — | 13,154 | ||||||||
Adjusted funds from operations (AFFO) | $ | 53,012,786 | $ | 49,024,120 | $ | 50,536,194 | |||||
Weighted Average Shares of Common Stock Outstanding: | |||||||||||
Basic | 13,041,613 | 11,935,021 | 11,900,516 | ||||||||
Diluted | 15,425,747 | 15,389,180 | 15,355,061 | ||||||||
NAREIT FFO attributable to Common Stockholders | |||||||||||
Basic | $ | 1.29 | $ | 3.92 | $ | 3.89 | |||||
Diluted (1) | $ | 1.29 | $ | 3.61 | $ | 3.59 | |||||
FFO attributable to Common Stockholders | |||||||||||
Basic | $ | 1.29 | $ | 4.02 | $ | 3.87 | |||||
Diluted (1) | $ | 1.29 | $ | 3.69 | $ | 3.57 | |||||
AFFO attributable to Common Stockholders | |||||||||||
Basic | $ | 4.06 | $ | 4.11 | $ | 4.25 | |||||
Diluted (2) | $ | 3.83 | $ | 3.70 | $ | 3.81 | |||||
(1) The year ended December 31, 2019 diluted per share calculations exclude dilutive adjustments for convertible note interest expense, discount amortization and deferred debt issuance amortization because such impact is antidilutive. The years ended December 31, 2018 and 2017 include these dilutive adjustments. For periods presented without per share dilution, the number of weighted average diluted shares is equal to the number of weighted average basic shares presented. Refer to the Convertible Note Interest Expense table in Part IV, Item 15, Note 11 ("Debt") for additional details. | |||||||||||
(2) Diluted per share calculations include a dilutive adjustment for convertible note interest expense. Refer to the Convertible Note Interest Expense table in Part IV, Item 15, Note 11 ("Debt") for additional details. | |||||||||||
52
NAREIT FFO, FFO Adjusted for Securities Investment, and AFFO Reconciliation | |||||||||||||||
For the Fiscal 2019 Quarters Ended | |||||||||||||||
March 31 | June 30 | September 30 | December 31 | ||||||||||||
Net Income (Loss) attributable to CorEnergy Stockholders | $ | 3,866,441 | $ | 9,824,926 | $ | (19,419,600 | ) | $ | 9,807,728 | ||||||
Less: | |||||||||||||||
Preferred Dividend Requirements | 2,314,128 | 2,313,780 | 2,313,780 | 2,313,780 | |||||||||||
Net Income (Loss) attributable to Common Stockholders | $ | 1,552,313 | $ | 7,511,146 | $ | (21,733,380 | ) | $ | 7,493,948 | ||||||
Add: | |||||||||||||||
Depreciation | 5,511,121 | 5,511,274 | 5,511,367 | 5,512,279 | |||||||||||
NAREIT funds from operations (NAREIT FFO) | $ | 7,063,434 | $ | 13,022,420 | $ | (16,222,013 | ) | $ | 13,006,227 | ||||||
Add: | |||||||||||||||
Distributions received from investment securities | 256,615 | 285,259 | 360,182 | 426,797 | |||||||||||
Income tax expense (benefit) from investment securities | 151,793 | 6,912 | 45,205 | (216,494 | ) | ||||||||||
Less: | |||||||||||||||
Net distributions and other income | 256,615 | 285,259 | 360,182 | 426,797 | |||||||||||
Funds from operations adjusted for securities investments (FFO) | $ | 7,215,227 | $ | 13,029,332 | $ | (16,176,808 | ) | $ | 12,789,733 | ||||||
Add: | |||||||||||||||
Loss of extinguishment of debt | 5,039,731 | — | 28,920,834 | — | |||||||||||
Transaction costs | 53,970 | 88,611 | 14,799 | 28,115 | |||||||||||
Amortization of debt issuance costs | 298,432 | 281,630 | 313,022 | 333,055 | |||||||||||
Amortization of deferred lease costs | 22,983 | 22,983 | 22,983 | 22,983 | |||||||||||
Accretion of asset retirement obligation | 110,992 | 110,993 | 110,992 | 110,992 | |||||||||||
Less: | |||||||||||||||
Income tax (expense) benefit | (295,542 | ) | (55,787 | ) | 137,911 | (33,784 | ) | ||||||||
Adjusted funds from operations (AFFO) | $ | 13,036,877 | $ | 13,589,336 | $ | 13,067,911 | $ | 13,318,662 | |||||||
Weighted Average Shares of Common Stock Outstanding: | |||||||||||||||
Basic | 12,604,943 | 12,811,171 | 13,188,546 | 13,549,797 | |||||||||||
Diluted | 15,042,567 | 14,934,886 | 15,609,545 | 16,102,310 | |||||||||||
NAREIT FFO attributable to Common Stockholders | |||||||||||||||
Basic | $ | 0.56 | $ | 1.02 | $ | (1.23 | ) | $ | 0.96 | ||||||
Diluted (1) | $ | 0.56 | $ | 0.96 | $ | (1.23 | ) | $ | 0.93 | ||||||
FFO attributable to Common Stockholders | |||||||||||||||
Basic | $ | 0.57 | $ | 1.02 | $ | (1.23 | ) | $ | 0.94 | ||||||
Diluted (1) | $ | 0.57 | $ | 0.96 | $ | (1.23 | ) | $ | 0.92 | ||||||
AFFO attributable to Common Stockholders | |||||||||||||||
Basic | $ | 1.03 | $ | 1.06 | $ | 0.99 | $ | 0.98 | |||||||
Diluted (2) | $ | 0.96 | $ | 0.99 | $ | 0.94 | $ | 0.94 | |||||||
(1) The fiscal 2019 quarters ended for March 31 and September 30 diluted per share calculations exclude dilutive adjustments for convertible note interest expense, discount amortization and deferred debt issuance amortization because such impact is antidilutive. The fiscal 2019 quarters ended June 30 and December 31 include these dilutive adjustments. For periods presented without per share dilution, the number of weighted average diluted shares is equal to the number of weighted average basic shares presented. | |||||||||||||||
(2) Diluted per share calculations include a dilutive adjustment for convertible note interest expense. | |||||||||||||||
53
DIVIDENDS
Our portfolio of real property assets and promissory notes generates cash flow from which we pay distributions to stockholders. For the year ended December 31, 2019, the primary sources of our stockholder distributions include lease revenue and transportation and distribution revenue from our real property assets. Deterioration in the cash flows generated by any of these sources may impact our ability to fund distributions to stockholders. Based on our current asset base, we target a ratio of AFFO to dividends of 1.5 times. We believe that this level of coverage provides a prudent reserve level to achieve dividend stability and growth over the long term. For the year ended December 31, 2019, our ratio of AFFO to dividends is 1.35 times, which is below our target ratio.
To maintain AFFO coverage in 2020, we believe that a number of actions can be taken to adequately offset the lost revenue from the sale of the Portland Terminal, which include deleveraging of our balance sheet through preferred equity and debt repurchases, at attractive market prices. However, in the current market, we believe it is prudent to hold the net cash proceeds from the 5.875% Convertible Note Offering to utilize in additional investments in revenue generating assets. We regularly assess our ability to pay and to grow our dividend to common stockholders, and there is no assurance that we will continue to make regular dividend payments at current levels.
Distributions to common stockholders are recorded on the ex-dividend date and distributions to preferred stockholders are recorded when declared by the Board of Directors. The characterization of any distribution for federal income tax purposes will not be determined until after the end of the taxable year. Refer to Part IV, Item 15, Note 6 ("Income Taxes") included in this Report for information on characterization of distributions for federal income tax purposes for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017.
A REIT is generally required to distribute during the taxable year an amount equal to at least 90 percent of the REIT taxable income (determined under Internal Revenue Code section 857(b)(2), without regard to the deduction for dividends paid). We intend to adhere to this requirement in order to maintain our REIT status. The Board of Directors will continue to determine the amount of any distribution that we expect to pay our stockholders. Dividend payouts may be affected by cash flow requirements and remain subject to other risks and uncertainties.
The following table sets forth common stock distributions for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017. Distributions are shown in the period in which they were declared.
Common Dividends | |||
Amount | |||
2019 | |||
Fourth Quarter | $ | 0.7500 | |
Third Quarter | 0.7500 | ||
Second Quarter | 0.7500 | ||
First Quarter | 0.7500 | ||
2018 | |||
Fourth Quarter | $ | 0.7500 | |
Third Quarter | 0.7500 | ||
Second Quarter | 0.7500 | ||
First Quarter | 0.7500 | ||
2017 | |||
Fourth Quarter | $ | 0.7500 | |
Third Quarter | 0.7500 | ||
Second Quarter | 0.7500 | ||
First Quarter | 0.7500 | ||
54
The following table sets forth preferred stock distributions for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017:
Preferred Dividends | |||
Amount | |||
2019 | |||
Fourth Quarter | $ | 0.4609 | |
Third Quarter | 0.4609 | ||
Second Quarter | 0.4609 | ||
First Quarter | 0.4609 | ||
2018 | |||
Fourth Quarter | $ | 0.4609 | |
Third Quarter | 0.4609 | ||
Second Quarter | 0.4609 | ||
First Quarter | 0.4609 | ||
2017 | |||
Fourth Quarter | $ | 0.4609 | |
Third Quarter | 0.4609 | ||
Second Quarter | 0.4609 | ||
First Quarter | 0.4609 | ||
On February 28, 2020, we will pay fourth quarter dividends of $0.75 per share of common stock and $0.4609375 per depositary share for our 7.375% Series A Cumulative Redeemable Preferred Stock.
FEDERAL AND STATE INCOME TAXATION
In 2013 we qualified, and in March 2014 elected (effective as of January 1, 2013), to be treated as a REIT for federal income tax purposes (which we refer to as the "REIT Election"). Because certain of our assets may not produce REIT-qualifying income or be treated as interests in real property, those assets are held in wholly-owned TRSs in order to limit the potential that such assets and income could prevent us from qualifying as a REIT.
We elected to be taxed as a REIT for 2013 and subsequent years and generally will not pay federal income tax on taxable income of the REIT that is distributed to our stockholders. As a REIT, our distributions from earnings and profits will be treated as ordinary income and a return of capital, and generally will not qualify as qualified dividend income ("QDI"). To the extent that the REIT had accumulated C corporation earnings and profits from the periods prior to 2013, we distributed such earnings and profits in 2013. In addition, to the extent we receive taxable distributions from our TRSs, or the REIT received distributions of C corporation earnings and profits, such portion of our distribution is generally treated as QDI. While regular REIT dividends are not eligible for the reduced QDI tax rates, with respect to taxable years beginning after December 31, 2017 and before January 1, 2026, Section 199A of the Code typically permits a 20 percent deduction against taxable income for noncorporate taxpayers for qualified business income, which includes dividends from a REIT received during the tax year that is not a capital gain dividend or a dividend qualifying for the QDI rate, subject to certain income and holding period limitations.
As a REIT, we hold and operate certain of our assets through one or more wholly-owned TRSs. Our use of TRSs enables us to continue to engage in certain businesses while complying with REIT qualification requirements and also allows us to retain income generated by these businesses for reinvestment without the requirement of distributing those earnings. As was done with our subsidiary Omega in 2017, and as warranted in the future, we may elect to reorganize and transfer certain assets or operations from our TRSs to our C corporation or other subsidiaries, including qualified REIT subsidiaries.
Our other equity securities are limited partnerships or limited liability companies which are treated as partnerships for federal and state income tax purposes. As a limited partner, we report our allocable share of taxable income in computing our taxable income. To the extent held by a TRS, the TRS's tax expense or benefit is included in the Consolidated Statements of Income based on the component of income or gains and losses to which such expense or benefit relates. Deferred income taxes reflect the net tax effects of temporary differences between the carrying amounts of assets and liabilities for financial reporting purposes and the amounts used for income tax purposes. A valuation allowance is recognized if, based on the weight of available evidence, it is more likely than not that some portion or all of the deferred income tax asset will not be realized.
If we cease to qualify as a REIT, we, as a C corporation, would be obligated to pay federal and state income tax on our taxable income. For 2019, the federal income tax rate for a corporation was 21 percent.
55
The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (the "2017 Tax Act") was enacted on December 22, 2017. The 2017 Tax Act reduced the US federal corporate tax rate from 35 percent to 21 percent. The 2017 Tax Act also repealed the alternative minimum tax for corporations. We completed our accounting for the tax effects of enactment of the 2017 Tax Act in 2018. We remeasured deferred tax assets and liabilities based on the updated rates at which they are expected to reverse in the future, which resulted in a $1.3 million transition adjustment that reduced net deferred tax assets. We will continue to assess the impact of new tax legislation, as well as any future regulations and updates provided by the tax authorities. Refer to Part IV, Item 15, Note 6 ("Income Taxes") for additional information.
MAJOR TENANTS
As of December 31, 2019, we had two significant leases. For additional information concerning these leases, see Part I, Item 2, "Properties" and Part IV, Item 15, Note 3 ("Leased Properties And Leases") included in this Report. The table below displays the impact of significant leases on total leased properties and total lease revenues for the periods presented.
As a Percentage of (1) | ||||||||||||||
Leased Properties | Lease Revenues | |||||||||||||
As of December 31, | For the Years Ended December 31, | |||||||||||||
2019 | 2018 | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | ||||||||||
Pinedale LGS (2) | 44.4 | % | 44.5 | % | 39.2 | % | 35.2 | % | 31.2 | % | ||||
Grand Isle Gathering System | 55.3 | % | 55.2 | % | 60.6 | % | 55.9 | % | 59.1 | % | ||||
Portland Terminal Facility (3) | — | % | — | % | — | % | 8.8 | % | 9.6 | % | ||||
(1) Insignificant leases are not presented; thus percentages may not sum to 100%. | ||||||||||||||
(2) Pinedale LGS lease revenues include variable rent of $4.6 million, $4.3 million and $587 thousand for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, respectively. | ||||||||||||||
(3) On December 21, 2018, the Portland Terminal Facility was sold to Zenith Terminals, terminating the Portland Lease Agreement. | ||||||||||||||
ASSET PORTFOLIO AND RELATED DEVELOPMENTS
Descriptions of our asset portfolio and related operations, are included in Part I, Item 2, "Properties" and in Part IV, Item 15, Note 3 ("Leased Properties And Leases") and Note 5 ("Financing Notes Receivable") included in this Report. This section provides additional information concerning material developments related to our asset portfolio during the year ended December 31, 2019 and through the date of this Report.
Grand Isle Gathering System
On October 18, 2018, EGC was acquired by an affiliate of the privately-held Gulf of Mexico operator, Cox Oil, for approximately $322.0 million. With the purchase of EGC by Cox Oil, it is anticipated that EGC will remain a separate subsidiary owned by an affiliate of Cox Oil and that EGC (not Cox Oil) will continue to be the guarantor of the tenant's obligation under the Lease Agreement. To date, EGC has met its obligations to make lease payments. We are currently engaged in efforts to enforce the reporting requirements in the lease. For additional information, refer to Part I, Item 3, Legal Proceedings and Part IV, Item 15, Note 3 ("Leased Properties And Leases").
Pinedale LGS
Effective August 8, 2019, UPL's common stock was delisted from the NASDAQ Global Select Market and commenced trading on the OTCQX marketplace under the symbol "UPLC." UPL plans to continue to make all required SEC filings, including those on Forms 10-K, 10-Q and 8-K, and will remain subject to all SEC rules and regulations applicable to reporting companies under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934.
On September 16, 2019, UPL announced that it entered into an amended credit facility to remove financial maintenance covenants among other provisional changes, while also announcing plans to suspend its drilling program by the end of September while natural gas pricing remains near multi-year lows. In connection with the approved credit facility amendment, UPL also announced a fall borrowing base redetermination of $1.175 billion, including $200 million of the commitment allocated to the credit facility. The amended credit facility also established maximum capital expenditures of $65 million, $10 million and $5 million, respectively, for the quarters ended September 30, 2019, December 31, 2019 and quarterly thereafter.
On November 7, 2019, UPL updated full-year 2019 capital investment guidance to a range of $240 million to $250 million. UPL also announced expected 2020 production to be between 182 and 192 Bcfe, which assumes suspended drilling and the maximum capital expenditures outlined above. UPL also stated it continues proactive efforts to reduce debt and affirms its ongoing advisor engagements that are focused on liability management and assisting management and its board of directors in evaluating a range of strategic alternatives.
56
On February 18, 2020, UPL announced a spring borrowing base redetermination, effective April 1, 2020, which will reduce the borrowing base to $1.075 billion, with $100 million of the commitment attributed to its credit facility. Additionally, UPL announced full-year 2019 production of 240.2 Bcfe.
MoGas Pipeline
Effective March 1, 2017, MoGas entered into a long-term firm transportation services agreement with Spire, its largest customer. The agreement extends the termination date for Spire's existing firm transportation agreement to October 31, 2030. During the entire extended term, Spire will continue to reserve 62,800 dekatherms per day of firm transportation capacity on MoGas. This service continued at the full tariff rate of $12.385 per dekatherm per month until October 31, 2018, at which time the rate was reduced to $6.386 per dekatherm per month for the remainder of the agreement.
On May 31, 2018, MoGas filed a general rate case before FERC. The proposed change in rates sought to (i) recover increases in capital, operating and maintenance expenditures incurred; (ii) mitigate for the substantial decrease in volumes due to the loss of a firm transportation contract with a St. Louis natural gas marketing entity; (iii) mitigate for the substantial decrease in revenue from Spire; and (iv) reflect changes in the corporate income tax rate associated with the 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act. The proposed rates went into effect on December 1, 2018. On August 22, 2019, the FERC approved a settlement agreed to by MoGas and all intervenors in the rate case to provide annual rates of approximately $14.8 million, effective September 1, 2019. As a result of the approved and effective settlement, MoGas has begun to refund the difference between the filed rates and the settlement rates. In conjunction with the settlement, MoGas entered into 5-year firm transportation service agreements with its customers in exchange for modest discounts. The agreements, which amend prior year-to-year agreements, extend the termination date for the existing firm transportation service agreements to December 31, 2023.
CONTRACTUAL OBLIGATIONS
The following table summarizes our significant contractual payment obligations as of December 31, 2019:
Contractual Obligations | |||||||||||||||||||
Notional Value | Less than 1 year | 1-3 years | 3-5 years | More than 5 years | |||||||||||||||
Pinedale LP Debt | $ | 33,944,000 | $ | 3,528,000 | $ | 30,416,000 | $ | — | $ | — | |||||||||
Interest payments on Pinedale LP Debt | 2,107,331 | 3,607,076 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
7.00% Convertible Debt(1) | 2,092,000 | 2,092,000 | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||
Interest payments on 7.00% Convertible Debt(1) | 73,220 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
5.875% Convertible Debt | 120,000,000 | — | — | — | 120,000,000 | ||||||||||||||
Interest payments on 5.875% Convertible Debt | 7,108,750 | 14,100,000 | 14,100,000 | 7,050,000 | |||||||||||||||
Totals | $ | 14,909,301 | $ | 48,123,076 | $ | 14,100,000 | $ | 127,050,000 | |||||||||||
(1) Subsequent to December 31, 2019, holders of the 7.00% Convertible Notes converted $416 thousand face amount of notes for 12,605 shares of common stock, reducing (i) the 7.00% Convertible Notes outstanding to $1.7 million and (ii) interest expense to $59 thousand in 2020. | |||||||||||||||||||
Fees paid to Corridor under the Management Agreement and the Administrative Agreement are not included because they vary as a function of the value of our total asset base. For additional information see Part IV, Item 15, Note 9 ("Management Agreement") included in this Report.
SEASONALITY
Our operating companies, MoGas and Omega, have stable revenues throughout the year and will complete necessary pipeline maintenance during the "non-heating" season, or quarters two and three. Therefore, operating results for the interim periods are not necessarily indicative of the results that may be expected for the full year.
OFF-BALANCE SHEET ARRANGEMENTS
We do not have, and are not expected to have, any off-balance sheet arrangements that have or are reasonably likely to have a current or future effect on our financial condition, changes in financial condition, revenues or expenses, results of operations, liquidity, capital expenditures or capital resources.
IMPACT OF INFLATION AND DEFLATION
Deflation can result in a decline in general price levels, often caused by a decrease in the supply of money or credit. The predominant effects of deflation are high unemployment, credit contraction, and weakened consumer demand. Restricted lending practices could impact our ability to obtain financings or to refinance our properties and our tenants' ability to obtain credit. During inflationary
57
periods, we intend for substantially all of our tenant leases to be designed to mitigate the impact of inflation. Often, our leases include rent escalators that are based on the CPI, or other agreed upon metrics that increase with inflation.
LIQUIDITY AND CAPITAL RESOURCES
Overview
At December 31, 2019, we had liquidity of approximately $257.3 million comprised of cash of $120.9 million plus revolver availability of $136.4 million. During 2019, our liquidity was enhanced by the net proceeds from the 5.875% Convertible Note offering, partially offset by cash utilized to complete two exchanges of the 7.00% Convertible Notes. The results of the MoGas rate case settlement discussed in the "Asset Portfolio and Related Developments" section above had a positive impact on revolver availability at the end of 2019 and going forward.
We use cash flows generated from our operations to fund current obligations, projected working capital requirements, debt service payments and dividend payments. Management expects that future operating cash flows, along with access to financial markets, will be sufficient to fund future operating requirements and acquisition opportunities. If our ability to access the capital markets is restricted, as currently is the case as discussed in Part IV, Item 15, Note 13 ("Stockholders' Equity") or if debt or equity capital were unavailable on favorable terms, or at all, our ability to fund acquisition opportunities or to comply with the REIT distribution rules could be adversely affected.
There are acquisition opportunities that are in preliminary stages of review, and consummation of any of these opportunities may depend on a number of factors beyond our control. There can be no assurance that any of these acquisition opportunities will result in consummated transactions. As part of our disciplined investment philosophy, we plan to use a moderate level of leverage, approximately 25 percent to 50 percent of assets, supplemented with accretive equity issuance as needed, subject to current market conditions. We may invest in assets subject to greater leverage which could be both recourse and non-recourse to us.
Cash Flows - Operating, Investing, and Financing Activities
The following table presents our consolidated cash flows for the periods indicated below:
For the Years Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2019 | 2018 | 2017 | |||||||||
Net cash provided by (used in): | |||||||||||
Operating activities | $ | 61,779,104 | $ | 48,622,740 | $ | 56,791,571 | |||||
Investing activities | 4,699,066 | 56,816,490 | 7,595,477 | ||||||||
Financing activities | (14,901,704 | ) | (51,939,122 | ) | (56,495,063 | ) | |||||
Net increase in cash and cash equivalents | $ | 51,576,466 | $ | 53,500,108 | $ | 7,891,985 | |||||
Cash Flows from Operating Activities
Net cash flows provided by operating activities for the year ended December 31, 2019 were primarily generated by (i) lease receipts of $63.2 million ($67.1 million lease revenue, net of $3.9 million of straight-line rent accrued during the period) and (ii) $17.1 million in net contributions from our operating subsidiaries MoGas and Omega, partially offset by (iii) $10.6 million in general and administrative expenses and (iv) $6.8 million in cash paid for interest.
Net cash flows provided by operating activities for the year ended December 31, 2018 were primarily generated by (i) lease receipts of $62.3 million ($72.7 million lease revenue, net of $7.0 million of straight-line rent accrued during the period and $3.4 million of unearned revenue received in 2017) and (ii) $12.5 million in net contributions from our operating subsidiaries MoGas and Omega, partially offset by (iii) $13.0 million in general and administrative expenses, (iv) $11.2 million in cash paid for interest and (v) a $1.3 million increase in accounts and other receivables during the period.
Net cash flows provided by operating activities for the year ended December 31, 2017 were primarily generated by (i) lease receipts of $61.6 million ($68.8 million lease revenue, net of $7.2 million of straight-line rent accrued during the period), (ii) $13.2 million in net contributions from our operating subsidiaries MoGas and Omega, (iii) an additional $2.9 million in unearned lease receipts associated with January 2018 revenues received in 2017 and (iv) $853 thousand in distributions and dividends received, partially offset by (v) $10.8 million in general and administrative expenses and (vi) $10.8 million in cash paid for interest.
Cash Flows from Investing Activities
Net cash flows provided by investing activities for the year ended December 31, 2019 were primarily attributed to a $5.0 million payment received on January 7, 2019 related to the promissory note entered into as part of the Portland Terminal Facility sale.
58
Net cash flows provided by investing activities for the year ended December 31, 2018 were primarily attributed to (i) the proceeds from the sale of the Portland Terminal Facility and equity interest in Joliet to Zenith Terminals, which generated proceeds of approximately $56.0 million, (ii) return of capital distributions on our Lightfoot investment of $664 thousand and (iii) principal payments associated with the Four Wood financing note receivable of $237 thousand.
Net cash flows provided by investing activities for the year ended December 31, 2017 were primarily attributed to $7.6 million in proceeds received from the sale of the majority of our equity securities. Refer to Part IV, Item 15, Note 10 ("Fair Value") for additional details.
Cash Flows from Financing Activities
Net cash flows used in financing activities for the year ended December 31, 2019 were primarily attributable to (i) cash paid for the extinguishment of the 7.00% Convertible Notes of $78.9 million, (ii) common and preferred dividends paid of $39.1 million and $9.3 million, respectively and (iii) principal payments of $3.5 million on our secured credit facilities, partially offset by (iv) net proceeds from the 5.875% Convertible Notes offering of $116.4 million.
Net cash flows used in financing activities for the year ended December 31, 2018 were primarily attributable to (i) common and preferred dividends paid of $34.3 million and $9.6 million, respectively, (ii) cash used to repurchase Series A Preferred Stock of $4.3 million, (iii) principal payments of $3.5 million on our secured credit facilities and (iv) $264 thousand of payments related to debt financing costs.
Net cash flows used in financing activities for the year ended December 31, 2017 were primarily attributable to (i) net payments on the CorEnergy Revolver of $44.0 million, (ii) principal payments of $45.6 million on our secured credit facilities, (iii) common and preferred dividends paid of $34.7 million and $8.2 million, respectively, (iv) purchase of the non-controlling interest in Pinedale LP for $32.8 million, (v) payment of $1.5 million for debt issuance costs related to the CorEnergy Credit Facility and Amended Pinedale Term Credit Facility refinancings and (vi) distributions of $1.8 million to our non-controlling interest, partially offset by (vii) net offering proceeds on Series A Preferred Stock of $71.2 million and (viii) $41.0 million in proceeds from the Amended Pinedale Term Credit Facility.
Revolving and Term Credit Facilities
CorEnergy Credit Facility
Prior to 2017, we had a credit facility with Regions Bank (as lender and administrative agent for the other participating lenders) providing borrowing capacity of $153.0 million, consisting of (i) the CorEnergy Revolver of $105.0 million, (ii) the CorEnergy Term Loan of $45.0 million and (iii) the MoGas Revolver of $3.0 million.
On July 28, 2017, we entered into an amended and restated CorEnergy Credit Facility with Regions Bank (as lender and administrative agent for other participating lenders). The amended facility provides for commitments of up to $161.0 million, comprised of (i) increased commitments on the CorEnergy Revolver of up to $160.0 million, subject to borrowing base limitations, and (ii) a $1.0 million commitment on the MoGas Revolver.
The amended facility has a 5-year term maturing on July 28, 2022, and provided for a springing maturity on February 28, 2020, and thereafter, if we failed to meet certain liquidity requirements from the springing maturity date through the maturity of our 7.00% Convertible Notes on June 15, 2020. This springing maturity would have been triggered on the first date on or after February 28, 2020 that both (i) the outstanding principal amount of the 7.00% Convertible Notes exceeded $28,750,000 and (ii) our unrestricted cash liquidity (including, for purposes of this calculation, the undrawn portion of the Borrowing Base then available for borrowing under the CorEnergy Credit Facility) was less than the sum of (x) the outstanding principal amount of the 7.00% Convertible Notes plus (y) $5,000,000. We will not trigger the springing maturity as a result of the 7.00% Convertible Note exchange completed in August of 2019, which reduced the outstanding principal balance of the 7.00% Convertible Notes below the springing maturity threshold. Refer to Part IV, Item 15, Note 11 ("Debt") included in this Report for further details on convertible debt transactions.
Under the terms of the amended and restated CorEnergy Credit Facility, we are subject to certain financial covenants as follows: (i) a minimum debt service coverage ratio of 2.0 to 1.0; (ii) a maximum total leverage ratio of 5.0 to 1.0; (iii) a maximum senior secured recourse leverage ratio (which generally excludes debt from certain subsidiaries that are not obligors under the CorEnergy Credit Facility) of 3.0 to 1.0.; and (iv) a maximum total funded debt to capitalization ratio of 50 percent. In addition, there is a covenant related to our ability to make distributions that is tied to AFFO and applicable REIT distribution requirements, and provides that, in the absence of any acceleration of maturity following an Event of Default, we may make distributions equal to the greater of the amount required to maintain our REIT status and 100 percent of AFFO for the trailing 12-month period.
59
Borrowings under the credit facility will typically bear interest on the outstanding principal amount using a LIBOR pricing grid that is expected to equal a LIBOR rate plus an applicable margin of 2.75 percent to 3.75 percent, based on our senior secured recourse leverage ratio. The facility contains, among other restrictions, certain default and cross-default provisions customary for transactions of this nature (with applicable customary grace periods), all of which are substantially the same as under the prior facility.
We were in compliance with all covenants at December 31, 2019 and had approximately $136.4 million of available borrowing capacity on the CorEnergy Revolver. For a summary of the additional material terms of the CorEnergy Credit Facility, please see Part IV, Item 15, Note 11 ("Debt") included in this Report.
Amended Pinedale Term Credit Facility
In December 2012, Pinedale LP entered into a $70.0 million secured term credit facility with a lender that provided for monthly payments of principal and interest and was secured by the Pinedale LGS. The credit facility accrued interest at a variable annual rate linked to LIBOR.
On March 30, 2016, we and Prudential (collectively, "the Refinancing Lenders"), refinanced the remaining $58.5 million principal balance of the $70.0 million credit facility (on a pro rata basis equal to the respective equity interests in Pinedale LP, with our 81.05 percent share being approximately $47.4 million) and executed a series of agreements assigning the credit facility to the Refinancing Lenders, with CorEnergy Infrastructure Trust, Inc. as Agent for the Refinancing Lenders. Our portion of the debt and interest was eliminated in consolidation and Prudential's portion of the debt was shown as a related-party liability.
On December 29, 2017, Pinedale LP entered into the Amended Pinedale Term Credit Facility, with Prudential and a group of lenders affiliated with Prudential as lenders and Prudential serving as administrative agent. The new amended facility is a 5-year $41.0 million term loan facility, bearing interest at a fixed rate of 6.5 percent, which matures on December 29, 2022. Principal payments of $294 thousand, plus accrued interest, are payable monthly. Proceeds from the Amended Pinedale Term Credit Facility were utilized by Pinedale LP to pay off the balance due to the Refinancing Lenders under the previously existing Pinedale LP credit facility. We utilized our portion of the proceeds from the repayment of the prior facility to finance the purchase of Prudential's 18.95 percent outstanding equity interest in Pinedale LP.
The Amended Pinedale Term Credit Facility limits distributions by Pinedale LP to us, although such distributions are permitted to the extent required for us to maintain REIT qualification so long as Pinedale LP's obligations under the credit facility have not been accelerated following an Event of Default (as defined in the Amended Term Credit Facility).
Outstanding balances under the facility are secured by the Pinedale LGS assets. The Amended Term Credit Facility is subject to (i) a minimum interest coverage ratio of 3.0 to 1.0, (ii) a maximum leverage ratio of 3.25 to 1.0 and (iii) a minimum net worth of $115.0 million, each measured at the Pinedale LP level and not at the Company level. We were in compliance with all covenants at December 31, 2019. For a summary of the additional material terms of the Pinedale Credit Facility, please see Part IV, Item 15, Note 11 ("Debt") included in this Report for additional information.
MoGas Revolver
In conjunction with the MoGas Transaction, MoGas Pipeline LLC and United Property Systems, LLC, as co-borrowers, entered into a revolving credit agreement dated November 24, 2014 (the "MoGas Revolver"), with certain lenders, including Regions Bank as agent for such lenders. Following subsequent amendments and restatements made on July 8, 2015 and July 28, 2017 in connection with the amendments and restatements of the CorEnergy Credit Facility, discussed above, commitments under the MoGas Revolver were reduced from the original level of $3.0 million to a current total of $1.0 million. Interest accrues under the MoGas Revolver at the same rate and pursuant to the same terms as it accrues under the CorEnergy Revolver. Refer to Part IV, Item 15, Note 11 ("Debt") for further information. As of December 31, 2019, the co-borrowers were in compliance with all covenants and there were no borrowings outstanding on the MoGas Revolver.
Mowood/Omega Revolver
On July 31, 2015, a $1.5 million revolving line of credit ("Mowood/Omega Revolver") was established with Regions Bank with a maturity date of July 31, 2016. Following annual extensions, the current maturity of the facility has been amended and extended to July 31, 2020. The Mowood/Omega Revolver is used by Omega for working capital and general business purposes and is guaranteed and secured by the assets of Omega. Interest accrues at LIBOR plus 4 percent and is payable monthly in arrears with no unused fee. There was no outstanding balance at December 31, 2019.
60
Convertible Notes
7.00% Convertible Notes
On June 29, 2015, we completed a public offering of $115.0 million aggregate principal amount of 7.00% Convertible Senior Notes Due 2020. The Convertible Notes mature on June 15, 2020 and bear interest at a rate of 7.0 percent per annum, payable semi-annually in arrears on June 15 and December 15 of each year, beginning on December 15, 2015.
As authorized by our Board of Directors, during May 2016, we repurchased $1.0 million of face value of 7.00% Convertible Notes. During the year ended December 31, 2018, certain holders elected to convert $42 thousand of 7.00% Convertible Notes for 1,271 shares of our common stock.
On January 16, 2019, we agreed with three holders of our 7.00% Convertible Notes, pursuant to privately negotiated agreements, to exchange $43.8 million face amount of such notes for an aggregate of 837,040 shares of our common stock, par value $0.001 per share, plus aggregate cash consideration of $19.8 million, including $315 thousand of interest expense. Our agent and lenders under the CorEnergy Credit Facility provided a consent for the convertible note exchange. We recorded a loss on extinguishment of debt of approximately $5.0 million in the Consolidated Statements of Income for the first quarter of 2019. The loss on extinguishment of debt included the write-off of a portion of the underwriter's discount and deferred debt costs of $409 thousand and $27 thousand, respectively.
On August 15, 2019, we used a portion of the net proceeds from the offering of the 5.875% Convertible Notes discussed further below, together with shares of our common stock, to exchange $63.9 million face amount of its 7.00% Convertible Notes pursuant to privately negotiated agreements with three holders. The total cash and stock consideration for the exchange was valued at approximately $93.2 million. This included an aggregate of 703,432 shares of common stock plus cash consideration of approximately $60.2 million, including $733 thousand of interest expense. We recorded a loss on extinguishment of debt of approximately $28.9 million in the Consolidated Statements of Income for the third quarter of 2019. The loss on extinguishment of debt included the write-off of a portion of the underwriter's discount and deferred debt costs of $360 thousand and $24 thousand, respectively. Collectively, for the two exchange transactions described above, we recorded a loss on extinguishment of debt of $34.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2019.
Additionally, during the year ended December 31, 2019, certain holders elected to convert $4.2 million of 7.00% Convertible Notes for approximately 127,143 shares of common stock, respectively. As of December 31, 2019, the Company has $2.1 million aggregate principal amount of 7.00% Convertible Notes outstanding.
At the present time, we may not redeem the remaining 7.00% Convertible Notes prior to the maturity date without the consent of the agent and lenders of the CorEnergy Credit Facility. Holders may convert their 7.00% Convertible Notes into shares of our common stock at their option until the close of business on the second scheduled trading day immediately preceding the maturity date. The current conversion rate for the 7.00% Convertible Notes is 30.3030 shares of common stock per $1,000 principal amount of the 7.00% Convertible Notes, equivalent to an initial conversion price of $33.00 per share of our common stock. Such conversion rate will be subject to adjustment in certain events as specified in the Indenture.
Refer to Part IV, Item 15, Note 11 ("Debt") included in this Report for additional information concerning the 7.00% Convertible Notes.
5.875% Convertible Notes
On August 12, 2019, we completed a private placement offering of $120.0 million aggregate principal amount of 5.875% Convertible Senior Notes due 2025 to the initial purchasers of such notes for cash in reliance on an exemption from registration provided by Section 4(a)(2) of the Securities Act. The initial purchasers then resold the 5.875% Convertible Notes for cash equal to 100 percent of the aggregate principal amount thereof to qualified institutional buyers, as defined in Rule 144A under the Securities Act, in reliance on an exemption from registration provided by Rule 144A. The 5.875% Convertible Notes mature on August 15, 2025 and bear interest at a rate of 5.875 percent per annum, payable semiannually in arrears on February 15 and August 15 of each year, beginning on February 15, 2020.
Holders may convert all or any portion of their 5.875% Convertible Notes into shares of our common stock at their option at any time prior to the close of business on the business day immediately preceding the maturity date. The initial conversion rate for the 5.875% Convertible Notes is 20.0 shares of common stock per $1,000 principal amount of the 5.875% Convertible Notes, equivalent to an initial conversion price of $50.00 per share of our common stock. Such conversion rate will be subject to adjustment in certain events as specified in the Indenture.
61
Refer to Part IV, Item 15, Note 11 ("Debt") included in this Report for additional information concerning the 5.875% Convertible Notes.
Shelf Registration Statements
On October 30, 2018, we registered 1,000,000 shares of common stock for issuance under our dividend reinvestment plan pursuant to a separate shelf registration statement filed with the SEC. As of December 31, 2019, we have issued 22,003 shares of common stock under our dividend reinvestment plan pursuant to the shelf resulting in remaining availability (subject to the current limitation discussed below) of approximately 977,997 shares of common stock.
On November 9, 2018, we had a new shelf registration statement declared effective by the SEC replacing our previously filed shelf registration statement, pursuant to which we may publicly offer additional debt or equity securities with an aggregate offering price of up to $600.0 million. As described elsewhere in this Report, EGC and Cox Oil have refused to provide the financial statement information concerning EGC that we must file pursuant to SEC Regulation S-X. At least until we are able to file these EGC financial statements, we do not expect to be able to use this shelf registration statement, or the shelf registration statement filed for our dividend reinvestment plan, to sell our securities.
We have engaged in dialogue with the staff of the SEC in an effort to shorten the period during which we do not use our registration statements. We do not expect this period to be shortened until the EGC financial statement information has been received and filed. However, there can be no assurance that we will be successful in obtaining such relief.
Liquidity and Capitalization
Our principal investing activities are acquiring and financing midstream and downstream real estate assets within the U.S. energy infrastructure sector and concurrently entering into long-term triple-net participating leases with energy companies. These investing activities have often been financed from the proceeds of our public equity and debt offerings as well as the term and credit facilities mentioned above. Continued growth of our asset portfolio will depend in part on our continued ability to access funds through additional borrowings and securities offerings. Additionally, our liquidity and capitalization may be impacted by the optional redemption of Series A Preferred Stock. As disclosed in Part IV, Item 15, Note 13 ("Stockholders' Equity"), the depositary shares may be redeemed on or after January 27, 2020, at our option, in whole or in part, at the $25.00 liquidation preference plus all accrued and unpaid dividends to, but not including, the date of redemption.
The following table presents our liquidity and capitalization as of December 31, 2019 and 2018:
Liquidity and Capitalization | |||||||
December 31, 2019 | December 31, 2018 | ||||||
Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 120,863,643 | $ | 69,287,177 | |||
Revolver availability | $ | 136,358,445 | $ | 122,721,258 | |||
Revolving credit facility | $ | — | $ | — | |||
Long-term debt (including current maturities) (1) | 152,109,426 | 150,038,380 | |||||
Stockholders' equity: | |||||||
Series A Cumulative Redeemable Preferred Stock 7.375%, $0.001 par value | 125,493,175 | 125,555,675 | |||||
Capital stock, non-convertible, $0.001 par value | 13,639 | 11,960 | |||||
Additional paid-in capital | 360,844,497 | 320,295,969 | |||||
Retained earnings (deficit) | (9,611,872 | ) | 9,147,701 | ||||
CorEnergy equity | 476,739,439 | 455,011,305 | |||||
Total CorEnergy capitalization | $ | 628,848,865 | $ | 605,049,685 | |||
(1) Long-term debt is presented net of discount and deferred debt costs. | |||||||
We also have two lines of credit for working capital purposes for two of our subsidiaries with maximum availability of $1.5 million and $1.0 million at both December 31, 2019 and 2018.
SUBSEQUENT EVENTS
For additional information regarding transactions that occurred subsequent to December 31, 2019, see Part IV, Item 15, Note 16 ("Subsequent Events") included in this annual Report on Form 10-K.
62
CRITICAL ACCOUNTING ESTIMATES
The financial statements included in this Report are based on the selection and application of critical accounting policies, which require management to make significant estimates and assumptions. Critical accounting policies are those that are both important to the presentation of our financial condition and results of operations and require management's most difficult, complex, or subjective judgments. The preparation of the consolidated financial statements in conformity with U.S. GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amount of assets and liabilities, recognition of revenues and expenses, and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the consolidated financial statements. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
See Part IV, Item 15, Note 2 ("Significant Accounting Policies") included in this Report for further information related to our significant accounting policies.
Long-Lived Assets
Our long-lived assets consist primarily of a subsea midstream pipeline system, liquids gathering system and natural gas pipelines that have been obtained through a business combination and asset acquisitions. Depreciation is computed using the straight-line method over the estimated useful life of the asset. Expenditures for repairs and maintenance are charged to operations as incurred, and improvements, which extend the useful lives of our assets, are capitalized and depreciated over the remaining estimated useful life of the asset.
We continually monitor our business, the business environment, and performance of our operations to determine if an event has occurred that indicates that the carrying value of a long-lived asset may be impaired. When a triggering event occurs, which is a determination that involves judgment, we utilize cash flow projections to assess the ability to recover the carrying value of our assets based on our long-lived assets' ability to generate future cash flows on an undiscounted basis. This differs from the evaluation of goodwill, for which the recoverability assessment utilizes fair value estimates that include discounted cash flows in the estimation process, and accordingly any goodwill impairment recognized may not be indicative of a similar impairment of the related underlying long-lived assets.
The projected cash flows of long-lived assets are primarily based on contractual cash flows relating to existing leases that extend many years into the future. If those cash flow projections indicate that the long-lived asset's carrying value is not recoverable, we record an impairment charge for the excess of carrying value of the asset over its fair value. The estimate of fair value considers a number of factors, including the potential value that would be received if the asset were sold, discount rates, and projected cash flows. Due to the imprecise nature of these projections and assumptions, actual results can differ from our estimates. There were no impairments of long-lived assets recorded during the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 or 2017.
Asset Retirement Obligations
We follow ASC 410-20, Asset Retirement Obligations, which requires that an asset retirement obligation ("ARO") associated with the retirement of a long-lived asset be recognized as a liability in the period in which it is incurred and becomes determinable, with an offsetting increase in the carrying amount of the associated asset. We recognized an existing ARO in conjunction with the acquisition of the GIGS in June 2015.
We measure changes in the ARO liability due to passage of time by applying an interest method of allocation to the amount of the liability at the beginning of the period. The increase in the carrying amount of the liability is recognized as an expense classified as an operating item in the Consolidated Statements of Income, hereinafter referred to as ARO accretion expense. We periodically reassess the timing and amount of cash flows anticipated associated with the ARO and adjusts the fair value of the liability accordingly under the guidance in ASC 410-20.
The fair value of the obligation at the acquisition date was capitalized as part of the carrying amount of the related long-lived assets and is being depreciated over the asset's remaining useful life. The useful lives of most pipeline gathering systems are primarily derived from available supply resources and ultimate consumption of those resources by end users. Adjustments to the ARO resulting from reassessments of the timing and amount of cash flows will result in changes to the retirement costs capitalized as part of the carrying amount of the asset.
Upon decommissioning of the ARO or a portion thereof, we reduce the fair value of the liability and recognize a (gain) loss on settlement of ARO as an operating item in the Consolidated Statements of Income for the difference between the liability and actual decommissioning costs incurred.
Federal and State Income Taxation
We qualify as a REIT under Sections 856 to 860 of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, and intend to continue to remain so qualified. For further information, see "Federal and State Income Taxation" above in this Item 7 and "Federal and State Income Taxation" under
63
Item 5 "Market for Registrant's Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities" of this Report.
ITEM 7A. QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK
Our business activities contain elements of market risk. Historically, we have considered fluctuations in the value of our securities portfolio to be our principal market risk. With respect to our equity securities, there has been a substantial decline in our market risk exposure as compared to prior years, as certain private equity investments were sold or disposed of by the end of 2018 and liquidated by the end of 2019. Refer to Part IV, Item 15, Note 10 ("Fair Value") for additional details.
Long-term debt used to finance our acquisitions may be based on floating or fixed rates. As of December 31, 2019, we had long-term debt (net of current maturities) with a carrying value of $146.5 million, all of which represents fixed-rate debt. Borrowings under our CorEnergy Revolver are variable-rate, based on a LIBOR pricing spread. There were no outstanding borrowings under the CorEnergy Revolver at December 31, 2019, and accordingly, no market risk exposure on outstanding variable rate debt.
We consider the management of risk essential to conducting our businesses. Accordingly, our risk management systems and procedures are designed to identify and analyze our risks, to set appropriate policies and limits and to continually monitor these risks and limits by means of reliable administrative and information systems and other policies and programs.
ITEM 8. FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTARY DATA
Our financial statements and financial statement schedules are set forth beginning on page F-1 in this Annual Report and are incorporated herein by reference.
ITEM 9. CHANGES IN AND DISAGREEMENTS WITH ACCOUNTANTS ON ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE
None.
ITEM 9A. CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES
Our management is responsible for the preparation, consistency, integrity, and fair presentation of the financial statements. The financial statements have been prepared in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles applied on a consistent basis and, in management's opinion, are fairly presented. The financial statements include amounts that are based on management's informed judgments and best estimates.
Conclusion Regarding Effectiveness of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
Under the supervision and with the participation of our management, including our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Accounting Officer (our principal executive and principal financial officers, respectively), we have evaluated the effectiveness of our disclosure controls and procedures, as defined in Rule 13a-15(e) under the Exchange Act, as of the end of the period covered by this Report. Based on that evaluation, these officers concluded that our disclosure controls and procedures were effective to ensure that the information required to be disclosed by us in the reports that we file or submit under the Exchange Act is recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in the SEC rules and forms, and is accumulated and communicated to our management, including our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Accounting Officer, as appropriate, to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure.
Changes in Internal Control over Financial Reporting
There have been no changes in our internal control over financial reporting, as defined in rule 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f) of the Exchange Act, that occurred during the quarterly period ending December 31, 2019, that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
Management's Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
Our management, under the supervision and with the participation of our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Accounting Officer (our principal executive and principal financial officers, respectively), is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over our financial reporting. Our management has established and maintains comprehensive systems of internal control designed to provide reasonable assurance as to the consistency, integrity, and reliability of the preparation and presentation of financial statements and the safeguarding of assets. The concept of reasonable assurance is based upon the recognition that the cost of the controls should not exceed the benefit derived. Our management monitors the systems of internal control and maintains an internal auditing program that assesses the effectiveness of internal control.
64
Our management assessed our systems of internal control over financial reporting for financial presentations in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles as of December 31, 2019. This assessment was based on criteria for effective internal control established in Internal Control—Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (2013 framework) (the COSO Report). Based on this assessment, our management has determined that our internal control over financial reporting was effective as of December 31, 2019.
The Board of Directors exercises its oversight role with respect to the systems of internal control primarily through its Audit Committee, which is comprised solely of independent outside directors. The Committee oversees systems of internal control and financial reporting to assess whether their quality, integrity, and objectivity are sufficient to protect stockholders' investments.
Ernst & Young has issued an audit report on our internal control over financial reporting. This report begins on the next page.
65
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Stockholders and the Board of Directors of CorEnergy Infrastructure Trust, Inc.
Opinion on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
We have audited CorEnergy Infrastructure Trust, Inc.'s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2019, based on criteria established in Internal Control-Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (2013 framework) (the COSO criteria). In our opinion, CorEnergy Infrastructure Trust, Inc. (the Company) maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2019, based on the COSO criteria.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB), the consolidated balance sheets of CorEnergy Infrastructure Trust, Inc. as of December 31, 2019 and 2018, the related consolidated statements of income and comprehensive income, equity and cash flow for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2019, and the related notes and financial statement schedules listed in the Index at Item 15 and our report dated February 27, 2020 expressed an unqualified opinion thereon.
Basis for Opinion
The Company's management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting included in the accompanying Management's Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company's internal control over financial reporting based on our audit. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects.
Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk, and performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Definition and Limitations of Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
A company's internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company's internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company's assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
/s/ Ernst & Young LLP
Kansas City, Missouri
February 27, 2020
66
ITEM 9B. OTHER INFORMATION
None.
PART III
ITEM 10. DIRECTORS, EXECUTIVE OFFICERS AND CORPORATE GOVERNANCE
Codes of Ethics
We have adopted a code of ethics, which applies to our principal executive officer and principal financial officer. We have also adopted a code of ethics that establishes procedures for personal investments and restricts certain personal securities transactions. Personnel subject to the code of ethics may invest in securities for their personal investment accounts, including securities that may be purchased or held by us, so long as such investments are made in accordance with the code of ethics. This information may be obtained, without charge, upon request by calling us at (816) 875-3705 or toll-free at (877) 699-2677 and on our web site at http://corenergy.reit. The codes of ethics are available on the EDGAR Database on the Securities and Exchange Commission's Internet site at http://www.sec.gov.
Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002
The Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 (the "Sarbanes-Oxley Act") imposes a wide variety of regulatory requirements on publicly-held companies and their insiders. The Sarbanes-Oxley Act requires us to review our policies and procedures to determine whether we comply with the Sarbanes-Oxley Act and the regulations promulgated thereunder. We will continue to monitor our compliance with all future regulations that are adopted under the Sarbanes-Oxley Act and will take actions necessary to ensure that we are in compliance therewith.
As of December 31, 2019, we are an accelerated filer. As an accelerated filer for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2019, we are required to prepare and include in our annual report to stockholders for such period a report regarding management's assessment of our internal control over financial reporting under the Exchange Act and have included this report in Item 9A of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Additional information is incorporated herein by reference to the sections captioned "Nominees for Directors," "Incumbent Directors Continuing in Office," "Information About Executive Officers," "Board of Directors Meetings and Committees," "Section 16(a) Beneficial Ownership Reporting Compliance" and "Stockholder Proposals and Nominations for the 2021 Annual Meeting" in our proxy statement for our 2020 Annual Stockholder Meeting, which will be filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission within 120 days after the end of the fiscal year covered by this Annual Report.
ITEM 11. EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION
Incorporated by reference to the sections captioned "Director Compensation Table" and "Compensation Committee Interlocks and Insider Participation" in our proxy statement for our 2020 Annual Stockholder Meeting to be filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission within 120 days after the end of the fiscal year covered by this Annual Report.
ITEM 12. SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT AND RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS
Incorporated by reference to the sections captioned "Security Ownership of Management and Certain Beneficial Owners" and "Director Compensation" in our proxy statement for our 2020 Annual Stockholder Meeting to be filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission within 120 days after the end of the fiscal year covered by this Annual Report.
ITEM 13. CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED TRANSACTIONS, AND DIRECTOR INDEPENDENCE
Incorporated by reference to the sections captioned "Nominees for Director," "Incumbent Directors Continuing in Office," "Board of Directors Meetings and Committees" and "Certain Relationships and Related Party Transactions" in our proxy statement for our 2020 Annual Stockholder Meeting to be filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission within 120 days after the end of the fiscal year covered by this Annual Report.
ITEM 14. PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTING FEES AND SERVICES
Incorporated by reference to the section captioned "Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm Fees and Services" in our proxy statement for our 2020 Annual Stockholder Meeting to be filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission within 120 days after the end of the fiscal year covered by this Annual Report.
67
PART IV
ITEM 15. EXHIBITS AND FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULES
The following documents are filed as part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K:
1. The Financial Statements listed in the Index to Financial Statements on Page F-1.
2. The Exhibits listed in the Exhibit Index below.
Exhibit No. | Description of Document |
3.1 | |
3.2 | |
3.3 | |
3.4 | |
4.1 | |
4.2 | |
4.3.1 | |
4.3.2 | |
4.4 | |
4.5 | |
4.6 | |
10.1.1 | |
10.1.2 | |
10.2.1 | |
10.2.2 | |
10.2.3 | |
10.2.4 | |
10.2.5 | |
10.2.6 | |
10.2.7 | |
10.2.8 | |
10.2.9 | |
68
10.3.1 | |
10.3.2 | |
10.4.1 | |
10.4.2 | |
10.5 | |
10.6.1 | |
10.6.2 | |
10.6.3 | |
10.7 | |
10.8 | |
10.9 | |
10.9.1 | |
10.9.2 | |
10.10 | |
10.10.1 | |
10.11.1 | |
10.11.2 | |
10.11.3 | |
10.12.1 | |
10.12.2 | |
10.12.3 | |
10.12.4 | |
10.12.5 | |
10.12.6 | |
10.13.1 | |
10.13.2 | |
10.14 | |
10.15.1 | |
10.15.2 | |
69
10.15.3 | |
10.15.4 | |
10.15.5 | |
10.16 | |
21.1 | |
23.1 | |
31.1 | |
31.2 | |
32.1 | |
101 | The following materials from CorEnergy Infrastructure Trust, Inc.'s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2019, formatted in XBRL (Extensible Business Reporting Language): (i) the Consolidated Balance Sheets, (ii) the Consolidated Statements of Income and Comprehensive Income, (iii) the Consolidated Statement of Equity, (iv) the Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows and (v) the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements - furnished herewith |
* | Management contract or compensatory plan or arrangement. |
All exhibits incorporated by reference were filed under SEC File No. 001-33292.
All other exhibits for which provision is made in the applicable regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission are not required under the related instruction or are inapplicable and therefore have been omitted.
70
INDEX TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Page No. | |||
F-1
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Stockholders and the Board of Directors of CorEnergy Infrastructure Trust, Inc.
Opinion on the Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of CorEnergy Infrastructure Trust, Inc. (the Company) as of December 31, 2019 and 2018, the related consolidated statements of income and comprehensive income, equity and cash flow for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2019, and the related notes and financial statement schedules listed in the Index at Item 15 (collectively referred to as the "consolidated financial statements"). In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company at December 31, 2019 and 2018, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2019, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB), the Company's internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2019, based on criteria established in Internal Control-Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (2013 framework) and our report dated February 27, 2020 expressed an unqualified opinion thereon.
Basis for Opinion
These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company's management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company's financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
/s/ Ernst & Young LLP
We have served as the Company's auditor since 2006.
Kansas City, Missouri
February 27, 2020
F-2

CorEnergy Infrastructure Trust, Inc.
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
December 31, 2019 | December 31, 2018 | ||||||
Assets | |||||||
Leased property, net of accumulated depreciation of $105,825,816 and $87,154,095 | $ | 379,211,399 | $ | 398,214,355 | |||
Property and equipment, net of accumulated depreciation of $19,304,610 and $15,969,346 | 106,855,677 | 109,881,552 | |||||
Financing notes and related accrued interest receivable, net of reserve of $600,000 and $600,000 | 1,235,000 | 1,300,000 | |||||
Note receivable | — | 5,000,000 | |||||
Cash and cash equivalents | 120,863,643 | 69,287,177 | |||||
Deferred rent receivable | 29,858,102 | 25,942,755 | |||||
Accounts and other receivables | 4,143,234 | 5,083,243 | |||||
Deferred costs, net of accumulated amortization of $1,956,710 and $1,290,236 | 2,171,969 | 2,838,443 | |||||
Prepaid expenses and other assets | 804,341 | 668,584 | |||||
Deferred tax asset, net | 4,593,561 | 4,948,203 | |||||
Goodwill | 1,718,868 | 1,718,868 | |||||
Total Assets | $ | 651,455,794 | $ | 624,883,180 | |||
Liabilities and Equity | |||||||
Secured credit facilities, net of debt issuance costs of $158,070 and $210,891 | 33,785,930 | 37,261,109 | |||||
Unsecured convertible senior notes, net of discount and debt issuance costs of $3,768,504 and $1,180,729 | 118,323,496 | 112,777,271 | |||||
Asset retirement obligation | 8,044,200 | 7,956,343 | |||||
Accounts payable and other accrued liabilities | 6,000,981 | 3,493,490 | |||||
Management fees payable | 1,669,950 | 1,831,613 | |||||
Unearned revenue | 6,891,798 | 6,552,049 | |||||
Total Liabilities | $ | 174,716,355 | $ | 169,871,875 | |||
Equity | |||||||
Series A Cumulative Redeemable Preferred Stock 7.375%, $125,493,175 and $125,555,675 liquidation preference ($2,500 per share, $0.001 par value), 10,000,000 authorized; 50,197 and 50,222 issued and outstanding at December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, respectively | $ | 125,493,175 | $ | 125,555,675 | |||
Capital stock, non-convertible, $0.001 par value; 13,638,916 and 11,960,225 shares issued and outstanding at December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018 (100,000,000 shares authorized) | 13,639 | 11,960 | |||||
Additional paid-in capital | 360,844,497 | 320,295,969 | |||||
Retained earnings (deficit) | (9,611,872 | ) | 9,147,701 | ||||
Total Equity | 476,739,439 | 455,011,305 | |||||
Total Liabilities and Equity | $ | 651,455,794 | $ | 624,883,180 | |||
See accompanying Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements. | |||||||
F-3

CorEnergy Infrastructure Trust, Inc.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF INCOME AND COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
For the Years Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2019 | 2018 | 2017 | |||||||||
Revenue | |||||||||||
Lease revenue | $ | 67,050,506 | $ | 72,747,362 | $ | 68,803,804 | |||||
Transportation and distribution revenue | 18,778,237 | 16,484,236 | 19,945,573 | ||||||||
Financing revenue | 116,827 | — | — | ||||||||
Total Revenue | 85,945,570 | 89,231,598 | 88,749,377 | ||||||||
Expenses | |||||||||||
Transportation and distribution expenses | 5,242,244 | 7,210,748 | 6,729,707 | ||||||||
General and administrative | 10,596,848 | 13,042,847 | 10,786,497 | ||||||||
Depreciation, amortization and ARO accretion expense | 22,581,942 | 24,947,453 | 24,047,710 | ||||||||
Provision for loan gain | — | (36,867 | ) | — | |||||||
Total Expenses | 38,421,034 | 45,164,181 | 41,563,914 | ||||||||
Operating Income | $ | 47,524,536 | $ | 44,067,417 | $ | 47,185,463 | |||||
Other Income (Expense) | |||||||||||
Net distributions and other income | $ | 1,328,853 | $ | 106,795 | $ | 680,091 | |||||
Net realized and unrealized gain (loss) on other equity securities | — | (1,845,309 | ) | 1,531,827 | |||||||
Interest expense | (10,578,711 | ) | (12,759,010 | ) | (12,378,514 | ) | |||||
Gain on the sale of leased property, net | — | 11,723,257 | — | ||||||||
Loss on extinguishment of debt | (33,960,565 | ) | — | (336,933 | ) | ||||||
Total Other Expense | (43,210,423 | ) | (2,774,267 | ) | (10,503,529 | ) | |||||
Income before income taxes | 4,314,113 | 41,293,150 | 36,681,934 | ||||||||
Taxes | |||||||||||
Current tax expense (benefit) | (120,024 | ) | (585,386 | ) | 2,831,658 | ||||||
Deferred tax expense (benefit) | 354,642 | (1,833,340 | ) | (486,340 | ) | ||||||
Income tax expense (benefit), net | 234,618 | (2,418,726 | ) | 2,345,318 | |||||||
Net Income | 4,079,495 | 43,711,876 | 34,336,616 | ||||||||
Less: Net Income attributable to non-controlling interest | — | — | 1,733,826 | ||||||||
Net Income attributable to CorEnergy Stockholders | $ | 4,079,495 | $ | 43,711,876 | $ | 32,602,790 | |||||
Preferred dividend requirements | 9,255,468 | 9,548,377 | 7,953,988 | ||||||||
Net Income (Loss) attributable to Common Stockholders | $ | (5,175,973 | ) | $ | 34,163,499 | $ | 24,648,802 | ||||
Net Income | $ | 4,079,495 | $ | 43,711,876 | $ | 34,336,616 | |||||
Other comprehensive income: | |||||||||||
Changes in fair value of qualifying hedges / AOCI attributable to CorEnergy stockholders | — | — | 11,196 | ||||||||
Changes in fair value of qualifying hedges / AOCI attributable to non-controlling interest | — | — | 2,617 | ||||||||
Net Change in Other Comprehensive Income | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 13,813 | |||||
Total Comprehensive Income | 4,079,495 | 43,711,876 | 34,350,429 | ||||||||
Less: Comprehensive income attributable to non-controlling interest | — | — | 1,736,443 | ||||||||
Comprehensive Income attributable to CorEnergy Stockholders | $ | 4,079,495 | $ | 43,711,876 | $ | 32,613,986 | |||||
Earnings (Loss) Per Common Share: | |||||||||||
Basic | $ | (0.40 | ) | $ | 2.86 | $ | 2.07 | ||||
Diluted | $ | (0.40 | ) | $ | 2.79 | $ | 2.07 | ||||
Weighted Average Shares of Common Stock Outstanding: | |||||||||||
Basic | 13,041,613 | 11,935,021 | 11,900,516 | ||||||||
Diluted | 13,041,613 | 15,389,180 | 11,900,516 | ||||||||
Dividends declared per share | $ | 3.000 | $ | 3.000 | $ | 3.000 | |||||
See accompanying Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements. | |||||||||||
F-4

CorEnergy Infrastructure Trust, Inc.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF EQUITY
Capital Stock | Preferred Stock | Additional Paid-in Capital | Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (Loss) | Retained Earnings (Deficit) | Non-Controlling Interest | Total | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Shares | Amount | Amount | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Balance at December 31, 2016 | 11,886,216 | $ | 11,886 | $ | 56,250,000 | $ | 350,217,746 | $ | (11,196 | ) | $ | — | $ | 27,441,044 | $ | 433,909,480 | ||||||||||||||
Net Income | — | — | — | — | — | 32,602,790 | 1,733,826 | 34,336,616 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Amortization related to de-designated cash flow hedges | — | — | — | — | 11,196 | — | 2,617 | 13,813 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Total comprehensive income | — | — | — | — | 11,196 | 32,602,790 | 1,736,443 | 34,350,429 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Issuance of Series A preferred stock | — | — | 73,750,000 | (2,588,469 | ) | — | — | — | 71,161,531 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Series A preferred stock dividends | — | — | — | (727,001 | ) | — | (7,500,733 | ) | — | (8,227,734 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
Common stock dividends | — | — | — | (10,592,143 | ) | — | (25,102,057 | ) | — | (35,694,200 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
Common stock issued under director's compensation plan | 1,979 | 2 | — | 67,498 | — | — | — | 67,500 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Distributions to Non-controlling interest | — | — | — | — | — | — | (1,833,650 | ) | (1,833,650 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||
Purchase of non-controlling interest | — | — | — | (5,566,195 | ) | — | — | (27,343,837 | ) | (32,910,032 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
Reinvestment of dividends paid to common stockholders | 27,635 | 28 | — | 962,280 | — | — | — | 962,308 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Balance at December 31, 2017 | 11,915,830 | 11,916 | 130,000,000 | 331,773,716 | — | — | — | 461,785,632 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Cumulative transition adjustment upon the adoption of ASC 606, net of tax | — | — | — | (2,449,245 | ) | — | — | — | (2,449,245 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||
Net income | — | — | — | — | 43,711,876 | — | 43,711,876 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Series A preferred stock dividends | — | — | — | — | — | (9,587,500 | ) | — | (9,587,500 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||
Preferred stock repurchases(1) | — | — | (4,444,325 | ) | 158,218 | — | 10,554 | — | (4,275,553 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||
Common stock dividends | — | — | — | (10,806,660 | ) | — | (24,987,229 | ) | — | (35,793,889 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
Common stock issued under director's compensation plan | 1,807 | 2 | — | 67,498 | — | — | — | 67,500 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Common stock issued upon conversion of convertible notes | 1,271 | 1 | — | 42,653 | — | — | — | 42,654 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Reinvestment of dividends paid to common stockholders | 41,317 | 41 | — | 1,509,789 | — | — | — | 1,509,830 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Balance at December 31, 2018 (2) | 11,960,225 | 11,960 | 125,555,675 | 320,295,969 | — | 9,147,701 | — | 455,011,305 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Net income | — | — | — | — | — | 4,079,495 | — | 4,079,495 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Series A preferred stock dividends | — | — | — | (4,627,561 | ) | — | (4,627,560 | ) | — | (9,255,121 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
Preferred stock repurchases(3) | — | — | (62,500 | ) | 2,195 | — | (245 | ) | — | (60,550 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
Common stock dividends | — | — | — | (21,293,224 | ) | — | (18,211,263 | ) | — | (39,504,487 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
Common stock issued upon exchange of convertible notes | 1,540,472 | 1,540 | — | 61,869,762 | — | — | — | 61,871,302 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Common stock issued upon conversion of convertible notes | 127,143 | 128 | — | 4,193,536 | — | — | — | 4,193,664 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Reinvestment of dividends paid to common stockholders | 11,076 | 11 | — | 403,820 | — | — | — | 403,831 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Balance at December 31, 2019 | 13,638,916 | $ | 13,639 | $ | 125,493,175 | $ | 360,844,497 | $ | — | $ | (9,611,872 | ) | $ | — | $ | 476,739,439 | ||||||||||||||
See accompanying Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(1) In connection with the repurchases of Series A Preferred Stock during 2018, the deduction to preferred dividends of $10,554 represents the discount in the repurchase price paid compared to the carrying amount derecognized. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(2) The retained earnings balance at December 31, 2018 was generated due to the timing of quarterly dividends and quarterly net income. In the fourth quarter of 2018, net income was greater than dividends due to the gain on sale of leased property, net from the sale of the Portland Terminal Facility resulting in a retained earnings balance as of December 31, 2018. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(3) In connection with the repurchases of Series A Preferred Stock during 2019, the addition to preferred dividends of $245 represents the premium in the repurchase price paid compared to the carrying amount derecognized. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
F-5

CorEnergy Infrastructure Trust, Inc.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOW
For the Years Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2019 | 2018 | 2017 | |||||||||
Operating Activities | |||||||||||
Net Income | $ | 4,079,495 | $ | 43,711,876 | $ | 34,336,616 | |||||
Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities: | |||||||||||
Deferred income tax, net | 354,642 | (1,845,710 | ) | (486,340 | ) | ||||||
Depreciation, amortization and ARO accretion | 23,808,083 | 26,361,907 | 25,708,891 | ||||||||
Gain on sale of leased property, net | — | (11,723,257 | ) | — | |||||||
Provision for loan gain | — | (36,867 | ) | — | |||||||
Loss on extinguishment of debt | 33,960,565 | — | 336,933 | ||||||||
Non-cash settlement of accounts payable | — | — | (221,609 | ) | |||||||
(Gain) loss on sale of equipment | (7,390 | ) | (8,416 | ) | 4,203 | ||||||
Net distributions and other income, including recharacterization of income | — | — | 148,649 | ||||||||
Net realized and unrealized (gain) loss on other equity securities | — | 1,845,309 | (1,531,827 | ) | |||||||
Loss on settlement of asset retirement obligation | — | 310,941 | — | ||||||||
Common stock issued under directors' compensation plan | — | 67,500 | 67,500 | ||||||||
Changes in assets and liabilities: | |||||||||||
Increase in deferred rent receivables | (3,915,347 | ) | (7,038,848 | ) | (7,184,005 | ) | |||||
(Increase) decrease in accounts and other receivables | 940,009 | (1,297,207 | ) | 752,848 | |||||||
(Increase) decrease in prepaid expenses and other assets | (136,108 | ) | 73,505 | (16,717 | ) | ||||||
Increase (decrease) in management fee payable | (161,663 | ) | 83,187 | 13,402 | |||||||
Increase (decrease) in accounts payable and other accrued liabilities | 2,517,069 | 476,223 | (225,961 | ) | |||||||
Increase (decrease) in income tax liability | — | (2,204,626 | ) | 2,204,626 | |||||||
Increase (decrease) in unearned revenue | 339,749 | (152,777 | ) | 2,884,362 | |||||||
Net cash provided by operating activities | $ | 61,779,104 | $ | 48,622,740 | $ | 56,791,571 | |||||
Investing Activities | |||||||||||
Proceeds from the sale of leased property | — | 55,553,975 | — | ||||||||
Proceeds from sale of other equity securities | — | 449,067 | 7,591,166 | ||||||||
Purchases of property and equipment, net | (372,934 | ) | (105,357 | ) | (116,595 | ) | |||||
Proceeds from asset sale | 7,000 | 17,999 | — | ||||||||
Principal payment on financing note receivable | 65,000 | 236,867 | — | ||||||||
Principal payment on note receivable | 5,000,000 | — | — | ||||||||
Return of capital on distributions received | — | 663,939 | 120,906 | ||||||||
Net cash provided by investing activities | $ | 4,699,066 | $ | 56,816,490 | $ | 7,595,477 | |||||
Financing Activities | |||||||||||
Debt financing costs | (372,759 | ) | (264,010 | ) | (1,462,741 | ) | |||||
Net offering proceeds on Series A preferred stock | — | — | 71,161,531 | ||||||||
Cash paid for extinguishment of convertible notes | (78,939,743 | ) | — | — | |||||||
Net offering proceeds on convertible debt | 116,355,125 | — | — | ||||||||
Repurchases of Series A preferred stock | (60,550 | ) | (4,275,553 | ) | — | ||||||
Dividends paid on Series A preferred stock | (9,255,121 | ) | (9,587,500 | ) | (8,227,734 | ) | |||||
Dividends paid on common stock | (39,100,656 | ) | (34,284,059 | ) | (34,731,892 | ) | |||||
Distributions to non-controlling interest | — | — | (1,833,650 | ) | |||||||
Advances on revolving line of credit | — | — | 10,000,000 | ||||||||
Payments on revolving line of credit | — | — | (54,000,000 | ) | |||||||
Proceeds from term debt | — | — | 41,000,000 | ||||||||
Principal payments on secured credit facilities | (3,528,000 | ) | (3,528,000 | ) | (45,600,577 | ) | |||||
Purchase of non-controlling interest | — | — | (32,800,000 | ) | |||||||
Net cash used in financing activities | $ | (14,901,704 | ) | $ | (51,939,122 | ) | $ | (56,495,063 | ) | ||
F-6
For the Years Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2019 | 2018 | 2017 | |||||||||
Net Change in Cash and Cash Equivalents | $ | 51,576,466 | $ | 53,500,108 | $ | 7,891,985 | |||||
Cash and Cash Equivalents at beginning of period | 69,287,177 | 15,787,069 | 7,895,084 | ||||||||
Cash and Cash Equivalents at end of period | $ | 120,863,643 | $ | 69,287,177 | $ | 15,787,069 | |||||
Supplemental Disclosure of Cash Flow Information | |||||||||||
Interest paid | $ | 6,834,439 | $ | 11,200,835 | $ | 10,780,150 | |||||
Income taxes paid (net of refunds) | 89,433 | 2,136,563 | 199,772 | ||||||||
Non-Cash Investing Activities | |||||||||||
Note receivable in consideration of the sale of leased property | $ | — | $ | 5,000,000 | $ | — | |||||
Investment in other equity securities | — | — | (1,161,034 | ) | |||||||
Non-Cash Financing Activities | |||||||||||
Change in accounts payable and accrued expenses related to debt financing costs | $ | — | $ | (255,037 | ) | $ | 255,037 | ||||
Reinvestment of distributions by common stockholders in additional common shares | 403,831 | 1,509,830 | 962,308 | ||||||||
Common stock issued upon exchange and conversion of convertible notes | 66,064,966 | 42,654 | — | ||||||||
See accompanying Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements. | |||||||||||
F-7

NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
December 31, 2019
1. INTRODUCTION AND BASIS OF PRESENTATION
Introduction
CorEnergy Infrastructure Trust, Inc. (referred to as "CorEnergy" or "the Company"), was organized as a Maryland corporation and commenced operations on December 8, 2005. The Company's common shares are listed on the New York Stock Exchange ("NYSE") under the symbol "CORR" and its depositary shares representing Series A Preferred Stock are listed on the NYSE under the symbol "CORR PrA".
The Company is primarily focused on acquiring and financing real estate assets within the U.S. energy infrastructure sector and concurrently entering into long-term triple-net participating leases with energy companies. The Company also may provide other types of capital, including loans secured by energy infrastructure assets. Targeted assets include pipelines, storage tanks, transmission lines, and gathering systems, among others. These sale-leaseback or real property mortgage transactions provide the energy company with a source of capital that is an alternative to other sources such as corporate borrowing, bond offerings, or equity offerings. Many of the Company's leases contain participation features in the financial performance or value of the underlying infrastructure real property asset. The triple-net lease structure requires that the tenant pay all operating expenses of the business conducted by the tenant, including real estate taxes, insurance, utilities, and expenses of maintaining the asset in good working order. CorEnergy considers its investments in these energy infrastructure assets to be a single business segment and reports them accordingly in its financial statements.
Basis of Presentation
The accompanying consolidated financial statements include CorEnergy accounts and the accounts of its wholly-owned subsidiaries and have been prepared in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles ("GAAP") set forth in the Accounting Standards Codification ("ASC"), as published by the Financial Accounting Standards Board ("FASB"), and with the Securities and Exchange Commission ("SEC") instructions to Form 10-K. The accompanying consolidated financial statements reflect all adjustments that are, in the opinion of management, necessary for a fair presentation of the Company's financial position, results of operations and cash flows for the periods presented. There were no adjustments that, in the opinion of management, were not of a normal and recurring nature. All intercompany transactions and balances have been eliminated in consolidation, and the Company's net earnings have been reduced by the portion of net earnings attributable to non-controlling interests, when applicable.
The FASB issued ASU 2015-02 Consolidations (Topic 810) - Amendments to the Consolidation Analysis ("ASU 2015-02"), which amended previous consolidation guidance, including introducing a separate consolidation analysis specific to limited partnerships and other similar entities. Under this analysis, limited partnerships and other similar entities are considered a variable interest entity ("VIE") unless the limited partners hold substantive kick-out rights or participating rights. Management determined that Pinedale LP and Grand Isle Corridor LP are VIEs under the amended guidance because the limited partners of both partnerships lack both substantive kick-out rights and participating rights. As such, management evaluated the qualitative criteria under FASB ASC Topic 810 in conjunction with ASU 2015-02 to make a determination whether these partnerships should be consolidated in the Company's financial statements. ASC Topic 810-10 requires the primary beneficiary of a variable interest entity's activities to consolidate the VIE. The primary beneficiary is identified as the enterprise that has a) the power to direct the activities of the VIE that most significantly impact the entity's economic performance and b) the obligation to absorb losses of the entity that could potentially be significant to the VIE or the right to receive benefits from the entity that could potentially be significant to the VIE. The standard requires an ongoing analysis to determine whether the variable interest gives rise to a controlling financial interest in the VIE. Based on the general partners' roles and rights as afforded by the partnership agreements and its exposure to losses and benefits of each of the partnerships through its significant limited partner interests, management determined that CorEnergy is the primary beneficiary of both Pinedale LP and Grand Isle Corridor LP. Based upon this evaluation and the Company's 100 percent ownership interest in Pinedale LP (2018-2019) and Grand Isle Corridor LP (2017-2019) and the majority ownership interest in Pinedale LP (2017) of the limited partnership interests, the consolidated financial statements presented include full consolidation with respect to both partnerships.
2. SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
A. Use of Estimates – The preparation of the consolidated financial statements in conformity with GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amount of assets and liabilities, the disclosure of contingent assets and
F-8
liabilities at the date of the consolidated financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
B. Leased Property and Leases – In February of 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-02, Leases ("ASU 2016-02" or "ASC 842"), which amends the existing accounting standards for lease accounting, including requiring lessees to recognize most leases on their balance sheets and making targeted changes to lessor accounting. The Company adopted ASC 842 effective January 1, 2019 using the modified retrospective approach by applying the transition provisions at the beginning of the period of adoption. The adoption of the new standard resulted in the recording of right-of-use assets and lease liabilities of approximately $75 thousand each, included in prepaid expenses and other assets and accounts payable and other accrued liabilities, respectively, as of January 1, 2019. There was no difference between the right-of-use assets and lease liabilities resulting in an adjustment to retained earnings. Refer to Note 3 ("Leased Properties And Leases") for further details of the ASC 842 adoption impact. The standard did not materially impact the Company's Consolidated Statements of Income and had no impact on the Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows. The Company will continue to apply legacy guidance in ASC 840, "Leases," including its disclosure requirements, in the comparative periods presented in the year of adoption.
In adopting ASC 842, the Company elected the package of practical expedients permitted under the transition guidance within the new standard, which among other things, allowed the carry forward of historical lease classification. For the underlying lessee asset class related to single-use office space, the Company also elected the lessee separation and allocation practical expedient to not separate lease and non-lease components and instead to account for each separate lease component and non-lease component as a single lease component. For the underlying lessor asset class related to pipelines residing on military bases, the Company elected the lessor separation and allocation practical expedient to not separate lease and non-lease components and instead to account for each separate lease component and non-lease component as a single lease component if the non-lease components otherwise will be accounted for in accordance with the revenue standard, and both the following criteria are met: (i) the timing and pattern of revenue recognition are the same for the non-lease component(s) and the related lease component and (ii) the lease component will be classified as an operating lease. Additionally, the Company elected the practical expedient related to land easements, allowing the carry forward of accounting treatment for land easements on existing agreements, which are currently accounted for within property, plant and equipment.
The Company's current leased properties are classified as operating leases and are recorded as leased property, net of accumulated depreciation, in the Consolidated Balance Sheets. Initial direct costs incurred in connection with the creation and execution of a lease prior to January 1, 2019 are capitalized and amortized over the lease term. The Company did not reassess initial indirect cost as it elected the package of practical expedients. Subsequent to January 1, 2019, initial direct costs under ASC 842 are incremental costs of a lease that would not have been incurred if the lease had not been obtained and may include commissions or payments made to an existing tenant as an incentive to terminate its lease. Base rent related to the Company's leased property is recognized on a straight-line basis over the term of the lease when collectability is probable. Participating rent is recognized when it is earned, based on the achievement of specified performance criteria. Base and participating rent are recorded as lease revenue in the Consolidated Statements of Income. Rental payments received in advance are classified as unearned revenue and included as a liability within the Consolidated Balance Sheets. Unearned revenue is amortized ratably over the lease period as revenue recognition criteria are met. Rental payments received in arrears are accrued and classified as deferred rent receivable and included in assets within the Consolidated Balance Sheets.
Under the Company's triple-net leases, the tenant is required to pay property taxes and insurance directly to the applicable third-party provider. Consistent with guidance in ASC 842, the Company will present the cost and the lessee's direct payment to the third-party under the triple-net leases on a net basis in the Consolidated Statements of Income.
C. Property and Equipment – Property and equipment are stated at cost less accumulated depreciation. Depreciation is computed using the straight-line method over the estimated useful life of the asset. Expenditures for repairs and maintenance are charged to operations as incurred, and improvements, which extend the useful lives of assets, are capitalized and depreciated over the remaining estimated useful life of the asset. The Company initially records long-lived assets at their purchase price plus any direct acquisition costs, unless the transaction is accounted for as a business combination, in which case the acquisition costs are expensed as incurred. If the transaction is accounted for as a business combination, the Company allocates the purchase price to the acquired tangible and intangible assets and liabilities based on their estimated fair values.
D. Long-Lived Asset Impairment – The Company's long-lived assets consist primarily of a subsea midstream pipeline system, liquids gathering system and natural gas pipelines that have been obtained through asset acquisitions and a business combination. Management continually monitors its business, the business environment and performance of its operations to determine if an event has occurred that indicates that the carrying value of a long-lived asset may be impaired. When a triggering event occurs, which is a determination that involves judgment, management utilizes cash flow projections to assess its ability to recover the carrying value of its assets based on the Company's long-lived assets' ability to generate future cash flows on an undiscounted basis. This differs from the evaluation of goodwill, for which the recoverability assessment utilizes fair value estimates that include discounted cash flows in
F-9
the estimation process and accordingly any goodwill impairment recognized may not be indicative of a similar impairment of the related underlying long-lived assets.
Management's projected cash flows of long-lived assets are primarily based on contractual cash flows relating to existing leases that extend many years into the future. If those cash flow projections indicate that the long-lived asset's carrying value is not recoverable, management records an impairment charge for the excess of carrying value of the asset over its fair value. The estimate of fair value considers a number of factors, including the potential value that would be received if the asset were sold, discount rates and projected cash flows. Due to the imprecise nature of these projections and assumptions, actual results can differ from management's estimates. There were no impairments of long-lived assets recorded during the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 or 2017.
E. Financing Notes Receivable – Financing notes receivable are presented at face value plus accrued interest receivable and deferred loan origination costs and net of related direct loan origination income. Each quarter the Company reviews its financing notes receivable to determine if the balances are realizable based on factors affecting the collectability of those balances. Factors may include credit quality, timeliness of required periodic payments, past due status and management discussions with obligors. The Company evaluates the collectability of both interest and principal of each of its loans to determine if an allowance is needed. An allowance will be recorded when based on current information and events, the Company determines it is probable that it will be unable to collect all amounts due according to the existing contractual terms. If the Company does determine an allowance is necessary, the amount deemed uncollectable is expensed in the period of determination. An insignificant delay or shortfall in the amount of payments does not necessarily result in the recording of an allowance. Generally, when interest and/or principal payments on a loan become past due, or if the Company does not otherwise expect the borrower to be able to service its debt and other obligations, the Company will place the loan on non-accrual status and will typically cease recognizing financing revenue on that loan until all principal and interest have been brought current. Interest income recognition is resumed if and when the previously reserved-for financing notes become contractually current and performance has been demonstrated. Payments received subsequent to the recording of an allowance will be recorded as a reduction to principal. During the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, the Company recorded provisions for loan gain of approximately $0, $37 thousand and $0, respectively. The Company's financing notes receivable are discussed more fully in Note 5 ("Financing Notes Receivable").
F. Investment Securities – The Company's investments in securities were classified as other equity securities and represented interests in private companies which the Company elected to report at fair value under the fair value option. These investments were subject to restrictions on resale, have no established trading market and were valued on a quarterly basis. Because of the inherent uncertainty of valuation, the fair values of such investments, which were determined in accordance with procedures approved by the Company's Board of Directors, may differ materially from the values that would have been used had a ready market existed for the investments. The Company determines fair value to be the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date. The Company has determined the principal market, or the market in which the Company exits its private portfolio investments with the greatest volume and level of activity, to be the private secondary market. Typically, private companies are bought and sold based on multiples of EBITDA, cash flows, net income, revenues, or in limited cases, book value. For private company investments, value is often realized through a liquidity event. As a result of the sale or disposition of the Company's other equity securities in 2018, the Company no longer holds investments in other equity securities as of December 31, 2019 and 2018.
G. Fair Value Measurements – FASB ASC 820, Fair Value Measurements and Disclosure ("ASC 820"), defines fair value, establishes a framework for measuring fair value and expands disclosures about fair value measurements. Various inputs are used in determining the fair value of the Company's assets and liabilities. These inputs are summarized in the three broad levels listed below:
• | Level 1 - quoted prices in active markets for identical investments |
• | Level 2 - other significant observable inputs (including quoted prices for similar investments, market corroborated inputs, etc.) |
• | Level 3 - significant unobservable inputs (including the Company's own assumptions in determining the fair value of investments) |
See Note 10 ("Fair Value") for further discussion of the Company's fair value measurements.
H. Cash and Cash Equivalents – The Company maintains cash balances at financial institutions in amounts that regularly exceed FDIC insured limits. The Company's cash equivalents are comprised of short-term, liquid money market instruments.
I. Accounts and other receivables – Accounts receivable are presented at face value net of an allowance for doubtful accounts within accounts and other receivables on the balance sheet. Accounts are considered past due based on the terms of sale with the customers. The Company reviews accounts for collectability based on an analysis of specific outstanding receivables, current economic conditions and past collection experience. For the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018, the Company determined that an allowance for doubtful accounts was not necessary.
F-10
J. Deferred rent receivables – Lease receivables are determined according to the terms of the lease agreements entered into by the Company and its lessees, as discussed within Note 3 ("Leased Properties And Leases"). Lease receivables primarily represent timing differences between straight-line revenue recognition and contractual lease receipts. As of December 31, 2019, lease payments by the Company's tenants have remained timely and without lapse.
K. Goodwill – Goodwill represents the excess of the amount paid for the MoGas business over the fair value of the net identifiable assets acquired. To comply with ASC 350, Intangibles - Goodwill and Other ("ASC 350"), the Company performs an impairment test for goodwill annually, or more frequently in the event that a triggering event has occurred. December 31st is the Company's annual testing date associated with its MoGas reporting unit.
In January 2017, the FASB issued ASU 2017-04, Simplifying the Test for Goodwill Impairment, which simplifies how an entity is required to test goodwill for impairment by eliminating step two from the goodwill impairment test. Effective January 1, 2017, the Company elected to early adopt this standard.
In accordance with ASC 350, a company may elect to perform a qualitative assessment to determine whether the quantitative impairment test is required. If the company elects to perform a qualitative assessment, the quantitative impairment test is required only if the conclusion is that it is more likely than not that the reporting unit's fair value is less than its carrying amount. If a company bypasses the qualitative assessment, the quantitative goodwill impairment test should be followed in step one.
Step one compares the fair value of the reporting unit to its carrying value to identify and measure any potential impairment. The reporting unit fair value is based upon consideration of various valuation methodologies, one of which is projecting future cash flows discounted at rates commensurate with the risks involved ("Discounted Cash Flow" or "DCF"). Assumptions used in a DCF require the exercise of significant judgment, including judgment about appropriate discount rates and terminal values, growth rates and the amount and timing of expected future cash flows. Forecasted cash flows require management to make judgments and assumptions, including estimates of future volumes and rates. Declines in volumes or rates from those forecasted, or other changes in assumptions, may result in a change in management's estimate and result in an impairment.
For the year ended December 31, 2019 annual impairment test, management proceeded directly to the step one quantitative approach as a result of the MoGas FERC rate case settlement approved in August of 2019. As of the December 31, 2019 testing date, the fair value of the MoGas reporting unit was determined to be greater than its carrying value and no impairment was recorded. The Company elected to perform a qualitative goodwill impairment assessment for the years ended December 31, 2018 and 2017. In performing the qualitative assessment, the Company analyzed the key drivers and other external factors that impact the business in order to determine if any significant events, transactions or other factors had occurred or were expected to occur that would impair earnings or competitiveness, therefore impairing the fair value of the MoGas reporting unit. After assessing the totality of events and circumstances, it was determined that it was not more likely than not that the fair value of the MoGas reporting unit was less than the carrying value, and so it was not necessary to perform the quantitative step one valuation. Key drivers that were considered in the qualitative evaluation of the MoGas reporting unit included: general economic conditions, continued recovery of the energy markets, natural gas pricing, input costs, liquidity and capital resources and customer outlook.
L. Debt Discount and Debt Issuance Costs – Costs incurred for the issuance of new debt are capitalized and amortized into interest expense over the debt term. Issuance costs related to long-term debt are recorded as a direct deduction from the carrying amount of that debt liability, net of accumulated amortization. Issuance costs related to line-of-credit arrangements however, are presented as an asset instead of a direct deduction from the carrying amount of the debt. In accordance with ASC 470, Debt ("ASC 470"), the Company recorded its Convertible Notes at the aggregate principal amount, less discount. The Company is amortizing the debt discount over the life of the Convertible Notes as additional non-cash interest expense utilizing the effective interest method. Refer to Note 11 ("Debt") for additional information.
M. Asset Retirement Obligations – The Company follows ASC 410-20, Asset Retirement Obligations, which requires that an asset retirement obligation ("ARO") associated with the retirement of a long-lived asset be recognized as a liability in the period in which it is incurred and becomes determinable, with an offsetting increase in the carrying amount of the associated asset. The Company recognized an existing ARO in conjunction with the acquisition of the GIGS in June of 2015.
The Company measures changes in the ARO liability due to passage of time by applying an interest method of allocation to the amount of the liability at the beginning of the period. The increase in the carrying amount of the liability is recognized as an expense classified as an operating item in the Consolidated Statements of Income, hereinafter referred to as ARO accretion expense. The Company periodically reassesses the timing and amount of cash flows anticipated associated with the ARO and adjusts the fair value of the liability accordingly under the guidance in ASC 410-20.
The fair value of the obligation at the acquisition date was capitalized as part of the carrying amount of the related long-lived assets and is being depreciated over the asset's remaining useful life. The useful lives of most pipeline gathering systems are primarily derived from available supply resources and ultimate consumption of those resources by end users. Adjustments to the ARO resulting
F-11
from reassessments of the timing and amount of cash flows will result in changes to the retirement costs capitalized as part of the carrying amount of the asset.
Upon decommissioning of the ARO or a portion thereof, the Company reduces the fair value of the liability and recognizes a (gain) loss on settlement of ARO as an operating item in the Consolidated Statements of Income for the difference between the liability and actual decommissioning costs incurred.
Refer to Note 12 ("Asset Retirement Obligation") for additional information.
N. Revenue Recognition – In May 2014, the FASB issued ASU No. 2014-09, Revenue from Contracts with Customers ("ASU 2014-09" or "ASC 606"), which became effective for all public entities on January 1, 2018. ASC 606 supersedes previously existing revenue recognition standards with a single model unless those contracts are within the scope of other standards (e.g. leases). The model requires an entity to recognize as revenue the amount of consideration to which it expects to be entitled for the transfer of promised goods or services to customers. A substantial portion of the Company's revenue consists of rental income from leasing arrangements, which is specifically excluded from ASC 606. However, the Company's transportation and distribution revenue is within the scope of the new guidance. The Company adopted ASC 606 effective on January 1, 2018 using the modified retrospective method. The Company elected to apply the guidance only to open contracts as of the effective date. The Company recognized the cumulative effect of applying the new standard as an adjustment to the opening balance of stockholders' equity. The comparative information has not been restated and continues to be reported under accounting standards in effect for those periods. Refer to Note 4 ("Transportation And Distribution Revenue") for further discussion of the transition impact and related disclosures under ASC 606.
Specific recognition policies for the Company's revenue items are as follows:
• | Lease revenue – Refer to Leased Property and Leases for the Company's lease revenue recognition policy. |
• | Transportation and distribution revenue – The Company's contracts related to transportation and distribution revenue are primarily comprised of a mix of natural gas supply, transportation and distribution performance obligations, as well as limited performance obligations related to system maintenance and improvement. Transportation revenues are recognized by MoGas and distribution revenues are recognized by Omega and Omega Gas Marketing, LLC. |
◦ | Under the Company's natural gas supply, transportation and distribution performance obligations, the customer simultaneously receives and consumes the benefit of the services as natural gas is delivered. Therefore, the transaction price is allocated proportionally over the series of identical performance obligations with each contract. The transaction price is calculated based on (i) index price, plus a contractual markup in the case of natural gas supply agreements (considered variable due to fluctuations in the index), (ii) FERC regulated rates or negotiated rates in the case of transportation agreements and (iii) contracted amounts (with annual CPI escalators) in the case of the Company's distribution agreement. Based on the nature of the agreements, revenue for all but one of the Company's natural gas supply, transportation and distribution performance obligations is recognized on a right to invoice basis as the performance obligations are met, which represents what the Company expects to receive in consideration and is representative of value delivered to the customer. The Company has a contract with one customer, Spire, that has fixed pricing which varies over the contract term. For this specific contract, the transaction price has been allocated ratably over the contractual performance obligation beginning in 2018 with the adoption of ASC 606. All invoicing is done in the month following service, with payment typically due a month from invoice date. |
◦ | The Company's contracts also contain performance obligations related to system maintenance and improvement, which are completed on an as-needed basis. The work performed is specific and tailored to the customer's needs and there are no alternative uses for the services provided. Therefore, as the work is being completed, control is transferring to the customer. These services are billed at the Company's cost, plus an agreed upon margin, and the Company has an enforceable right to payment as the services are provided. The Company invoices for this service on a monthly basis according to an agreed upon billing schedule. Revenue is recognized on an input method, based on the actual cost of a service as a measure of performance obligations satisfaction, which the Company determined to be the method which faithfully depicts the transfer of services. Differences between the amounts invoiced and revenue recognized under the input method are reflected as an asset or liability on the Consolidated Balance Sheets. Any differences are typically expected to be recognized within a year. As discussed in Note 3 ("Leased Properties And Leases"), the costs of system improvement projects are recognized as a financing arrangement in accordance with guidance in the lease standard while the margin is recognized in accordance with the revenue standard as discussed above. |
◦ | Beginning February 1, 2016, due to changes that commenced under a new contract with the Department of Defense ("DOD"), gas sales and cost of gas sales are presented on a net basis in the transportation and distribution revenue |
F-12
line. The Company continues to present the gas sales and cost of gas sales on a net basis upon adoption of ASC 606.
• | Financing revenue – Historically, financing notes receivable have been considered a core product offering and therefore the related income is presented as a component of operating income. For increasing rate loans, base interest income is recorded ratably over the life of the loan, using the effective interest rate. The net amount of deferred loan origination income and costs are amortized on a straight-line basis over the life of the loan and reported as an adjustment to yield in financing revenue. Participating financing revenues are recorded when specific performance criteria have been met. |
O. Transportation and distribution expense – Included here are both MoGas' costs of operating and maintaining the natural gas transmission line and Omega's costs of operating and maintaining the natural gas distribution system. These costs are incurred both internally and externally. The internal costs relate to system control, pipeline operations, maintenance, insurance and taxes. Other internal costs include payroll for employees associated with gas control, field employees and management. The external costs consist of professional services such as audit and accounting, legal and regulatory and engineering.
Historically, Omega's amounts paid for gas and propane delivered to customers were presented as cost of sales. Beginning February 1, 2016, under a new contract with the DOD, amounts paid by Omega for gas and propane are netted against sales and are presented in the transportation and distribution revenue line. See paragraph (N) above.
P. Other Income Recognition – Specific policies for the Company's other income items are as follows:
• | Net distributions and other income from investments – Distributions and dividends from investments are recorded on their ex-dates and are reflected as other income within the accompanying Consolidated Statements of Income. Distributions received from the Company's investments are generally characterized as ordinary income, capital gains and distributions received from investment securities. The portion characterized as return of capital is paid by the Company's investees from their cash flow from operations. The Company records investment income, capital gains and distributions received from investment securities based on estimates made at the time such distributions are received. Such estimates are based on information available from each company and other industry sources. These estimates may subsequently be revised based on information received from the entities after their tax reporting periods are concluded, as the actual character of these distributions is not known until after the fiscal year end of the Company. |
• | Net realized and unrealized gain (loss) from investments – Securities transactions are accounted for on the date the securities are purchased or sold. Realized gains and losses are reported on an identified cost basis. The Company records investment income and return of capital based on estimates made at the time such distributions are received. Such estimates are based on information available from the portfolio company and other industry sources. These estimates may subsequently be revised based on information received from the portfolio company after their tax reporting periods are concluded, as the actual character of these distributions are not known until after the Company's fiscal year end. |
Q. Asset Acquisition Expenses – Costs incurred in connection with the research of real property acquisitions not accounted for as business combinations are expensed until it is determined that the acquisition of the real property is probable. Upon such determination, costs incurred in connection with the acquisition of the property are capitalized as described in paragraph (C) above. Deferred costs related to an acquisition that the Company has determined, based on management's judgment, not to pursue are expensed in the period in which such determination is made. Costs incurred in connection with a business combination are expensed as incurred.
R. Offering Costs – Offering costs related to the issuance of common or preferred stock are charged to additional paid-in capital when the stock is issued.
S. Earnings Per Share – Basic earnings per share ("EPS") is computed using the weighted average number of common shares outstanding during the period. Diluted EPS is computed using the weighted average number of common and dilutive common equivalent shares outstanding during the period except for periods of net loss for which no common share equivalents are included because their effect would be anti-dilutive. Dilutive common equivalent shares consist of shares issuable upon conversion of the Convertible Notes calculated using the if-converted method.
T. Federal and State Income Taxation – In 2013 the Company qualified for REIT status, and in March 2014 elected (effective as of January 1, 2013), to be treated as a REIT for federal income tax purposes. Because certain of its assets may not produce REIT-qualifying income or be treated as interests in real property, those assets are held in wholly-owned TRSs in order to limit the potential that such assets and income could prevent the Company from qualifying as a REIT.
As a REIT, the Company holds and operates certain of its assets through one or more wholly-owned TRSs. The Company's use of TRSs enables it to continue to engage in certain businesses while complying with REIT qualification requirements and also allows it to retain income generated by these businesses for reinvestment without the requirement of distributing those earnings. In the
F-13
future, the Company may elect to reorganize and transfer certain assets or operations from its TRSs to the Company or other subsidiaries, including qualified REIT subsidiaries.
The Company's other equity securities are limited partnerships or limited liability companies which are treated as partnerships for federal and state income tax purposes. As a limited partner, the Company reports its allocable share of taxable income in computing its own taxable income. To the extent held by a TRS, the TRS's tax expense or benefit is included in the Consolidated Statements of Income based on the component of income or gains and losses to which such expense or benefit relates. Deferred income taxes reflect the net tax effects of temporary differences between the carrying amounts of assets and liabilities for financial reporting purposes and the amounts used for income tax purposes. A valuation allowance is recognized if, based on the weight of available evidence, it is more likely than not that some portion or all of the deferred income tax asset will not be realized. It is expected that for the year ended December 31, 2019, and future periods, any deferred tax liability or asset generated will be related entirely to the assets and activities of the Company's TRSs.
If the Company ceased to qualify as a REIT, the Company, as a C corporation, would be obligated to pay federal and state income tax on its taxable income.
U. Recent Accounting Pronouncements – In June of 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-13, Financial Instruments - Credit Losses ("ASU 2016-13"), which introduces an approach based on expected losses to estimate credit losses on certain types of financial instruments. The new model, referred to as the current expected credit losses ("CECL model"), will apply to financial assets subject to credit losses and measured at amortized cost, and certain off-balance sheet credit exposures. ASU 2016-13 is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2019, including interim periods within those fiscal years. In November of 2019, the FASB issued ASU 2019-10, Financial Instruments - Credit Losses (Topic 326), Derivatives and Hedging (Topic 815), and Leases (Topic 842) Effective Dates, which deferred the effective dates of these standards for certain entities. Based on the guidance for smaller reporting companies, the effective date of ASU 2016-13 is deferred for the Company until fiscal year 2023, and the Company has elected to defer adoption of this standard.
Although the Company has elected to defer adoption of ASU 2016-13, it will continue to evaluate the potential impact of the standard on its consolidated financial statements. As part of its ongoing assessment work, the Company has formed an implementation team, completed training on the CECL model and has begun developing policies, processes and internal controls.
3. LEASED PROPERTIES AND LEASES
The Company primarily acquires mid-stream and downstream assets in the U.S. energy sector such as pipelines, storage terminals, and gas and electric distribution systems and leases these assets to operators under triple-net leases. These leases typically include a contracted base rent with escalation clauses and participating rents that are tied to contract-specific criteria. Base rents under the Company's leases are structured on an estimated fair market value rent structure over the initial term, which includes assumptions related to the terminal value of the assets and expectations of tenant renewals. At the conclusion of the initial lease term, the Company's leases may contain fair market value repurchase options or fair market rent renewal terms. These clauses also act as safeguards against the Company's tenants pursuing activities which would undermine or degrade the value of the assets faster than the underlying reserves are depleted. Participating rents are structured to provide exposure to the successful commercial activity of the tenant, and as such, also provide protection in the event that the economic life of the assets is reduced based on accelerated production by the Company's tenants. While the Company is primarily a lessor, certain of its operating subsidiaries are lessees and have entered into lease agreements as discussed further below.
LESSOR - LEASED PROPERTIES
As of December 31, 2019, the Company had two significant leases. The properties, located in Wyoming, Louisiana and the Gulf of Mexico, are leased on a triple-net basis to major tenants, described in the table below. These major tenants are responsible for the payment of all taxes, maintenance, repairs, insurance and other operating expenses relating to the leased properties. The long-term, triple-net leases generally have an initial term of 11 to 15 years with options for renewals. Lease payments are scheduled to increase at varying intervals during the initial term of the leases. The following table summarizes the significant leased properties, major tenants and lease terms:
F-14
Summary of Leased Properties, Major Tenants and Lease Terms | ||
Property | Grand Isle Gathering System | Pinedale LGS |
Location | Gulf of Mexico/Louisiana | Pinedale, WY |
Tenant | Energy XXI GIGS Services, LLC | Ultra Wyoming LGS, LLC |
Asset Description | Approximately 137 miles of offshore pipeline with total capacity of 120 thousand Bbls/d, including a 16-acre onshore terminal and saltwater disposal system. | Approximately 150 miles of pipelines and four central storage facilities. |
Date Acquired | June 2015 | December 2012 |
Initial Lease Term | 11 years | 15 years |
Renewal Option | Equal to the lesser of 9-years or 75 percent of the remaining useful life | 5-year terms |
Current Monthly Rent Payments | 7/1/18 - 6/30/19: $2,860,917 7/1/19 - 6/30/20: $3,223,917 | $1,812,307(1) |
Estimated Useful Life | 27 years | 26 years |
(1) Monthly rent payments increased to $1,844,748 beginning January 1, 2020. | ||
The Company also concluded that Omega's long-term contract with the Department of Defense ("DOD") to provide natural gas distribution to Fort Leonard Wood through Omega's pipeline distribution system on the military post meets the definition of a lease under ASC 842. Omega is the lessor in the contract and the lease is classified as an operating lease. The Company noted the non-lease component is the predominant component in the lease, and the timing and pattern of transfer of the lease component and the associated non-lease component are the same. As discussed in Note 2 ("Significant Accounting Policies"), the Company elected a practical expedient that allows lessors to not separate lease and related non-lease components if the non-lease components otherwise would be accounted for in accordance with the revenue standard under ASC 606. With the election of this practical expedient, the Company continues to account for the DOD contract under the revenue standard.
In the second quarter of 2019, the Company started a system improvement project on Omega's pipeline distribution system, which is considered a "built to suit" transaction under ASC 842. The system improvement project is a separate lease component and the DOD is deemed to control the system improvement due to certain contract provisions. As a result, the Company is accounting for the costs of the system improvement as a financing arrangement, which is included in accounts and other receivables in the Consolidated Balance Sheets. The margin the Company earns on the system improvement project is a non-lease component accounted for under the revenue standard. Refer to Note 2 ("Significant Accounting Policies") for further details.
The future contracted minimum rental receipts for all leases as of December 31, 2019, are as follows:
Future Minimum Lease Receipts | |||
Year Ending December 31, | Amount | ||
2020 | $ | 65,772,473 | |
2021 | 71,734,473 | ||
2022 | 70,711,973 | ||
2023 | 67,663,973 | ||
2024 | 65,874,973 | ||
Thereafter | 129,321,920 | ||
Total | $ | 471,079,785 | |
The table below displays the Company's individually significant leases as a percentage of total leased properties and total lease revenues for the periods presented:
As a Percentage of (1) | ||||||||||||||
Leased Properties | Lease Revenues | |||||||||||||
As of December 31, | For the Years Ended December 31, | |||||||||||||
2019 | 2018 | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | ||||||||||
Pinedale LGS (2) | 44.4 | % | 44.5 | % | 39.2 | % | 35.2 | % | 31.2 | % | ||||
Grand Isle Gathering System | 55.3 | % | 55.2 | % | 60.6 | % | 55.9 | % | 59.1 | % | ||||
Portland Terminal Facility (3) | — | % | — | % | — | % | 8.8 | % | 9.6 | % | ||||
(1) Insignificant leases are not presented; thus percentages may not sum to 100%. | ||||||||||||||
(2) Pinedale LGS lease revenues include variable rent of $4.6 million, $4.3 million and $587 thousand for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, respectively. | ||||||||||||||
(3) On December 21, 2018, the Portland Terminal Facility was sold to Zenith Terminals, terminating the Portland Lease Agreement. | ||||||||||||||
F-15
The following table reflects the depreciation and amortization included in the accompanying Consolidated Statements of Income associated with the Company's leases and leased properties:
For the Years Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2019 | 2018 | 2017 | |||||||||
Depreciation Expense | |||||||||||
GIGS | $ | 9,763,163 | $ | 10,836,590 | $ | 9,754,596 | |||||
Pinedale | 8,869,440 | 8,869,440 | 8,869,440 | ||||||||
Portland Terminal Facility (1) | — | 1,243,769 | 1,275,660 | ||||||||
United Property Systems | 39,117 | 36,662 | 36,298 | ||||||||
Total Depreciation Expense | $ | 18,671,720 | $ | 20,986,461 | $ | 19,935,994 | |||||
Amortization Expense - Deferred Lease Costs | |||||||||||
GIGS | $ | 30,564 | $ | 30,564 | $ | 30,564 | |||||
Pinedale | 61,368 | 61,368 | 61,368 | ||||||||
Total Amortization Expense - Deferred Lease Costs | $ | 91,932 | $ | 91,932 | $ | 91,932 | |||||
ARO Accretion Expense | |||||||||||
GIGS | $ | 443,969 | $ | 499,562 | $ | 663,065 | |||||
Total ARO Accretion Expense | $ | 443,969 | $ | 499,562 | $ | 663,065 | |||||
(1) On December 21, 2018, the Portland Terminal Facility was sold to Zenith Terminals, terminating the Portland Lease Agreement. | |||||||||||
The following table reflects the deferred costs that are included in the accompanying Consolidated Balance Sheets associated with the Company's leased properties:
December 31, 2019 | December 31, 2018 | ||||||
Net Deferred Lease Costs | |||||||
GIGS | $ | 198,755 | $ | 229,319 | |||
Pinedale | 488,981 | 550,349 | |||||
Total Deferred Lease Costs, net | $ | 687,736 | $ | 779,668 | |||
TENANT INFORMATION
Substantially all of the lease tenants' financial results are driven by exploiting naturally occurring oil and natural gas hydrocarbon deposits beneath the Earth's surface. As a result, the tenants' financial results are highly dependent on the performance of the oil and natural gas industry, which is highly competitive and subject to volatility. During the terms of the leases, management monitors the credit quality of its tenants by reviewing their published credit ratings, if available, reviewing publicly available financial statements, or reviewing financial or other operating statements, monitoring news reports regarding the tenants and their respective businesses and monitoring the timeliness of lease payments and the performance of other financial covenants under their leases.
Ultra Petroleum
On March 14, 2017, the bankruptcy court issued an order confirming its plan of reorganization and on April 12, 2017, UPL emerged from bankruptcy. UPL is currently subject to the reporting requirements under the Exchange Act and is required to file with the SEC annual reports containing audited financial statements and quarterly reports containing unaudited financial statements. Its SEC filings can be found at www.sec.gov. Its common stock traded on the NASDAQ under the symbol UPL until August 8, 2019 at which time it commenced trading on the OTCQX marketplace under the symbol UPLC. The Company makes no representation as to the accuracy or completeness of the audited and unaudited financial statements of UPL but has no reason to doubt the accuracy or completeness of such information. In addition, UPL has no duty, contractual or otherwise, to advise the Company of any events that might have occurred subsequent to the date of such financial statements which could affect the significance or accuracy of such information. None of the information in the public reports of UPL that are filed with the SEC is incorporated by reference into, or in any way form, a part of this filing.
Energy Gulf Coast/Cox Oil
Prior to October 29, 2018, EGC was subject to the reporting requirements of the Exchange Act and was required to file with the SEC annual reports containing audited financial statements and quarterly reports containing unaudited financial statements. So long as EGC remained a public reporting company, the Grand Isle Lease Agreement provided this requirement was fulfilled by EGC making its financial statements and reports publicly available through the SEC’s EDGAR system, in lieu of delivering such information directly to the Company. On October 18, 2018, EGC was acquired by an affiliate of privately-held Cox Oil. Upon the filing by EGC of a Form 15 with the SEC on October 29, 2018, EGC's SEC reporting obligations were suspended and it ceased to file such reports.
F-16
The Company believes the terms of the Grand Isle Lease Agreement require copies of certain financial statement information be provided that the Company is required to file pursuant to SEC Regulation S-X, as described in Section 2340 of the SEC Financial Reporting Manual. When EGC's financial information ceased to be publicly available, the Company encouraged officials of EGC and Cox Oil and, through Company counsel, the legal counsel to such entities, to satisfy their obligations under the Grand Isle Lease Agreement to provide the required information to the Company for inclusion in its SEC reports. To date, EGC and Cox Oil have refused to fulfill these obligations. The Company sought to enforce the obligations of EGC and Cox Oil and obtained a temporary restraining order ("TRO") from a Texas state court, mandating that they deliver the required EGC financial statements for the year ended December 31, 2018. The TRO was stayed pending an appeal by EGC and Cox Oil and, pursuant to its own terms, had lapsed by the time that appeal was denied on January 6, 2020. The case has been remanded to the trial court for further proceedings. The Company is requesting a hearing for as early in April 2020 as possible to obtain a temporary injunction mandating our tenant deliver the required financial statements, and will continue to pursue all viable options to obtain and file the necessary financial statements. The Company expects to file the financial statement information that is required by Regulation S-X by amendment to its Annual Reports on Form 10-K for the years ended December 31, 2018 and 2019, once such information is made available in accordance with the terms of the lease.
EGC's SEC filings prior to October 29, 2018 can be found at www.sec.gov. The Company makes no representation as to the accuracy or completeness of the audited and unaudited financial statements of EGC but has no reason to doubt the accuracy or completeness of such information. In addition, EGC has no duty, contractual or otherwise, to advise the Company of any events that might have occurred subsequent to the date of such financial statements which could affect the significance or accuracy of such information. None of the information in the public reports of EGC that are filed with the SEC is incorporated by reference into, or in any way form, a part of this filing.
Sale of the Portland Terminal Facility
On December 21, 2018, the Company entered into a Purchase and Sale Agreement with Zenith Energy Terminals Holdings, LLC ("Zenith Terminals"), the Company's tenant under the Portland Lease Agreement, to sell the Portland Terminal Facility and remaining interest in the Joliet Terminal ("Joliet") for an aggregate consideration of $61.0 million, net of transaction costs. Of the negotiated sale price of $61.0 million, approximately $56.0 million was paid in cash at closing, with the balance of $5.0 million in a promissory note, which was paid on January 7, 2019. The sale of the Portland Terminal Facility effectively terminated the Portland Lease Agreement, dated January 14, 2014, between the Company and Zenith Terminals.
The consideration was allocated to the Portland Terminal Facility ($60.6 million) and Joliet ($0.4 million) based on fair value information utilized in negotiating the transaction. As of December 21, 2018, the Portland Terminal Facility had a carrying value of $45.7 million. The sale of the Portland Terminal Facility resulted in a gain on sale of leased asset of approximately $11.7 million, net of deferred rent receivable of approximately $3.2 million. Prior to the sale of the Joliet interest, the equity interest was valued at its transacted value of $1.2 million from the required reinvestment during the Arc Logistics merger with Zenith in December 2017. The sale of the Joliet interest resulted in a realized loss on other equity securities of approximately $715 thousand. Both the gain on sale of leased asset, net and the realized loss on other equity securities are included as items in other income (expense) in the Consolidated Statements of Income for the year ended December 31, 2018. Refer to Note 10 ("Fair Value") for additional information on the sale of the interest in Joliet.
Acquisition of Pinedale LGS Non-Controlling Interest
On December 29, 2017, Pinedale LP I, a wholly-owned subsidiary of the Company, purchased Prudential's 18.95 percent non-controlling equity interest in Pinedale LP for considerations of approximately $32.9 million. The carrying value of Prudential's non-controlling interest at the transaction date was $27.3 million. As the transaction resulted in an increase in the Company's interest in Pinedale LP, but not a change in control, the purchase was accounted for as an equity transaction. The difference between the fair value of the purchase consideration and the carrying value of the non-controlling interest of $5.6 million was recognized in additional paid-in-capital and attributable to the Company. Upon closing the transaction, the Company indirectly owns 100 percent of Pinedale LP through its wholly-owned subsidiaries Pinedale GP and Pinedale LP I and there is no longer a noncontrolling interest in the Company's consolidated financial statements.
LESSEE - LEASED PROPERTIES
The Company's operating subsidiaries currently lease single-use office space and equipment with remaining lease terms of less than one year, some of which may include renewal options. These leases are classified as operating leases and immaterial to the consolidated financial statements. The Company recognizes lease expense in the Consolidated Statements of Income on a straight-line basis over the remaining lease term.
In accordance with ASC 842 transition disclosure requirements, the cumulative effect of changes made to the Consolidated Balance Sheets as of January 1, 2019 for the adoption of ASC 842 were as follows:
F-17
Balance Sheet | Balance at December 31, 2018 | Adjustments Due to ASC 842 | Balance at January 1, 2019 | |||||||||
Assets | ||||||||||||
Prepaid expenses and other assets | $ | 668,584 | $ | 74,534 | $ | 743,118 | ||||||
Liabilities | ||||||||||||
Accounts payable and other accrued liabilities | 3,493,490 | 74,534 | 3,568,024 | |||||||||
Equity | ||||||||||||
Retained earnings | 9,147,701 | — | 9,147,701 | |||||||||
4. TRANSPORTATION AND DISTRIBUTION REVENUE
The Company's contracts related to transportation and distribution revenue are primarily comprised of a mix of natural gas supply, transportation and distribution performance obligations, as well as limited performance obligations related to system maintenance and improvement. Refer to Note 2 ("Significant Accounting Policies") for additional details on the Company's revenue recognition guidance under ASC 606.
Based on a downward revision of the rate during the Company's contract with Spire, ASC 606 requires the Company to record the contractual transaction price, and therefore aggregate revenue, from the contract ratably over the term of the contract. Accordingly, on January 1, 2018, the Company recorded a cumulative adjustment to recognize a contract liability of approximately $3.3 million, and a corresponding reduction to beginning equity (net of deferred tax impact). The adjustment reflects the difference in amounts previously recognized as invoiced, versus cumulative revenues earned under the contract on a straight-line basis in accordance with ASC 606, as of the date of adoption. The contract liability continued to accumulate additional unrecognized performance obligations at a rate of approximately $992 thousand per quarter until the contractual rate decrease took effect in November 2018. Following the rate decline, recognized performance obligations exceeded amounts invoiced and the contract liability began to decline at a rate of approximately $138 thousand per quarter and will continue to decline at the same rate through the end of the contract in October 2030. As of December 31, 2019, the revenue allocated to the remaining performance obligation under this contract is approximately $58.1 million.
The table below summarizes the Company's contract liability balance related to its transportation and distribution revenue contracts as of December 31, 2019 and 2018:
Contract Liability(1) | |||||||
December 31, 2019 | December 31, 2018 | ||||||
Beginning Balance January 1 | $ | 6,522,354 | $ | — | |||
Cumulative Transition Adjustment Upon Adoption of ASC 606 | — | 3,307,109 | |||||
Unrecognized Performance Obligations | 887,916 | 3,307,109 | |||||
Recognized Performance Obligations | (559,480 | ) | (91,864 | ) | |||
Ending Balance December 31 | $ | 6,850,790 | $ | 6,522,354 | |||
(1) The contract liability balance is included in unearned revenue in the Consolidated Balance Sheets. | |||||||
The Company's contract asset balance was $206 thousand and $181 thousand as of December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively. The contract asset balance is included in prepaid expenses and other assets in the Consolidated Balance Sheets.
The following is a breakout of the Company's transportation and distribution revenue for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017:
For the Years Ended December 31, | ||||||||
2019 | 2018 | 2017 | ||||||
Natural gas transportation contracts | 67.8 | % | 64.3 | % | 71.5 | % | ||
Natural gas distribution contracts | 25.5 | % | 26.8 | % | 20.4 | % | ||
5. FINANCING NOTES RECEIVABLE
Four Wood Financing Note Receivable
On December 31, 2014, Four Wood Corridor entered into loan agreements with SWD Enterprises, which were placed on non-accrual status during the first quarter of 2016. On December 12, 2018, Four Wood Corridor granted SWD Enterprises approval to sell real and personal property that provide saltwater disposal services for the oil and natural gas industry to Compass SWD, LLC ("Compass SWD") in exchange for Compass SWD executing a loan agreement with Four Wood Corridor for $1.3 million (the "Compass REIT
F-18
Loan") and approximately $237 thousand in cash consideration, net of costs facilitating the close. The Compass REIT Loan was scheduled to mature on June 15, 2019 with interest accruing on the outstanding principal at an annual rate of LIBOR plus 6 percent. As a result of the transaction, SWD Enterprises was released from their loan agreements, and the Company recognized a provision for loan gain of $37 thousand in the Consolidated Statements of Income for the year ended December 31, 2018.
On June 12, 2019, Four Wood Corridor entered into an amended and restated Compass REIT Loan. The amended note has a two-year term maturing on June 30, 2021 with monthly principal payments of approximately $11 thousand and interest accruing on the outstanding principal at an annual rate of 8.5 percent. The amended and restated Compass REIT Loan is secured by real and personal property that provides saltwater disposal services for the oil and natural gas industry and pledged ownership interests of Compass SWD members. As of December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, the Compass REIT Loan was valued at $1.2 million and $1.3 million, respectively.
6. INCOME TAXES
Deferred income taxes reflect the net tax effect of temporary differences between the carrying amount of assets and liabilities for financial reporting and tax purposes. Components of the Company's deferred tax assets and liabilities as of December 31, 2019 and 2018, are as follows:
Deferred Tax Assets and Liabilities | |||||||
December 31, 2019 | December 31, 2018 | ||||||
Deferred Tax Assets: | |||||||
Deferred contract revenue | $ | 1,529,473 | $ | 1,691,899 | |||
Net operating loss carryforwards | 5,622,052 | 5,424,671 | |||||
Loan loss provision | — | 263,508 | |||||
Accrued liabilities | 424,604 | 83,325 | |||||
Capital loss carryforward | 104,595 | — | |||||
Other | 6,184 | 12,370 | |||||
Sub-total | $ | 7,686,908 | $ | 7,475,773 | |||
Valuation allowance | (104,595 | ) | — | ||||
Sub-total | $ | 7,582,313 | $ | 7,475,773 | |||
Deferred Tax Liabilities: | |||||||
Cost recovery of leased and fixed assets | $ | (2,953,319 | ) | $ | (2,508,547 | ) | |
Other | (35,433 | ) | (19,023 | ) | |||
Sub-total | $ | (2,988,752 | ) | $ | (2,527,570 | ) | |
Total net deferred tax asset | $ | 4,593,561 | $ | 4,948,203 | |||
As of December 31, 2019, the total deferred tax assets and liabilities presented above relate to the Company's TRSs. The Company recognizes the tax benefits of uncertain tax positions only when the position is "more likely than not" to be sustained upon examination by the tax authorities based on the technical merits of the tax position. The Company's policy is to record interest and penalties on uncertain tax positions as part of tax expense. Tax years subsequent to the year ended December 31, 2015, remain open to examination by federal and state tax authorities.
For the year ending December 31, 2019, the Company generated a capital loss carryforward resulting from the liquidation of Lightfoot. The amount of the carryforward for tax purposes was approximately $500 thousand, and if not utilized, this carryforward will expire as of December 31, 2024. Management assessed the available evidence and determined that it is more likely than not that the capital loss carryforward will not be utilized prior to expiration. Due to the uncertainty of realizing this deferred tax asset, a valuation allowance of $105 thousand was recorded equal to the amount of the tax benefit of this carryforward at December 31, 2019. In the future, if the Company concludes, based on existence of sufficient evidence, that it should realize more or less of its deferred tax assets, the valuation allowance will be adjusted accordingly in the period such conclusion is made.
The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (the "2017 Tax Act") was enacted on December 22, 2017. The 2017 Tax Act reduced the US federal corporate tax rate from 35 percent to 21 percent. The 2017 Tax Act also repealed the alternative minimum tax for corporations. In December 2018, the Company completed its accounting for the tax effects of enactment of the 2017 Tax Act as allowed under SEC Staff Accounting Bulletin 118. The Company remeasured deferred tax assets and liabilities based on the updated rates at which they are expected to reverse in the future, which resulted in a $1.3 million transition adjustment that reduced net deferred tax assets. One of the Company's TRSs qualifies for the regulated utility and real property business exceptions under the new proposed treasury regulations for Section 163(j). Therefore, previously disqualified interest from years prior to 2018 was deducted and resulted in a reclassification from other deferred tax assets to deferred tax assets for net operating loss carryforwards during the year ended
F-19
December 31, 2018. Refer to additional discussion of the Company's net operating loss carryforwards below. The Company will continue to assess the impact of new tax legislation, as well as any future regulations and updates provided by the tax authorities.
Total income tax expense (benefit) differs from the amount computed by applying the federal statutory income tax rate of 21 percent for the years ended December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018 and 35 percent for the year ended December 31, 2017, to income or loss from operations and other income and expense for the years presented, as follows:
Income Tax Expense (Benefit) | |||||||||||
For the Years Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2019 | 2018 | 2017 | |||||||||
Application of statutory income tax rate | $ | 904,111 | $ | 8,671,562 | $ | 12,231,838 | |||||
State income taxes, net of federal tax benefit | 409,839 | (583,186 | ) | 352,708 | |||||||
Income of Real Estate Investment Trust not subject to tax | (941,900 | ) | (10,339,520 | ) | (11,975,853 | ) | |||||
Tax reform impact | — | — | 1,262,444 | ||||||||
Other | (137,432 | ) | (167,582 | ) | 474,181 | ||||||
Total income tax expense (benefit) | $ | 234,618 | $ | (2,418,726 | ) | $ | 2,345,318 | ||||
Total income taxes are computed by applying the federal statutory rate of 21 percent plus a blended state income tax rate. Corridor Public and Corridor Private had a blended state rate of approximately 5.53 percent and 3.78 percent for the years ended December 31, 2018 and 2017, respectively. In the first quarter of 2019, the state rate for Corridor Public and Corridor Private was adjusted to zero for current and future state liabilities. The decrease in the state rate was the result of the 2018 sale or disposition of assets within the investments held by Corridor Private. CorEnergy BBWS had a blended state income tax rate of approximately 5 percent for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018 due to its operations in Missouri. CorEnergy BBWS did not record a provision for state income taxes for the year ended December 31, 2017 because it only operated in Wyoming, which does not have state income tax. Because Corridor MoGas primarily only operates in the state of Missouri, a blended state income tax rate of 5 percent was used for the operation of the TRS for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017. For CorEnergy BBWS and Corridor MoGas, the blended state rate includes the enacted decrease in the Missouri state income tax rate effective in 2020. As a result of the decreased rate, additional deferred state income taxes of $315 thousand resulting from the application of the newly enacted rate to existing deferred balances was recorded in the first quarter of 2019. Prior to its reorganization to a QRS at the end of 2017, Mowood Corridor, Inc. had a blended state income tax rate of 5 percent for the year ended December 31, 2017.
For the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, all of the income tax expense (benefit) presented above relates to the assets and activities held in the Company's TRSs. The components of income tax expense (benefit) include the following for the periods presented:
Components of Income Tax Expense (Benefit) | |||||||||||
For the Years Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2019 | 2018 | 2017 | |||||||||
Current tax expense (benefit) | |||||||||||
Federal | $ | (159,381 | ) | $ | (413,248 | ) | $ | 2,498,363 | |||
State (net of federal tax benefit) | 39,357 | (172,138 | ) | 333,295 | |||||||
Total current tax expense (benefit) | $ | (120,024 | ) | $ | (585,386 | ) | $ | 2,831,658 | |||
Deferred tax expense (benefit) | |||||||||||
Federal | $ | (15,840 | ) | $ | (1,422,292 | ) | $ | (505,753 | ) | ||
State (net of federal tax benefit) | 370,482 | (411,048 | ) | 19,413 | |||||||
Total deferred tax expense (benefit) | $ | 354,642 | $ | (1,833,340 | ) | $ | (486,340 | ) | |||
Total income tax expense (benefit), net | $ | 234,618 | $ | (2,418,726 | ) | $ | 2,345,318 | ||||
As of December 31, 2019 and 2018, the TRSs had a cumulative net operating loss of $23.5 million and $17.1 million, respectively. Net operating losses of $19.8 million generated during the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018 may be carried forward indefinitely, subject to limitation. Net operating losses generated for years prior to December 31, 2018 may be carried forward for 20 years. If not utilized, the net operating loss will expire as follows: $328 thousand, $176 thousand, $1.2 million and $2.0 million in the years ending December 31, 2034, 2035, 2036 and 2037, respectively.
F-20
The aggregate cost of securities for federal income tax purposes and securities with unrealized appreciation and depreciation, were as follows:
Aggregate Cost of Securities for Income Tax Purposes | |||||||
December 31, 2019 | December 31, 2018 | ||||||
Aggregate cost for federal income tax purposes | $ | 345,241 | $ | 408,051 | |||
Gross unrealized appreciation | — | — | |||||
Gross unrealized depreciation | — | — | |||||
Net unrealized appreciation | $ | — | $ | — | |||
The Company provides the following tax information to its common stockholders pertaining to the character of distributions paid during tax years 2019, 2018 and 2017. For a common stockholder that received all distributions in cash during 2019, 65.1 percent will be treated as ordinary dividend income, 32.9 percent will be treated as return of capital and 2.0 percent will be treated as capital gain distributions. Of the ordinary dividend income, none will be treated as qualified dividend income for a non-corporate taxpayer; all of the ordinary dividend income may be taken into account on an individual's section 199A deduction, subject to the applicable holding period. Of the capital gain distribution, 100.0 percent is subject to a maximum 20 percent federal income tax rate. The per share characterization by quarter is reflected in the following tables:
2019 Common Stock Tax Information | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Record Date | Ex-Dividend Date | Payable Date | Total Distribution per Share | Total Ordinary Dividends | Qualified Dividends | Capital Gain Distributions | Nondividend Distributions | Section 199A Dividends | ||||||||||||||||||||
2/14/2019 | 2/13/2019 | 2/28/2019 | $ | 0.7500 | $ | 0.5803 | $ | — | $ | 0.0156 | $ | 0.1541 | $ | 0.5803 | ||||||||||||||
5/17/2019 | 5/16/2019 | 5/31/2019 | 0.7500 | 0.4578 | — | 0.0150 | 0.2772 | 0.4578 | ||||||||||||||||||||
8/16/2019 | 8/15/2019 | 8/30/2019 | 0.7500 | 0.4578 | — | 0.0150 | 0.2772 | 0.4578 | ||||||||||||||||||||
11/15/2019 | 11/14/2019 | 11/29/2019 | 0.7500 | 0.4578 | — | 0.0150 | 0.2772 | 0.4578 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Total 2019 Distributions | $ | 3.0000 | $ | 1.9537 | $ | — | $ | 0.0606 | $ | 0.9857 | $ | 1.9537 | ||||||||||||||||
2018 Common Stock Tax Information | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Record Date | Ex-Dividend Date | Payable Date | Total Distribution per Share | Total Ordinary Dividends | Qualified Dividends | Capital Gain Distributions | Unrecaptured Section 1250 Gain | Section 199A Dividends | ||||||||||||||||||||
2/14/2018 | 2/13/2018 | 2/28/2018 | $ | 0.7500 | $ | 0.5346 | $ | — | $ | 0.2154 | $ | 0.1007 | $ | 0.5346 | ||||||||||||||
5/17/2018 | 5/16/2018 | 5/31/2018 | 0.7500 | 0.5346 | — | 0.2154 | 0.1007 | 0.5346 | ||||||||||||||||||||
8/17/2018 | 8/16/2018 | 8/31/2018 | 0.7500 | 0.5346 | — | 0.2154 | 0.1007 | 0.5346 | ||||||||||||||||||||
11/15/2018 | 11/14/2018 | 11/30/2018 | 0.7500 | 0.5346 | — | 0.2154 | 0.1007 | 0.5346 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Total 2018 Distributions | $ | 3.0000 | $ | 2.1384 | $ | — | $ | 0.8616 | $ | 0.4028 | $ | 2.1384 | ||||||||||||||||
2017 Common Stock Tax Information | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Record Date | Ex-Dividend Date | Payable Date | Total Distribution per Share | Total Ordinary Dividends | Qualified Dividends | Capital Gain Distributions | Nondividend Distributions | |||||||||||||||||
2/13/2017 | 2/9/2017 | 2/28/2017 | $ | 0.7500 | $ | 0.5925 | $ | 0.0785 | $ | — | $ | 0.1575 | ||||||||||||
5/16/2017 | 5/12/2017 | 5/31/2017 | 0.7500 | 0.5925 | 0.0785 | — | 0.1575 | |||||||||||||||||
8/17/2017 | 8/15/2017 | 8/31/2017 | 0.7500 | 0.5925 | 0.0785 | — | 0.1575 | |||||||||||||||||
11/15/2017 | 11/14/2017 | 11/30/2017 | 0.7500 | 0.5925 | 0.0785 | — | 0.1575 | |||||||||||||||||
Total 2017 Distributions | $ | 3.0000 | $ | 2.3700 | $ | 0.3140 | $ | — | $ | 0.6300 | ||||||||||||||
The Company provides the following tax information to its preferred stockholders pertaining to the character of distributions paid during the 2019, 2018 and 2017 tax years. For a preferred stockholder that received all distributions in cash during 2019, 96.9 percent will be treated as ordinary dividend income, none will be treated as return of capital and 3.1 percent will be treated as capital gain distributions. Of the ordinary dividend income, none will be treated as qualified dividend income for a non-corporate taxpayer; all of the ordinary dividend income may be taken into account on an individual's section 199A deduction, subject to the applicable holding period. Of the capital gain distribution, 100.0 percent is subject to a maximum 20 percent federal income tax rate. The per share characterization by quarter is reflected in the following tables:
F-21
2019 Preferred Stock Tax Information | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Record Date | Ex-Dividend Date | Payable Date | Total Distribution per Share | Total Ordinary Dividends | Qualified Dividends | Capital Gain Distributions | Nondividend Distributions | Section 199A Dividends | ||||||||||||||||||||
2/14/2019 | 2/13/2019 | 2/28/2019 | $ | 0.4609 | $ | 0.4483 | $ | — | $ | 0.0126 | $ | — | $ | 0.4483 | ||||||||||||||
5/17/2019 | 5/16/2019 | 5/31/2019 | 0.4609 | 0.4463 | — | 0.0146 | — | 0.4463 | ||||||||||||||||||||
8/16/2019 | 8/15/2019 | 8/30/2019 | 0.4609 | 0.4463 | — | 0.0146 | — | 0.4463 | ||||||||||||||||||||
11/15/2019 | 11/14/2019 | 11/29/2019 | 0.4609 | 0.4463 | — | 0.0146 | — | 0.4463 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Total 2019 Distributions | $ | 1.8436 | $ | 1.7872 | $ | — | $ | 0.0564 | $ | — | $ | 1.7872 | ||||||||||||||||
2018 Preferred Stock Tax Information | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Record Date | Ex-Dividend Date | Payable Date | Total Distribution per Share | Total Ordinary Dividends | Qualified Dividends | Capital Gain Distributions | Unrecaptured Section 1250 Gain | Section 199A Dividends | ||||||||||||||||||||
2/14/2018 | 2/13/2018 | 2/28/2018 | $ | 0.4609 | $ | 0.3285 | $ | — | $ | 0.1324 | $ | 0.0619 | $ | 0.3285 | ||||||||||||||
5/17/2018 | 5/16/2018 | 5/31/2018 | 0.4609 | 0.3285 | — | 0.1324 | 0.0619 | 0.3285 | ||||||||||||||||||||
8/17/2018 | 8/16/2018 | 8/31/2018 | 0.4609 | 0.3285 | — | 0.1324 | 0.0619 | 0.3285 | ||||||||||||||||||||
11/15/2018 | 11/14/2018 | 11/30/2018 | 0.4609 | 0.3285 | — | 0.1324 | 0.0619 | 0.3285 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Total 2018 Distributions | $ | 1.8436 | $ | 1.3140 | $ | — | $ | 0.5296 | $ | 0.2476 | $ | 1.3140 | ||||||||||||||||
2017 Preferred Stock Tax Information | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Record Date | Ex-Dividend Date | Payable Date | Total Distribution per Share | Total Ordinary Dividends | Qualified Dividends | Capital Gain Distributions | Nondividend Distributions | |||||||||||||||||
02/13/2017 | 2/9/2017 | 2/28/2017 | $ | 0.4609 | $ | 0.4609 | $ | 0.0611 | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||||||||
05/16/2017 | 5/12/2017 | 5/31/2017 | 0.4609 | 0.4609 | 0.0611 | — | — | |||||||||||||||||
8/17/2017 | 8/15/2017 | 8/31/2017 | 0.4609 | 0.4609 | 0.0611 | — | — | |||||||||||||||||
11/15/2017 | 11/14/2017 | 11/30/2017 | 0.4609 | 0.4609 | 0.0611 | — | — | |||||||||||||||||
Total 2017 Distributions | $ | 1.8436 | $ | 1.8436 | $ | 0.2444 | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||||||||||
The Company elected, effective for the 2013 tax year, to be treated as a REIT for federal income tax purposes. The Company's REIT election, assuming continued compliance with the applicable tests, will continue in effect for subsequent tax years. The Company satisfied the annual income test and the quarterly asset tests necessary for us to qualify to be taxed as a REIT for 2019, 2018 and 2017. Distributions made during 2017 were treated as qualifying dividend income related to taxable dividends received from the Company's TRSs that were received and distributed in the same year.
7. PROPERTY AND EQUIPMENT
Property and equipment consist of the following:
Property and Equipment | |||||||
December 31, 2019 | December 31, 2018 | ||||||
Land | $ | 605,070 | $ | 580,000 | |||
Natural gas pipeline | 124,614,696 | 124,306,175 | |||||
Vehicles and trailers | 671,962 | 696,164 | |||||
Office equipment and computers | 268,559 | 268,559 | |||||
Gross property and equipment | $ | 126,160,287 | $ | 125,850,898 | |||
Less: accumulated depreciation | (19,304,610 | ) | (15,969,346 | ) | |||
Net property and equipment | $ | 106,855,677 | $ | 109,881,552 | |||
Depreciation expense was $3.4 million for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, respectively.
F-22
8. CONCENTRATIONS
The Company has customer concentrations through major tenants at its two significant leased properties as discussed fully in Note 3 ("Leased Properties And Leases"). In addition to these lease concentrations, contracted transportation revenues from the Company's subsidiary, MoGas, to its largest customer, Spire (formally Laclede Gas Company), represented approximately 7 percent, 6 percent and 11 percent of consolidated revenues for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, respectively. The Company's contracted transportation revenues with Spire beginning with the year ended December 31, 2018 were impacted by the adoption of ASC 606, which required the Company to record the contract with Spire on a straight-line basis and record a transition adjustment on January 1, 2018. Refer to Note 4 ("Transportation And Distribution Revenue") for additional details.
9. MANAGEMENT AGREEMENT
The Company has executed a Management Agreement with Corridor InfraTrust Management, LLC ("Corridor"), a related party. Under the Management Agreement, Corridor (i) presents the Company with suitable acquisition opportunities consistent with the investment policies and objectives of the Company, (ii) is responsible for the day-to-day operations of the Company and (iii) performs such services and activities relating to the assets and operations of the Company as may be appropriate. The Management Agreement, which does not have a specific term and will remain in place unless terminated by the Company or Corridor in accordance with its terms, does give a majority of the stockholders of the Company, or two-thirds of the independent directors, the ability to terminate the agreement for any reason on thirty (30) days' prior written notice, so long as that notice is delivered with a termination payment equal to three times the base management fee and incentive fee paid to the manager in the last four quarters.
The terms of the Management Agreement provide for a quarterly management fee to be paid to Corridor equal to 0.25 percent (1.00 percent annualized) of the value of the Company's Managed Assets as of the end of each quarter. "Managed Assets" means the total assets of the Company (including any securities receivables, other personal property or real property purchased with or attributable to any borrowed funds) minus (A) the initial invested value of all non-controlling interests, (B) the value of any hedged derivative assets, (C) any prepaid expenses and (D) all of the accrued liabilities other than (1) deferred taxes and (2) debt entered into for the purpose of leverage. For purposes of the definition of Managed Assets, the Company's securities portfolio will be valued at then current market value. For purposes of the definition of Managed Assets, other personal property and real property assets will include real and other personal property owned and the assets of the Company invested, directly or indirectly, in equity interests in or loans secured by real estate or personal property (including acquisition related costs and acquisition costs that may be allocated to intangibles or are unallocated), valued at the aggregate historical cost, before reserves for depreciation, amortization, impairment charges or bad debts or other similar noncash reserves. In light of previous provisions for loan losses on certain of the Company's energy infrastructure financing investments, the Manager voluntarily recommended, and the Company agreed, that effective on and after the Company's March 31, 2016 balance sheet date, solely for the purpose of computing the value of the Company's Managed Assets in calculating the quarterly management fee under the terms of the Management Agreement, that portion of the Management Fee attributable to such loans shall be based on the estimated net realizable value of the loans, which shall not exceed the amount invested in the loans as of the end of the quarter for which the Management Fee is to be calculated.
The Management Agreement also provides for payment of a quarterly incentive fee of 10 percent of the increase in distributions paid over a distribution threshold equal to $0.625 per share per quarter, and requires that at least half of any incentive fees that are paid be reinvested in the Company's common stock. The foregoing description of the terms of the May 1, 2015 Management Agreement is qualified in its entirety by reference to the full terms of such agreement, which is incorporated by reference as an exhibit to this Report.
During the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2017, the Company and the Manager agreed to the following modifications to the fee arrangements described above:
• | During the year ended December 31, 2017, the Manager voluntarily recommended, and the Company agreed, that the Manager would waive $100 thousand of the total $595 thousand incentive fee that would otherwise be payable under the provisions of the Management Agreement with respect to dividends paid on the Company's common stock. |
• | In order to ensure equitable application of the quarterly management fee provisions of the Management Agreement for the acquisition of Prudential's minority limited partner interest in Pinedale LP, which closed on December 29, 2017, the Manager waived any incremental management fee due as of the end of the fourth quarter of 2017 based on the net impact of the Pinedale LP acquisition. |
• | During the year ended December 31, 2019, the Manager voluntarily recommended, and the Company agreed, that the Manager would waive $470 thousand of the total $658 thousand incentive fee that would otherwise be payable under the provisions of the Management Agreement with respect to dividends paid on the Company's common stock. |
• | In reviewing the application of the quarterly management fee provisions of the Management Agreement to the net proceeds received during the third quarter of 2019 from the offering of 5.875% Convertible Notes, which closed on August 12, 2019, |
F-23
the Manager waived any incremental management fee due as of the end of the third and fourth quarters of 2019 based on such proceeds (other than the cash portion of such proceeds that was utilized in connection with the exchange of the Company’s 7.00% Convertible Notes).
Fees incurred under the Management Agreement for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017 were $6.8 million, $7.6 million and $7.2 million, respectively, and are reported in the General and Administrative line item on the Consolidated Statements of Income.
The Company pays Corridor, as the Company's Administrator pursuant to an Administrative Agreement, an administrative fee equal to an annual rate of 0.04 percent of the value of the Company's Managed Assets, with a minimum annual fee of $30 thousand. Fees incurred under the Administrative Agreement for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017 were $264 thousand, $280 thousand and $269 thousand, respectively, and are reported in the General and Administrative line item on the Consolidated Statements of Income.
10. FAIR VALUE
As a result of the sale or disposition of the Company's equity securities in 2018, there are no assets or liabilities measured at fair value on a recurring basis as of December 31, 2019 and 2018.
The changes for all Level 3 securities measured at fair value on a recurring basis using significant unobservable inputs for the year ended December 31, 2018, are as follows:
Level 3 Rollforward | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
For the Year Ended 2018 | Fair Value Beginning Balance | Acquisitions | Disposals | Total Realized and Unrealized Losses Included in Net Income | Return of Capital Adjustments Impacting Cost Basis of Securities | Fair Value Ending Balance | Changes in Unrealized Losses Included In Net Income, Relating to Securities Still Held | |||||||||||||||||||||
Other equity securities | $ | 2,958,315 | $ | — | $ | (449,067 | ) | $ | (1,845,309 | ) | $ | (663,939 | ) | $ | — | $ | — | |||||||||||
Total | $ | 2,958,315 | $ | — | $ | (449,067 | ) | $ | (1,845,309 | ) | $ | (663,939 | ) | $ | — | $ | — | |||||||||||
The Company utilizes the beginning of reporting period method for determining transfers between levels. There were no transfers between levels 1, 2 or 3 for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018.
Valuation Techniques and Unobservable Inputs
The Company's other equity securities, which represent securities issued by private companies, were classified as Level 3 assets and the Company elected to report at fair value under the fair value option. Significant judgment was required in selecting the assumptions used to determine the fair values of these investments.
Lightfoot
The Company's Lightfoot investment consisted of a 6.6 percent and 1.5 percent equity interest in Lightfoot LP and Lightfoot GP, respectively. On December 21, 2017, Zenith closed its acquisition of Arc Logistics. Subsequent to closing of the transaction, the Company received $7.6 million in cash proceeds related to its pro rata portion of the sale proceeds of Lightfoot, including proceeds related to Arc Logistics common units, the unconditional interest in Gulf LNG and membership interests in Arc Logistics GP. Amounts received are net of approximately $1.2 million related to the Company's required reinvestment in Joliet.
On March 1, 2016, an affiliate of Gulf LNG received a Notice of Disagreement and Disputed Statements and a Notice of Arbitration from Eni USA, one of the two companies that had entered into a terminal use agreement for capacity of the liquefied natural gas facility owned by Gulf LNG and its subsidiaries. On June 29, 2018, the arbitration panel delivered its award, and the panel's ruling calls for the termination of the agreement and Eni USA's payment of compensation to Gulf LNG. On September 25, 2018, Gulf LNG filed a lawsuit against Eni USA in the Delaware Court of Chancery to enforce the award. Further, on September 28, 2018, Gulf LNG filed a lawsuit against Eni S.p.A. in the Supreme Court of the State of New York in New York County to enforce a guarantee agreement entered by Eni S.p.A. in connection with the terminal use agreement.
During the third quarter of 2018, the fair value of the Lightfoot investment was reduced to zero due to additional market information. In the fourth quarter of 2018, the Company received a distribution representing a return of capital totaling approximately $667 thousand due to the disposition of the remaining asset interest. The Company recognized a realized loss of $1.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2018. The loss is recorded in net realized and unrealized gain (loss) on other equity
F-24
securities in the Consolidated Statements of Income. During the fourth quarter of 2019, Lightfoot LP and Lightfoot GP were fully liquidated.
Joliet
On December 21, 2018, the Company sold its 0.6 percent interest in Joliet, along with the Portland Terminal Facility, to Zenith Terminals for approximately $446 thousand. The sale resulted in a realized loss on other equity securities of approximately $715 thousand included in net realized and unrealized gain (loss) on other equity securities in the Consolidated Statements of Income for the year ended December 31, 2018.
The following section describes the valuation methodologies used by the Company for estimating fair value for financial instruments not recorded at fair value, but fair value is included for disclosure purposes only, as required under disclosure guidance related to the fair value of financial instruments.
Cash and Cash Equivalents — The carrying value of cash, amounts due from banks, federal funds sold and securities purchased under resale agreements approximates fair value.
Financing Notes Receivable — The financing notes receivable are valued on a non-recurring basis. The financing notes receivable are reviewed for impairment when events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of such assets may not be recoverable. Financing notes with carrying values that are not expected to be recovered through future cash flows are written-down to their estimated net realizable value. Estimates of realizable value are determined based on unobservable inputs, including estimates of future cash flow generation and value of collateral underlying the notes.
Secured Credit Facilities — The fair value of the Company's long-term variable-rate and fixed-rate debt under its secured credit facilities approximates carrying value.
Unsecured Convertible Senior Notes — The fair value of the unsecured convertible senior notes is estimated using quoted market prices from either active (Level 1) or generally active (Level 2) markets.
Carrying and Fair Value Amounts | |||||||||||||||||
Level within Fair Value Hierarchy | December 31, 2019 | December 31, 2018 | |||||||||||||||
Carrying Amount (1) | Fair Value | Carrying Amount (1) | Fair Value | ||||||||||||||
Financial Assets: | |||||||||||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents | Level 1 | $ | 120,863,643 | $ | 120,863,643 | $ | 69,287,177 | $ | 69,287,177 | ||||||||
Financing notes receivable (Note 5) | Level 3 | 1,235,000 | 1,235,000 | 1,300,000 | 1,300,000 | ||||||||||||
Financial Liabilities: | |||||||||||||||||
Secured credit facilities | Level 2 | $ | 33,785,930 | $ | 33,785,930 | $ | 37,261,109 | $ | 37,261,109 | ||||||||
7.00% Unsecured convertible senior notes | Level 1 | 2,084,178 | 2,820,832 | 112,777,271 | 119,378,982 | ||||||||||||
5.875% Unsecured convertible senior notes | Level 2 | 116,239,318 | 122,508,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||
(1) The carrying value of debt balances are presented net of unamortized original issuance discount and debt issuance costs. | |||||||||||||||||
F-25
11. DEBT
The following is a summary of debt facilities and balances as of December 31, 2019 and 2018:
Total Commitment or Original Principal | Quarterly Principal Payments | December 31, 2019 | December 31, 2018 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Maturity Date | Amount Outstanding | Interest Rate | Amount Outstanding | Interest Rate | |||||||||||||||||||
CorEnergy Secured Credit Facility: | |||||||||||||||||||||||
CorEnergy Revolver | $ | 160,000,000 | $ | — | 7/28/2022 | $ | — | 4.51 | % | $ | — | 5.25 | % | ||||||||||
MoGas Revolver | 1,000,000 | — | 7/28/2022 | — | 4.51 | % | — | 5.25 | % | ||||||||||||||
Omega Line of Credit | 1,500,000 | — | 7/31/2020 | — | 5.76 | % | — | 6.50 | % | ||||||||||||||
Pinedale Secured Credit Facility: | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Amended Pinedale Term Credit Facility | 41,000,000 | 882,000 | 12/29/2022 | 33,944,000 | 6.50 | % | 37,472,000 | 6.50 | % | ||||||||||||||
7.00% Unsecured Convertible Senior Notes | 115,000,000 | — | 6/15/2020 | 2,092,000 | 7.00 | % | 113,958,000 | 7.00 | % | ||||||||||||||
5.875% Unsecured Convertible Senior Notes | 120,000,000 | — | 8/15/2025 | 120,000,000 | 5.875 | % | — | — | % | ||||||||||||||
Total Debt | $ | 156,036,000 | $ | 151,430,000 | |||||||||||||||||||
Less: | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Unamortized deferred financing costs (1) | $ | 635,351 | $ | 283,278 | |||||||||||||||||||
Unamortized discount on 7.00% Convertible Senior Notes | 6,681 | 1,108,342 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Unamortized discount on 5.875% Convertible Senior Notes | 3,284,542 | — | |||||||||||||||||||||
Long-term debt, net of deferred financing costs | $ | 152,109,426 | $ | 150,038,380 | |||||||||||||||||||
Debt due within one year | $ | 5,612,178 | $ | 3,528,000 | |||||||||||||||||||
(1) Unamortized deferred financing costs related to the Company's revolving credit facilities are included in Deferred Costs in the Assets section of the Consolidated Balance Sheets. Refer to the "Deferred Financing Costs" paragraph below. | |||||||||||||||||||||||
CorEnergy Credit Facilities
Prior to 2017, the Company had a credit facility with Regions Bank (as lender and administrative agent for the other participating lenders) providing borrowing capacity of $153.0 million, consisting of (i) the CorEnergy Revolver of $105.0 million, (ii) the CorEnergy Term Loan of $45.0 million and (iii) the MoGas Revolver of $3.0 million.
On July 28, 2017, the Company entered into an amendment and restatement of the CorEnergy Credit Facility with Regions Bank (as lender and administrative agent for other participating lenders). The amended facility provides for borrowing commitments of up to $161.0 million, consisting of (i) $160.0 million on the CorEnergy Revolver, subject to borrowing base limitations, and (ii) $1.0 million on the MoGas Revolver, as detailed below.
The amended facility has 5-year term maturing on July 28, 2022, and provided for a springing maturity on February 28, 2020, and thereafter, if the Company failed to meet certain liquidity requirements from the springing maturity date through the maturity of the Company's 7.00% Convertible Notes on June 15, 2020. This springing maturity would have been triggered on the first date on or after February 28, 2020 that both (i) the outstanding principal amount of the 7.00% Convertible Notes exceeded $28,750,000 and (ii) the Company's unrestricted cash liquidity (including, for purposes of this calculation, the undrawn portion of the Borrowing Base then available for borrowing under the CorEnergy Credit Facility) was less than the sum of (x) the outstanding principal amount of the 7.00% Convertible Notes plus (y) $5,000,000. The Company will not trigger the springing maturity as a result of the 7.00% Convertible Note exchange completed in August of 2019, which reduced the outstanding principal balance of the 7.00% Convertible Notes below the springing maturity threshold. Refer to "Convertible Debt" section below for further details on convertible debt transactions during 2019.
Borrowings under the credit facility will generally bear interest on the outstanding principal amount using a LIBOR pricing grid that is expected to equal a LIBOR rate plus an applicable margin of 2.75 percent to 3.75 percent, based on the Company's senior secured recourse leverage ratio. Total availability is subject to a borrowing base. The CorEnergy Credit Facility contains, among other restrictions, certain financial covenants including the maintenance of certain financial ratios, as well as default and cross-default provisions customary for transactions of this nature (with applicable customary grace periods). As of December 31, 2019, the Company was in compliance with all covenants of the CorEnergy Credit Facility.
The CorEnergy Credit Facility is secured by substantially all of the assets owned by the Company and its subsidiaries other than (i) the assets held by Mowood, LLC, Omega, Pinedale LP and Pinedale GP (the "Unrestricted Subs") and (ii) the equity investments in the Unrestricted Subs.
F-26
As of December 31, 2019, the Company had approximately $136.4 million and $1.0 million of availability under the CorEnergy Revolver and MoGas Revolver, respectively.
MoGas Revolver
In conjunction with the MoGas Transaction, MoGas and United Property Systems, as co-borrowers, entered into a revolving credit agreement dated November 24, 2014 ("the MoGas Revolver") with certain lenders, including Regions Bank as agent for such lenders. Following subsequent amendments and restatements made on July 8, 2015 and July 28, 2017, in connection with the amendments and restatements of the CorEnergy Credit Facility discussed above, commitments under the MoGas Revolver were reduced from the original level of $3.0 million to a current total of $1.0 million.
The MoGas Revolver is secured by the assets held at MoGas and has a maturity date of July 28, 2022. Interest accrues under the MoGas Revolver at the same rate and pursuant to the same terms as it accrues under the CorEnergy Revolver. As of December 31, 2019, the co-borrowers were in compliance with all covenants, and there were no borrowings against the MoGas Revolver.
Mowood/Omega Revolver
On July 31, 2015, a $1.5 million revolving line of credit ("Mowood/Omega Revolver") was established with Regions Bank with a maturity date of July 31, 2016. Following annual extensions, the current maturity of the facility has been amended and extended to July 31, 2020. The Mowood/Omega Revolver is used by Omega for working capital and general business purposes and is guaranteed and secured by the assets of Omega. Interest accrues at LIBOR plus 4 percent and is payable monthly in arrears with no unused fee. There was no outstanding balance at December 31, 2019.
Amended Pinedale Term Credit Facility
On December 20, 2012, Pinedale LP closed on a $70.0 million secured term credit facility with a lender that provided for monthly payments of principal and interest and was secured by the Pinedale LGS. The credit facility accrued interest at a variable annual rate linked to LIBOR.
On March 4, 2016, the Company obtained a consent from its lenders under the CorEnergy Credit Facility, which permitted the Company to utilize the CorEnergy Credit Facility to refinance the Company's pro rata share of the remaining balance of the Pinedale secured term credit facility. On March 30, 2016, the Company and Prudential (collectively, "the Refinancing Lenders"), refinanced the remaining $58.5 million principal balance of the $70.0 million credit facility (on a pro rata basis equal to their respective equity interests in Pinedale LP, with the Company's 81.05 percent share being approximately $47.4 million) and executed a series of agreements assigning the credit facility to the Refinancing Lenders, with CorEnergy Infrastructure Trust, Inc. as Agent for the Refinancing Lenders. The Company's portion of the debt and interest was eliminated in consolidation and Prudential's portion of the debt was shown as a related-party liability.
Pinedale LP automatically entered into a Cash Control Period (as defined in the credit facility) with the Refinancing Lenders upon the April 29, 2016 bankruptcy filing by Ultra Wyoming and its parent guarantor, Ultra Petroleum. During a Cash Control Period, the Company as Agent swept all funds for the repayment of accrued interest, scheduled principal payments and principal prepayments on the loans. Ultra Petroleum emerged from bankruptcy in April 2017, resulting in the end of the Cash Control Period and, in May 2017, Pinedale LP resumed distributions. For the year ended December 31, 2017, pursuant to these additional cash sweep provisions, an additional $4.4 million was distributed (pro rata, based on ownership percentages) to the Refinancing Lenders as a reduction to the outstanding principal.
On December 29, 2017, Pinedale LP entered into the Amended Pinedale Term Credit Facility with Prudential and a group of lenders affiliated with Prudential as the sole lenders and Prudential serving as administrative agent. Under the terms of the Amended Term Credit Facility, Pinedale LP was provided with a 5-year $41.0 million term loan facility, bearing interest at a fixed rate of 6.5 percent, which matures on December 29, 2022. Principal payments of $294 thousand, plus accrued interest, are payable monthly. The Amended Pinedale Term Credit Facility was utilized to pay off the balance due to the Refinancing Lenders under the previously existing Pinedale LP credit facility.
Outstanding balances under the facility are secured by the Pinedale LGS assets. The Amended Pinedale Term Credit Facility contains, among other restrictions, specific financial covenants including the maintenance of certain financial coverage ratios and a minimum net worth requirement which, along with other provisions of the credit facility, limit cash dividends and loans by Pinedale LP to the Company. At December 31, 2019, the net assets of Pinedale LP were $131.5 million and Pinedale LP was in compliance with all of the financial covenants of the Amended Pinedale Term Credit Facility.
F-27
Deferred Financing Costs
A summary of deferred financing cost amortization expenses for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017 is as follows:
Deferred Financing Cost Amortization Expense (1)(2) | |||||||||||
For the Years Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2019 | 2018 | 2017 | |||||||||
CorEnergy Credit Facility | $ | 574,542 | $ | 574,541 | $ | 873,601 | |||||
Amended Pinedale Term Credit Facility | 52,821 | 52,728 | 392 | ||||||||
Total Deferred Debt Cost Amortization | $ | 627,363 | $ | 627,269 | $ | 873,993 | |||||
(1) Amortization of deferred debt issuance costs is included in interest expense in the Consolidated Statements of Income. | |||||||||||
(2) For the amount of deferred debt costs amortization relating to the Convertible Notes included in the Consolidated Statements of Income, refer to the Convertible Note Interest Expense table below. | |||||||||||
CorEnergy Credit Facilities
Prior to the July 28, 2017 credit facility amendment and restatement, previously existing deferred financing costs related to the CorEnergy Credit Facility were approximately $1.8 million, of which approximately $1.6 million continue to be deferred and amortized under the amended and restated facility. Additionally, the Company incurred approximately $1.3 million in new debt issuance costs which have been deferred and are being amortized over the term of the new facility. The total deferred financing costs of $2.9 million are being amortized on a straight-line basis over the 5-year term of the amended and restated CorEnergy Credit Facility. Approximately $234 thousand of existing deferred costs and new debt issuance costs were expensed as a loss on extinguishment of debt related to the amendment and restatement in the Consolidated Statements of Income for the year ended December 31, 2017.
Amended Pinedale Term Credit Facility
In connection with entering into the Amended Pinedale Term Credit Facility, Pinedale LP incurred approximately $367 thousand in new debt issuance costs, of which $264 thousand were deferred and are being amortized on a straight-line basis over the 5-year term of the Amended Pinedale Term Credit Facility. The remaining $103 thousand was expensed as a loss on extinguishment of debt in the Consolidated Statements of Income for the year ended December 31, 2017.
Contractual Payments
The remaining contractual principal payments as of December 31, 2019 under the Amended Pinedale Term Credit Facility are as follows:
Year | Amended Pinedale Term Credit Facility | |||
2020 | $ | 3,528,000 | ||
2021 | 3,528,000 | |||
2022 | 26,888,000 | |||
2023 | — | |||
2024 | — | |||
Thereafter | — | |||
Total | $ | 33,944,000 | ||
Convertible Debt
7.00% Convertible Notes
On June 29, 2015, the Company completed a public offering of $115.0 million aggregate principal amount of 7.00% Convertible Senior Notes Due 2020 (the "7.00% Convertible Notes"). The Convertible Notes mature on June 15, 2020 and bear interest at a rate of 7.0 percent per annum, payable semi-annually in arrears on June 15 and December 15 of each year, beginning on December 15, 2015.
The 7.00% Convertible Notes were initially issued with an underwriters' discount of $3.7 million which is being amortized over the life of the 7.00% Convertible Notes. Additionally, the Company incurred approximately $241 thousand in debt issuance costs associated with the 7.00% Convertible Notes which are being amortized over the life of the notes.
F-28
Holders may convert their 7.00% Convertible Notes into shares of the Company's common stock at their option until the close of business on the second scheduled trading day immediately preceding the maturity date. The initial conversion rate for the 7.00% Convertible Notes will be 30.3030 shares of common stock per $1,000 principal amount of the 7.00% Convertible Notes, equivalent to an initial conversion price of $33.00 per share of common stock. Such conversion rate will be subject to adjustment in certain events as specified in the Indenture.
On May 23, 2016, the Company repurchased $1.0 million of its 7.00% Convertible Notes on the open market. During the year ended December 31, 2018, certain holders elected to convert approximately $42 thousand of 7.00% Convertible Notes for 1,271 shares of CorEnergy common stock.
On January 16, 2019, the Company agreed with three holders of its 7.00% Convertible Notes, pursuant to privately negotiated agreements, to exchange $43.8 million face amount of such notes for an aggregate of 837,040 shares of the Company's common stock, par value $0.001 per share, plus aggregate cash consideration of $19.8 million, including $315 thousand of interest expense. The Company's agent and lenders under the CorEnergy Credit Facility provided a consent for the convertible note exchange. The Company recorded a loss on extinguishment of debt of approximately $5.0 million in the Consolidated Statements of Income for the first quarter of 2019. The loss on extinguishment of debt included the write-off of a portion of the underwriter's discount and deferred debt costs of $409 thousand and $27 thousand, respectively.
On August 15, 2019, the Company used a portion of the net proceeds from the offering of the 5.875% Convertible Notes discussed further below, together with shares of its common stock, to exchange $63.9 million face amount of its 7.00% Convertible Notes pursuant to privately negotiated agreements with three holders. The total cash and stock consideration for the exchange was valued at approximately $93.2 million. This included an aggregate of 703,432 shares of common stock plus cash consideration of approximately $60.2 million, including $733 thousand of interest expense. The Company recorded a loss on extinguishment of debt of approximately $28.9 million in the Consolidated Statements of Income for the third quarter of 2019. The loss on extinguishment of debt included the write-off of a portion of the underwriter's discount and deferred debt costs of $360 thousand and $24 thousand, respectively. Collectively, for the two exchange transactions described above, the Company recorded a loss on extinguishment of debt of $34.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2019.
Additionally, during the year ended December 31, 2019, certain holders elected to convert $4.2 million of 7.00% Convertible Notes for approximately 127,143 shares of common stock, respectively. As of December 31, 2019, the Company has $2.1 million aggregate principal amount of 7.00% Convertible Notes outstanding. Subsequent to December 31, 2019, certain holders elected to convert $416 thousand of 7.00% Convertible Notes for approximately 12,605 shares of common stock.
At the present time, the remaining 7.00% Convertible Notes may not be redeemed prior to the maturity date without the consent of the agent and lenders under the CorEnergy Credit Facility. However, upon the occurrence of a fundamental change (as defined in the Indenture), holders may require the Company to repurchase all or a portion of the 7.00% Convertible Notes for cash at a price equal to 100 percent of the principal amount of the 7.00% Convertible Notes to be purchased plus any accrued and unpaid interest, if any, to, but excluding, the applicable fundamental change repurchase date as prescribed in the Indenture. In addition, in certain circumstances the Company will increase the conversion rate for a holder that converts the 7.00% Convertible Notes in connection with any of a specified set of corporate events, each of which is deemed to constitute a make-whole adjustment event pursuant to the terms of the Indenture.
The 7.00% Convertible Notes rank equal in right of payment to any other current and future unsecured obligations of the Company and senior in right of payment to any other current and future indebtedness of the Company that is contractually subordinated to the 7.00% Convertible Notes. The 7.00% Convertible Notes are structurally subordinated to all liabilities (including trade payables) of the Company's subsidiaries. The 7.00% Convertible Notes are effectively junior to all of the Company's existing or future secured debt, to the extent of the value of the collateral securing such debt.
5.875% Convertible Notes
On August 12, 2019, the Company completed a private placement offering of $120.0 million aggregate principal amount of 5.875% Convertible Senior Notes due 2025 (the "5.875% Convertible Notes") to the initial purchasers of such notes for cash in reliance on an exemption from registration provided by Section 4(a)(2) of the Securities Act. The initial purchasers then resold the 5.875% Convertible Notes for cash equal to 100 percent of the aggregate principal amount thereof to qualified institutional buyers, as defined in Rule 144A under the Securities Act, in reliance on an exemption from registration provided by Rule 144A. The 5.875% Convertible Notes mature on August 15, 2025 and bear interest at a rate of 5.875 percent per annum, payable semiannually in arrears on February 15 and August 15 of each year, beginning on February 15, 2020.
F-29
The 5.875% Convertible Notes were issued with an initial purchasers' discount of $3.5 million, which is being amortized over the life of the notes. The Company also incurred approximately $508 thousand of deferred debt costs in issuing the 5.875% Convertible Notes, which are also being amortized over the life of the notes.
Holders may convert all or any portion of their 5.875% Convertible Notes into shares of the Company's common stock at their option at any time prior to the close of business on the business day immediately preceding the maturity date. The initial conversion rate for the 5.875% Convertible Notes is 20.0 shares of common stock per $1,000 principal amount of the 5.875% Convertible Notes, equivalent to an initial conversion price of $50.00 per share of the Company's common stock. Such conversion rate will be subject to adjustment in certain events as specified in the Indenture.
Upon the occurrence of a make-whole fundamental change (as defined in the Indenture), holders may require the Company to repurchase for cash all or any portion of their 5.875% Convertible Notes at a fundamental change repurchase price equal to 100 percent of the principal amount of the 5.875% Convertible Notes to be repurchased, plus any accrued and unpaid interest, if any, to, but excluding, the fundamental change repurchase date as prescribed in the Indenture. Following the occurrence of a make- whole fundamental change, or if the Company delivers a notice of redemption (as discussed below), the Company will, in certain circumstances, increase the applicable conversion rate for a holder that elects to convert its notes in connection with such make-whole fundamental change or notice of redemption.
The Company may not redeem the 5.875% Convertible Notes prior to August 15, 2023. On or after August 15, 2023, the Company may redeem for cash all or part of the 5.875% Convertible Notes, at its option, if the last reported sale price of its common stock has been at least 125 percent of the conversion price then in effect for at least 20 trading days (whether or not consecutive) during any 30 consecutive trading day period (including the last trading day of such period) ending on, and including, the trading day immediately preceding the date on which the Company provides notice of redemption. The redemption price will equal 100 percent of the principal amount of the 5.875% Convertible Notes to be redeemed, plus accrued and unpaid interest to, but excluding, the redemption date.
The 5.875% Convertible Notes rank equal in right of payment to any other current and future unsecured obligations, including the 7.00% Convertible Notes, of the Company and senior in right of payment to any other current and future indebtedness of the Company that is contractually subordinated to the 5.875% Convertible Notes. The 5.875% Convertible Notes are structurally subordinated to all liabilities (including trade payables) of the Company’s subsidiaries. The 5.875% Convertible Notes are effectively junior to all of the Company’s existing or future secured debt, to the extent of the value of the collateral securing such debt.
The following is a summary of the impact of Convertible Notes on interest expense for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017:
Convertible Note Interest Expense | |||||||||||
For the Years Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2019 | 2018 | 2017 | |||||||||
7.00% Convertible Notes: | |||||||||||
Interest Expense | $ | 3,354,178 | $ | 7,979,118 | $ | 7,980,000 | |||||
Discount Amortization | 320,821 | 738,912 | 738,912 | ||||||||
Deferred Debt Issuance Cost Amortization | 21,004 | 48,276 | 48,276 | ||||||||
Total 7.00% Convertible Notes | $ | 3,696,003 | $ | 8,766,306 | $ | 8,767,188 | |||||
5.875% Convertible Notes: | |||||||||||
Interest Expense | $ | 2,722,083 | $ | — | $ | — | |||||
Discount Amortization | 225,458 | — | — | ||||||||
Deferred Debt Issuance Amortization | 31,493 | — | — | ||||||||
Total 5.875% Convertible Notes | $ | 2,979,034 | $ | — | $ | — | |||||
Total Convertible Note Interest | $ | 6,675,037 | $ | 8,766,306 | $ | 8,767,188 | |||||
Including the impact of the convertible debt discount and related deferred debt issuance costs, (i) the effective interest rate on the 7.00% Convertible Notes was approximately 7.7 percent for each of the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017 and (ii) the effective interest rate on the 5.875% Convertible Notes is approximately 6.4 percent for the year ended December 31, 2019.
12. ASSET RETIREMENT OBLIGATION
A component of the consideration exchanged to purchase the GIGS assets in June 2015 was the assumption of the seller's asset retirement obligation ("ARO") associated with such assets. The ARO represents the estimated costs of decommissioning the GIGS pipelines and onshore oil receiving and separation facilities in Grand Isle, Louisiana at retirement. The Company recognized the
F-30
ARO at its estimated fair value on the date of acquisition with a corresponding ARO asset capitalized as part of the carrying amount of the related long-lived assets to be depreciated over the assets' remaining useful lives.
The Company's tenant, EGC Tenant, has an ARO related to the platform which is currently attached to the GIGS pipelines. If in the future, EGC Tenant is unable to fulfill their obligation, the Company may be required to assume the liability for the related asset removal costs.
In periods subsequent to the initial measurement of an ARO, the Company recognizes changes in the liability resulting from (a) the passage of time through accretion expense and (b) revisions to either the timing or the amount of the estimate of undiscounted cash flows based on periodic revaluations. Future expected cash flows are based on subjective estimates and assumptions, which inherently include significant uncertainties which are beyond the Company's control. These assumptions represent Level 3 inputs in the fair value hierarchy. The Company has no assets that are legally restricted for purposes of settling asset retirement obligations.
In December 2019 and 2018, the Company revised its estimates to reflect a decrease in (i) average marketplace rates for labor and other costs, (ii) for the expected timing of work and for (iii) recent decommissioning estimates. During the fourth quarter of 2018, the Company decommissioned a segment of the GIGS pipeline system. The Company incurred decommissioning costs of approximately $939 thousand compared to the estimated segment ARO liability of $628 thousand resulting in a loss on settlement of ARO of $311 thousand. The loss on settlement of ARO is recorded in general and administrative expenses in the Consolidated Statements of Income for the year ended December 31, 2018. For the year ended December 31, 2019, the change in estimate did not result in any charge to income.
The following table is a reconciliation of the asset retirement obligation as of December 31, 2019 and 2018:
Asset Retirement Obligation | |||||||
For the Years Ended December 31, | |||||||
2019 | 2018 | ||||||
Beginning asset retirement obligation | $ | 7,956,343 | $ | 9,170,493 | |||
Liabilities assumed | — | — | |||||
ARO accretion expense | 443,969 | 499,562 | |||||
Liabilities settled | — | (628,300 | ) | ||||
Revision in cash flow estimates | (356,112 | ) | (1,085,412 | ) | |||
Ending asset retirement obligation | $ | 8,044,200 | $ | 7,956,343 | |||
13. STOCKHOLDERS' EQUITY
PREFERRED STOCK
The Company's authorized preferred stock consists of 10.0 million shares having a par value of $0.001 per share. On January 27, 2015, the Company sold, in an underwritten public offering, 2,250,000 depositary shares, each representing 1/100th of a share of 7.375% Series A Cumulative Redeemable Preferred Stock ("Series A Preferred Stock"). Pursuant to this offering, the Company issued 22,500 whole shares of Series A Preferred Stock and received net cash proceeds of approximately $54.2 million.
On April 18, 2017, the Company closed a follow-on underwritten public offering of 2,800,000 depository shares, each representing 1/100th of a share of 7.375% Series A Preferred Stock, at a price of $25.00 per depository share. On May 10, 2017, the Company sold an additional 150,000 depository shares at a public offering price of $25.00 per depository share in connection with the underwriters' exercise of their over-allotment option to purchase additional shares. Total proceeds from the offering were approximately $71.2 million, after deducting underwriting discounts and other offering expenses. A portion of the proceeds from the offering were utilized to repay $44.0 million in outstanding borrowings under the CorEnergy Revolver. Following the offering, the Company had a total of 5,200,000 depository shares outstanding, or 52,000 whole shares.
The depositary shares pay an annual dividend of $1.84375 per share, equivalent to 7.375 percent of the $25.00 liquidation preference. The depositary shares may be redeemed on or after January 27, 2020, at the Company's option, in whole or in part, at the $25.00 liquidation preference plus all accrued and unpaid dividends to, but not including, the date of redemption. The depositary shares have no stated maturity, are not subject to any sinking fund or mandatory redemption and are not convertible into any other securities of the Company except in connection with certain changes of control. Holders of the depositary shares generally have no voting rights, except for limited voting rights if the Company fails to pay dividends for six or more quarters (whether or not consecutive) and in certain other circumstances. The depositary shares representing the Series A Preferred Stock trade on the NYSE under the ticker "CORRPrA."
F-31
The Company's Board of Directors authorized a share repurchase program for the Company to buy up to $10.0 million of its depository shares of Series A Preferred Stock, which commenced August 6, 2018. Purchases were made through the program until it expired on August 5, 2019. During 2018, the Company repurchased 177,773 depository shares for approximately $4.3 million in cash. During 2019, the Company repurchased 2,500 depository shares of Series A Preferred Stock for approximately $61 thousand in cash. As of December 31, 2019, the Company had a total of 5,019,727 depository shares outstanding, or approximately 50,197 whole shares, with an aggregate par value of $50.20.
See Note 16 ("Subsequent Events"), for further information regarding the declaration of a dividend on the Series A Preferred Stock.
COMMON STOCK
As of December 31, 2019, the Company had 13,638,916 of common shares issued and outstanding. See Note 16 ("Subsequent Events"), for further information regarding the declaration of a dividend on the common stock.
SHELF REGISTRATION
On October 30, 2018, the Company filed a shelf registration statement with the SEC, pursuant to which it registered 1,000,000 shares of common stock for issuance under its dividend reinvestment plan. As of December 31, 2019, the Company has issued 22,003 shares of common stock under its dividend reinvestment plan pursuant to the shelf, resulting in remaining availability (subject to the current limitation discussed below) of approximately 977,997 shares of common stock.
On November 9, 2018, the Company had a new shelf registration statement declared effective by the SEC replacing the Company's previously filed shelf registration statement, pursuant to which it may publicly offer additional debt or equity securities with an aggregate offering price of up to $600.0 million. As of December 31, 2019, the Company has not issued any securities under this new shelf registration statement, so total availability remains at $600.0 million. As described elsewhere in this Report, EGC and Cox Oil have refused to provide the financial statement information concerning EGC required to be filed by the Company pursuant to SEC Regulation S-X. At least until it is able to file these EGC financial statements, the Company does not expect to be able to use this shelf registration statement, or the shelf registration statement filed for its dividend reinvestment plan, to sell its securities. As previously disclosed in the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K filed on April 24, 2019, the Company has suspended its dividend reinvestment plan.
The Company has engaged in dialogue with the staff of the SEC in an effort to shorten the period during which it does not use its registration statements. The Company does not expect this period to be shortened until the EGC financial statement information has been received and filed.
14. EARNINGS PER SHARE
Basic earnings per share data is computed based on the weighted-average number of shares of common stock outstanding during the periods. Diluted EPS data is computed based on the weighted-average number of shares of common stock outstanding, including all potentially issuable shares of common stock. Diluted EPS for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2017 excludes the impact to income and the number of shares outstanding from the conversion of the 7.00% Convertible Senior Notes and the 5.875% Convertible Senior Notes, as applicable, because such impact is antidilutive.
Under the if converted method, and after consideration of the common shares issued in the Convertible Notes exchanges and conversions discussed in Note 11 ("Debt"), the 7.00% Convertible Senior Notes and 5.875% Convertible Senior Notes would result in an additional 2,463,394 common shares outstanding for the year ended December 31, 2019. For the year ended December 31, 2018, the dilutive shares include 3,453,273 common shares outstanding from the if-converted method for the 7.00% Convertible Notes. For the year ended December 31, 2017, the if-converted method would have resulted in an additional 3,454,545 common shares outstanding.
F-32
Earnings Per Share | |||||||||||
For the Years Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2019 | 2018 | 2017 | |||||||||
Net Income attributable to CorEnergy Stockholders | $ | 4,079,495 | $ | 43,711,876 | $ | 32,602,790 | |||||
Less: preferred dividend requirements(1) (2) | 9,255,468 | 9,548,377 | 7,953,988 | ||||||||
Net Income (Loss) attributable to Common Stockholders | $ | (5,175,973 | ) | $ | 34,163,499 | $ | 24,648,802 | ||||
Weighted average shares - basic | 13,041,613 | 11,935,021 | 11,900,516 | ||||||||
Basic earnings (loss) per share | $ | (0.40 | ) | $ | 2.86 | $ | 2.07 | ||||
Net Income (Loss) attributable to Common Stockholders (from above) | $ | (5,175,973 | ) | $ | 34,163,499 | $ | 24,648,802 | ||||
Add: After tax effect of convertible interest | — | 8,766,306 | — | ||||||||
Income (Loss) attributable for dilutive securities | $ | (5,175,973 | ) | $ | 42,929,805 | $ | 24,648,802 | ||||
Weighted average shares - diluted | 13,041,613 | 15,389,180 | 11,900,516 | ||||||||
Diluted earnings (loss) per share | $ | (0.40 | ) | $ | 2.79 | $ | 2.07 | ||||
(1) In connection with the repurchases of Series A Preferred Stock during the year ended December 31, 2018, preferred dividend requirements were reduced by $10,554 representing the discount in the repurchase price paid compared to the carrying amount derecognized. | |||||||||||
(2) In connection with the repurchases of Series A Preferred Stock during the year ended December 31, 2019, preferred dividend requirements were increased by $245 representing the premium in the repurchase price paid compared to the carrying amount derecognized. | |||||||||||
F-33
15. QUARTERLY FINANCIAL DATA (Unaudited)
For the Fiscal 2019 Quarters Ended | |||||||||||||||
March 31 | June 30 | September 30 | December 31 | ||||||||||||
Revenue | |||||||||||||||
Lease revenue | $ | 16,717,710 | $ | 16,635,876 | $ | 16,984,903 | $ | 16,712,017 | |||||||
Transportation and distribution revenue | 4,871,582 | 4,868,144 | 4,068,338 | 4,970,173 | |||||||||||
Financing revenue | 33,540 | 27,989 | 28,003 | 27,295 | |||||||||||
Total Revenue | 21,622,832 | 21,532,009 | 21,081,244 | 21,709,485 | |||||||||||
Expenses | |||||||||||||||
Transportation and distribution expenses | 1,503,143 | 1,246,755 | 1,116,194 | 1,376,152 | |||||||||||
General and administrative | 2,870,407 | 2,739,855 | 2,494,240 | 2,492,346 | |||||||||||
Depreciation, amortization and ARO accretion expense | 5,645,096 | 5,645,250 | 5,645,342 | 5,646,254 | |||||||||||
Total Expenses | 10,018,646 | 9,631,860 | 9,255,776 | 9,514,752 | |||||||||||
Operating Income | $ | 11,604,186 | $ | 11,900,149 | $ | 11,825,468 | $ | 12,194,733 | |||||||
Other Income (Expense) | |||||||||||||||
Net distributions and other income | $ | 256,615 | $ | 285,259 | $ | 360,182 | $ | 426,797 | |||||||
Interest expense | (2,507,294 | ) | (2,297,783 | ) | (2,777,122 | ) | (2,996,512 | ) | |||||||
Loss on extinguishment of debt | (5,039,731 | ) | — | (28,920,834 | ) | — | |||||||||
Total Other Expense | (7,290,410 | ) | (2,012,524 | ) | (31,337,774 | ) | (2,569,715 | ) | |||||||
Income (loss) before income taxes | 4,313,776 | 9,887,625 | (19,512,306 | ) | 9,625,018 | ||||||||||
Taxes | |||||||||||||||
Current tax expense (benefit) | 353,744 | — | (1,270 | ) | (472,498 | ) | |||||||||
Deferred tax expense (benefit) | 93,591 | 62,699 | (91,436 | ) | 289,788 | ||||||||||
Income tax expense (benefit), net | 447,335 | 62,699 | (92,706 | ) | (182,710 | ) | |||||||||
Net income (loss) attributable to CorEnergy Stockholders | $ | 3,866,441 | $ | 9,824,926 | $ | (19,419,600 | ) | $ | 9,807,728 | ||||||
Preferred dividend requirements | 2,314,128 | 2,313,780 | 2,313,780 | 2,313,780 | |||||||||||
Net income (loss) attributable to Common Stockholders | $ | 1,552,313 | $ | 7,511,146 | $ | (21,733,380 | ) | $ | 7,493,948 | ||||||
Earnings (Loss) Per Common Share: | |||||||||||||||
Basic | $ | 0.12 | $ | 0.59 | $ | (1.65 | ) | $ | 0.55 | ||||||
Diluted | $ | 0.12 | $ | 0.59 | $ | (1.65 | ) | $ | 0.55 | ||||||
F-34
For the Fiscal 2018 Quarters Ended | |||||||||||||||
March 31 | June 30 | September 30 | December 31 | ||||||||||||
Revenue | |||||||||||||||
Lease revenue | $ | 17,591,859 | $ | 18,275,859 | $ | 18,391,983 | $ | 18,487,661 | |||||||
Transportation and distribution revenue | 3,952,979 | 3,874,157 | 4,244,722 | 4,412,378 | |||||||||||
Total Revenue | 21,544,838 | 22,150,016 | 22,636,705 | 22,900,039 | |||||||||||
Expenses | |||||||||||||||
Transportation and distribution expenses | 1,572,896 | 1,534,524 | 2,241,999 | 1,861,329 | |||||||||||
General and administrative | 2,727,057 | 3,107,776 | 3,046,481 | 4,161,533 | |||||||||||
Depreciation, amortization and ARO accretion expense | 6,289,330 | 6,290,082 | 6,289,459 | 6,078,582 | |||||||||||
Provision for loan (gain) loss | 500,000 | — | — | (536,867 | ) | ||||||||||
Total Expenses | 11,089,283 | 10,932,382 | 11,577,939 | 11,564,577 | |||||||||||
Operating Income | $ | 10,455,555 | $ | 11,217,634 | $ | 11,058,766 | $ | 11,335,462 | |||||||
Other Income (Expense) | |||||||||||||||
Net distributions and other income | $ | 3,951 | $ | 55,714 | $ | 5,627 | $ | 41,503 | |||||||
Net realized and unrealized gain (loss) on other equity securities | 13,966 | (881,100 | ) | (930,147 | ) | (48,028 | ) | ||||||||
Interest expense | (3,210,590 | ) | (3,196,248 | ) | (3,183,589 | ) | (3,168,583 | ) | |||||||
Gain on the sale of leased property, net | — | — | — | 11,723,257 | |||||||||||
Total Other Income (Expense) | (3,192,673 | ) | (4,021,634 | ) | (4,108,109 | ) | 8,548,149 | ||||||||
Income before income taxes | 7,262,882 | 7,196,000 | 6,950,657 | 19,883,611 | |||||||||||
Taxes | |||||||||||||||
Current tax benefit | (35,549 | ) | (10,785 | ) | (8,393 | ) | (530,659 | ) | |||||||
Deferred tax benefit | (409,277 | ) | (604,064 | ) | (738,274 | ) | (81,725 | ) | |||||||
Income tax benefit, net | (444,826 | ) | (614,849 | ) | (746,667 | ) | (612,384 | ) | |||||||
Net Income attributable to CorEnergy Stockholders | $ | 7,707,708 | $ | 7,810,849 | $ | 7,697,324 | $ | 20,495,995 | |||||||
Preferred dividend requirements | 2,396,875 | 2,396,875 | 2,396,875 | 2,357,752 | |||||||||||
Net Income attributable to Common Stockholders | $ | 5,310,833 | $ | 5,413,974 | $ | 5,300,449 | $ | 18,138,243 | |||||||
Earnings Per Common Share: | |||||||||||||||
Basic | $ | 0.45 | $ | 0.45 | $ | 0.44 | $ | 1.52 | |||||||
Diluted | $ | 0.45 | $ | 0.45 | $ | 0.44 | $ | 1.32 | |||||||
F-35
16. SUBSEQUENT EVENTS
The Company performed an evaluation of subsequent events through the date of the issuance of these financial statements and determined that no additional items require recognition or disclosure, except for the following:
Common Stock Dividend
On January 22, 2020, the Company's Board of Directors declared a 2019 fourth quarter dividend of $0.75 per share for CorEnergy common stock. The dividend will be paid on February 28, 2020, to stockholders of record on February 14, 2020.
Preferred Stock Dividend
On January 22, 2020, the Company's Board of Directors also declared a dividend of $0.4609375 per depositary share for its 7.375% Series A Preferred Stock. The preferred stock dividend will be paid on February 28, 2020, to stockholders of record on February 14, 2020.
F-36
SCHEDULE I - CONDENSED FINANCIAL INFORMATION OF REGISTRANT
CorEnergy Infrastructure Trust, Inc.
CONDENSED BALANCE SHEETS | December 31, 2019 | December 31, 2018 | |||||
Assets | |||||||
Leased property, net of accumulated depreciation of $1,296,598 and $1,112,218 | $ | 3,497,058 | $ | 3,681,438 | |||
Investments | 401,331,625 | 415,674,601 | |||||
Cash and cash equivalents | 113,264,989 | 64,574,701 | |||||
Due from subsidiary | 11,635,874 | 10,549,719 | |||||
Note receivable from subsidiary | 75,412,500 | 81,000,000 | |||||
Deferred costs, net of accumulated amortization of $1,198,023 and $712,182 | 1,283,744 | 1,769,585 | |||||
Prepaid expenses and other assets | 306,939 | 265,024 | |||||
Total Assets | $ | 606,732,729 | $ | 577,515,068 | |||
Liabilities and Equity | |||||||
Unsecured convertible senior notes, net of discount and debt issuance costs of $3,768,504 and $1,180,729 | 118,323,496 | 112,777,271 | |||||
Accounts payable and other accrued liabilities | 3,180,010 | 1,075,045 | |||||
Management fees payable | 1,669,950 | 1,831,613 | |||||
Due to affiliate | 153,640 | 153,640 | |||||
Total Liabilities | $ | 123,327,096 | $ | 115,837,569 | |||
Equity | |||||||
Series A Cumulative Redeemable Preferred Stock 7.375%, $125,493,175 and $125,555,675 liquidation preference ($2,500 per share, $0.001 par value), 10,000,000 authorized; 50,197 and 50,222 issued and outstanding at December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, respectively | $ | 125,493,175 | $ | 125,555,675 | |||
Capital stock, non-convertible, $0.001 par value; 13,638,916 and 11,960,225 shares issued and outstanding at December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018 (100,000,000 shares authorized) | 13,639 | 11,960 | |||||
Additional paid-in capital | 367,510,691 | 326,962,163 | |||||
Retained earnings (deficit) | (9,611,872 | ) | 9,147,701 | ||||
Total Equity | 483,405,633 | 461,677,499 | |||||
Total Liabilities and Equity | $ | 606,732,729 | $ | 577,515,068 | |||
See accompanying Schedule I Notes to Condensed Financial Statements. | |||||||
F-37
SCHEDULE I - CONDENSED FINANCIAL INFORMATION OF REGISTRANT - CorEnergy Infrastructure Trust, Inc. - Continued
CONDENSED STATEMENTS OF INCOME AND COMPREHENSIVE INCOME | For the Years Ended December 31, | ||||||||||
2019 | 2018 | 2017 | |||||||||
Revenue | |||||||||||
Earnings from subsidiary | $ | 41,073,290 | $ | 48,353,177 | $ | 36,222,221 | |||||
Total Revenue | 41,073,290 | 48,353,177 | 36,222,221 | ||||||||
Expenses | |||||||||||
General and administrative | 2,045,404 | 2,353,593 | 2,298,201 | ||||||||
Depreciation expense | 184,380 | 184,380 | 184,380 | ||||||||
Amortization expense | 5,316 | 5,316 | 5,316 | ||||||||
Total Expenses | 2,235,100 | 2,543,289 | 2,487,897 | ||||||||
Operating Income | $ | 38,838,190 | $ | 45,809,888 | $ | 33,734,324 | |||||
Other Income (Expense) | |||||||||||
Net distributions and other income | $ | 1,252,749 | $ | 56,827 | $ | 96,866 | |||||
Interest on loans to subsidiaries | 5,916,317 | 7,903,104 | 11,549,344 | ||||||||
Interest expense, net | (7,967,196 | ) | (10,057,943 | ) | (11,451,944 | ) | |||||
Loss on extinguishment of debt | (33,960,565 | ) | — | (225,801 | ) | ||||||
Total Other Expense | (34,758,695 | ) | (2,098,012 | ) | (31,535 | ) | |||||
Net Income | $ | 4,079,495 | $ | 43,711,876 | $ | 33,702,789 | |||||
Other comprehensive income: | |||||||||||
Changes in fair value of qualifying hedges | — | — | 11,196 | ||||||||
Total Comprehensive Income | $ | 4,079,495 | $ | 43,711,876 | $ | 33,713,985 | |||||
See accompanying Schedule I Notes to Condensed Financial Statements. | |||||||||||
F-38
SCHEDULE I - CONDENSED FINANCIAL INFORMATION OF REGISTRANT - CorEnergy Infrastructure Trust, Inc. - Continued
CONDENSED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOW | For the Years Ended December 31, | ||||||||||
2019 | 2018 | 2017 | |||||||||
Net cash provided by (used in) operating activities | $ | (939,775 | ) | $ | (6,257,124 | ) | $ | 1,661,123 | |||
Investing Activities | |||||||||||
Principal payments received from notes to subsidiaries | 5,587,500 | 2,250,000 | 40,092,095 | ||||||||
Investment in consolidated subsidiaries | — | (73,996 | ) | (33,900,000 | ) | ||||||
Cash distributions from consolidated subsidiaries | 55,416,267 | 110,140,459 | 46,774,111 | ||||||||
Net cash provided by investing activities | $ | 61,003,767 | $ | 112,316,463 | $ | 52,966,206 | |||||
Financing Activities | |||||||||||
Debt financing costs | (372,759 | ) | — | (1,360,241 | ) | ||||||
Net offering proceeds on Series A preferred stock | — | — | 71,161,531 | ||||||||
Net offering proceeds on convertible debt | 116,355,125 | — | — | ||||||||
Cash paid for extinguishment of convertible debt | (78,939,743 | ) | — | — | |||||||
Repurchases of preferred stock debt | (60,550 | ) | (4,275,553 | ) | — | ||||||
Dividends paid on Series A preferred stock | (9,255,121 | ) | (9,587,500 | ) | (8,227,734 | ) | |||||
Dividends paid on common stock | (39,100,656 | ) | (34,284,059 | ) | (34,731,892 | ) | |||||
Advances on revolving line of credit | — | — | 10,000,000 | ||||||||
Payments on revolving line of credit | — | — | (54,000,000 | ) | |||||||
Principal payments on term debt | — | — | (36,740,000 | ) | |||||||
Net cash used in financing activities | $ | (11,373,704 | ) | $ | (48,147,112 | ) | $ | (53,898,336 | ) | ||
Net Change in Cash and Cash Equivalents | $ | 48,690,288 | $ | 57,912,227 | $ | 728,993 | |||||
Cash and Cash Equivalents at beginning of period | 64,574,701 | 6,662,474 | 5,933,481 | ||||||||
Cash and Cash Equivalents at end of period | $ | 113,264,989 | $ | 64,574,701 | $ | 6,662,474 | |||||
Supplemental Disclosure of Cash Flow Information | |||||||||||
Interest Paid | $ | 4,504,263 | $ | 8,794,086 | $ | 10,080,764 | |||||
Non-Cash Investing Activities | |||||||||||
Conversion of note receivable from subsidiary to investments | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 4,902,495 | |||||
Dissolution of investment in subsidiary upon liquidation | — | (73,996 | ) | — | |||||||
Non-Cash Financing Activities | |||||||||||
Common stock issued upon exchange and conversion of convertible notes | $ | 66,064,966 | $ | 42,654 | $ | — | |||||
Reinvestment of distributions by common stockholders in additional common shares | 403,831 | 1,509,830 | 962,308 | ||||||||
See accompanying Schedule I Notes to Condensed Financial Statements. | |||||||||||
NOTES TO SCHEDULE I CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE A - BASIS OF PRESENTATION
In the parent-company-only financial statements, the Company's investment in subsidiaries is stated at cost plus equity in undistributed earnings of subsidiaries since the date of acquisition. The parent-company-only financial statements should be read in conjunction with the Company's consolidated financial statements.
NOTE B - DIVIDENDS FROM SUBSIDIARIES
Cash dividends paid to CorEnergy Infrastructure Trust, Inc. from the Company's consolidated subsidiaries were $55.4 million, $110.1 million and $46.8 million for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, respectively.
F-39
SCHEDULE III - REAL ESTATE AND ACCUMULATED DEPRECIATION - CorEnergy Infrastructure Trust, Inc.
Initial Cost to Company | Costs Capitalized Subsequent to Acquisition | Gross Amount Carried at Close of Period December 31, 2019 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Description | Location | Encumbrances | Land | Building & Fixtures | Improvements / Adjustments (4) | Land | Building & Fixtures | Total | Accumulated Depreciation | Investment in Real Estate, net, at 12/31/19 | Date Acquired | Life on which depreciation in latest income statement is computed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Pinedale LGS (1)(5) | Pinedale, WY | $ | 33,944,000 | $ | 105,485,063 | $ | 125,119,062 | $ | — | $ | 105,485,063 | $ | 125,119,062 | $ | 230,604,125 | $ | 62,370,978 | $ | 168,233,147 | 2012 | 26 years | |||||||||||||||||||||
United Property Systems (4) | St. Louis, MO | — | 210,000 | 1,188,000 | 103,497 | 210,000 | 1,291,497 | 1,501,497 | 177,214 | 1,324,283 | 2014 | 40 years | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Grand Isle Gathering System (2)(3)(4) | Gulf of Mexico | — | 960,000 | 258,471,397 | (6,499,804 | ) | 960,000 | 251,971,593 | 252,931,593 | 43,277,624 | 209,653,969 | 2015 | 27 years | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
$ | 33,944,000 | $ | 106,655,063 | $ | 384,778,459 | $ | (6,396,307 | ) | $ | 106,655,063 | $ | 378,382,152 | $ | 485,037,215 | $ | 105,825,816 | $ | 379,211,399 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
(1) In connection with the asset acquisition, CorEnergy and Pinedale LP incurred acquisition costs of $2,557,910, which are included in the total asset balance. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(2) In connection with the asset acquisition, Grand Isle Gathering System incurred acquisition costs of $1,931,396, which are included in the total asset balance. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(3) Initial costs associated with the GIGS asset include amounts capitalized related to an acquired asset retirement obligation (ARO). The negative subsequent adjustment relates to (i) downward revisions of the ARO based on periodic reevaluation as required under FASB ASC 410-20 and (ii) the settlement of a portion of the ARO when a segment of the GIGS pipeline system was decommissioned during the fourth quarter of 2018. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(4) These two properties serve as collateral under the CorEnergy Credit Facility. There are no amounts outstanding on the credit facility as of December 31, 2019. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(5) The amount outstanding for the Amended Pinedale Term Credit Facility is $33,944,000 as of December 31, 2019. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
NOTES TO SCHEDULE III - CONSOLIDATED REAL ESTATE AND ACCUMULATED DEPRECIATION
Reconciliation of Real Estate and Accumulated Depreciation
For the Years Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2019 | 2018 | 2017 | |||||||||
Investment in real estate: | |||||||||||
Balance, beginning of year | $ | 485,368,450 | $ | 538,112,220 | $ | 541,478,086 | |||||
Addition: Acquisitions and developments | 24,877 | 3,599 | 9,649 | ||||||||
Deduction: Dispositions and other(1)(2) | (356,112 | ) | (52,747,369 | ) | (3,375,515 | ) | |||||
Balance, end of year | $ | 485,037,215 | $ | 485,368,450 | $ | 538,112,220 | |||||
Accumulated depreciation: | |||||||||||
Balance, beginning of year | $ | 87,154,095 | $ | 72,155,753 | $ | 52,219,717 | |||||
Addition: Depreciation | 18,671,721 | 20,986,461 | 19,936,036 | ||||||||
Deduction: Dispositions and other(2) | — | (5,988,119 | ) | — | |||||||
Balance, end of year | $ | 105,825,816 | $ | 87,154,095 | $ | 72,155,753 | |||||
(1) The Grand Isle Gathering System had a change in estimate related to the ARO in 2019, 2018 and 2017. Refer to Note 12 ("Asset Retirement Obligation") for further details. | |||||||||||
(2) On December 21, 2018, the Company sold its Portland Terminal Facility with a net carrying value of $45.7 million (i.e. gross investment of $51.7 million less accumulated depreciation of $6.0 million). Refer to Note 3 ("Leased Properties and Leases") for further details. | |||||||||||
The aggregate cost of the properties is approximately $7.2 million lower for federal income tax purposes at December 31, 2019. The tax basis of the properties is unaudited.
F-40
SCHEDULE IV - MORTGAGE LOANS ON REAL ESTATE - CorEnergy Infrastructure Trust, Inc.
Description | Interest Rate | Final Maturity | Monthly Payment Amount | Prior Liens | Face Value | Carrying Amount of Mortgage | Principal Amount of Loans Subject to Delinquent Principal or Interest | |||||||||||||||
First Mortgages | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Billings, Dunn and McKenzie Counties, North Dakota (Morlock Well) | 8.50% | 6/30/2021 | $ | 10,833 | None | $ | 1,300,000 | $ | 1,235,000 | $ | — | |||||||||||
Total | $ | 1,300,000 | $ | 1,235,000 | $ | — | ||||||||||||||||
NOTES TO SCHEDULE IV - CONSOLIDATED MORTGAGE LOANS ON REAL ESTATE
Reconciliation of Mortgage Loans on Real Estate
For the Years Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2019 | 2018 | 2017 | |||||||||
Beginning balance | $ | 1,300,000 | $ | 1,500,000 | $ | 1,500,000 | |||||
Additions: | |||||||||||
New loans | — | — | — | ||||||||
Interest receivable | — | — | — | ||||||||
Total Additions | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | |||||
Deductions: | |||||||||||
Principal repayments(1) | $ | 65,000 | $ | 236,867 | $ | — | |||||
Foreclosures | — | — | — | ||||||||
Amortization of deferred costs | — | — | — | ||||||||
Principal, Interest and Deferred Costs Write Up(1) | — | (36,867 | ) | — | |||||||
Total deductions | $ | 65,000 | $ | 200,000 | $ | — | |||||
Ending balance | $ | 1,235,000 | $ | 1,300,000 | $ | 1,500,000 | |||||
(1) In 2018, Four Wood Corridor and Compass SWD executed a $1.3 million loan agreement and Compass SWD paid approximately $237 thousand in cash for assets secured by the previous $1.5 million loans. As a result, SWD Enterprises was released from the terms of its loans, and the Company recognized a provision for loan gain of $37 thousand in the Consolidated Statements of Income. Refer to Note 5 ("Financing Notes Receivable") for further details. | |||||||||||
F-41
ITEM 16. FORM 10-K SUMMARY
None.
CORENERGY INFRASTRUCTURE TRUST, INC.
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, the registrant has duly caused this Report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
CORENERGY INFRASTRUCTURE TRUST, INC. | ||
(Registrant) | ||
By: | /s/ Kristin M. Leitze | |
Kristin M. Leitze | ||
Chief Accounting Officer (Principal Accounting and Principal Financial Officer) | ||
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this Report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
SIGNATURE | TITLE | DATE | |
/s/ David J. Schulte | Chairman and Chief Executive Officer (Principal Executive Officer) | February 27, 2020 | |
David J. Schulte | |||
/s/ Kristin M. Leitze | Chief Accounting Officer (Principal Accounting and Principal Financial Officer) | February 27, 2020 | |
Kristin M. Leitze | |||
/s/ Todd Banks | Director | February 27, 2020 | |
Todd Banks | |||
/s/ Barrett Brady | Director | February 27, 2020 | |
Barrett Brady | |||
/s/ Conrad S. Ciccotello | Director | February 27, 2020 | |
Conrad S. Ciccotello | |||
/s/ Catherine A. Lewis | Director | February 27, 2020 | |
Catherine A. Lewis | |||
F-42